Construction of genetic logic gates based on the T7 RNA polymerase expression system in Rhodococcus opacus PD630
Abstract
Rhodococcus opacus PD630 (R. opacus) is a non-model, gram-positive bacterium which holds promise as a biological catalyst for the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into value-added products. In particular, it demonstrates both a high tolerance for and an ability to consume inhibitory lignin-derived aromatics, generates large quantities of lipids, exhibits a relatively rapid growth rate, and has a growing genetic toolbox for engineering. Yet, the availability of genetic parts for tunable, high-activity gene expression is still limited in R. opacus. Moreover, genetic logic circuits for sophisticated gene regulation have never been demonstrated in Rhodococcus spp. To address these shortcomings, two inducible T7 RNA polymerase-based expression systems were implemented for the first time in R. opacus and applied to constructing AND and NAND genetic logic gates. Additionally, three IPTG-inducible promoters were created by inserting LacI binding sites into newly-characterized constitutive promoters. Furthermore, four novel aromatic sensors for 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, sodium benzoate, and guaiacol were developed, expanding the gene expression toolbox. Lastly, the T7 RNA polymerase platform was combined with a synthetic IPTG-inducible promoter to create an IMPLY logic gate. Overall, this work represents the first demonstration of a heterologous RNA polymerase system and synthetic genetic logic in R. opacus, enablingmore »
- Authors:
-
- Washington Univ., St. Louis, MO (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Washington Univ., St. Louis, MO (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1545618
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0018324
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- ACS Synthetic Biology
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 8; Journal Issue: 8; Journal ID: ISSN 2161-5063
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society (ACS)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 59 BASIC BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES; T7 RNA polymerase; genetic circuit; Boolean logic; non-model organism; aromatic sensors
Citation Formats
DeLorenzo, Drew, and Moon, Tae Seok. Construction of genetic logic gates based on the T7 RNA polymerase expression system in Rhodococcus opacus PD630. United States: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1021/acssynbio.9b00213.
DeLorenzo, Drew, & Moon, Tae Seok. Construction of genetic logic gates based on the T7 RNA polymerase expression system in Rhodococcus opacus PD630. United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00213
DeLorenzo, Drew, and Moon, Tae Seok. Tue .
"Construction of genetic logic gates based on the T7 RNA polymerase expression system in Rhodococcus opacus PD630". United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00213. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1545618.
@article{osti_1545618,
title = {Construction of genetic logic gates based on the T7 RNA polymerase expression system in Rhodococcus opacus PD630},
author = {DeLorenzo, Drew and Moon, Tae Seok},
abstractNote = {Rhodococcus opacus PD630 (R. opacus) is a non-model, gram-positive bacterium which holds promise as a biological catalyst for the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into value-added products. In particular, it demonstrates both a high tolerance for and an ability to consume inhibitory lignin-derived aromatics, generates large quantities of lipids, exhibits a relatively rapid growth rate, and has a growing genetic toolbox for engineering. Yet, the availability of genetic parts for tunable, high-activity gene expression is still limited in R. opacus. Moreover, genetic logic circuits for sophisticated gene regulation have never been demonstrated in Rhodococcus spp. To address these shortcomings, two inducible T7 RNA polymerase-based expression systems were implemented for the first time in R. opacus and applied to constructing AND and NAND genetic logic gates. Additionally, three IPTG-inducible promoters were created by inserting LacI binding sites into newly-characterized constitutive promoters. Furthermore, four novel aromatic sensors for 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, sodium benzoate, and guaiacol were developed, expanding the gene expression toolbox. Lastly, the T7 RNA polymerase platform was combined with a synthetic IPTG-inducible promoter to create an IMPLY logic gate. Overall, this work represents the first demonstration of a heterologous RNA polymerase system and synthetic genetic logic in R. opacus, enabling complex and tunable gene regulation in this promising non-model host for bioproduction.},
doi = {10.1021/acssynbio.9b00213},
journal = {ACS Synthetic Biology},
number = 8,
volume = 8,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue Jul 30 00:00:00 EDT 2019},
month = {Tue Jul 30 00:00:00 EDT 2019}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
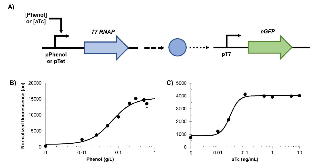 Figure 1: Inducible T7 RNAP system in R. opacus. A) Schematic of the phenol- or aTc-inducible T7 RNA polymerase (T7 RNAP) expression platform. A phenol-inducible promoter (pLPD06575; referred to as pPhenol) or an optimized pTet promoter was placed upstream of the T7 RNAP gene and integrated into the R. opacusmore »
Figure 1: Inducible T7 RNAP system in R. opacus. A) Schematic of the phenol- or aTc-inducible T7 RNA polymerase (T7 RNAP) expression platform. A phenol-inducible promoter (pLPD06575; referred to as pPhenol) or an optimized pTet promoter was placed upstream of the T7 RNAP gene and integrated into the R. opacusmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Metabolic Burden: Cornerstones in Synthetic Biology and Metabolic Engineering Applications
journal, August 2016
- Wu, Gang; Yan, Qiang; Jones, J. Andrew
- Trends in Biotechnology, Vol. 34, Issue 8
Improving fatty acids production by engineering dynamic pathway regulation and metabolic control
journal, July 2014
- Xu, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 111, Issue 31
Sensitive cells: enabling tools for static and dynamic control of microbial metabolic pathways
journal, December 2015
- Cress, Brady F.; Trantas, Emmanouil A.; Ververidis, Filippos
- Current Opinion in Biotechnology, Vol. 36
Programmable genetic circuits for pathway engineering
journal, December 2015
- Hoynes-O’Connor, Allison; Moon, Tae Seok
- Current Opinion in Biotechnology, Vol. 36
Synthesizing Biomolecule-Based Boolean Logic Gates
journal, December 2012
- Miyamoto, Takafumi; Razavi, Shiva; DeRose, Robert
- ACS Synthetic Biology, Vol. 2, Issue 2
Enabling complex genetic circuits to respond to extrinsic environmental signals: Genetic Circuits to Sense Environmental Signals
journal, March 2017
- Hoynes-O'Connor, Allison; Shopera, Tatenda; Hinman, Kristina
- Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Vol. 114, Issue 7
Oxygen-responsive genetic circuits constructed in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 : Oxygen-Responsive Gene Circuits for
journal, September 2015
- Immethun, Cheryl M.; Ng, Kenneth M.; DeLorenzo, Drew M.
- Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Vol. 113, Issue 2
Genetic circuit design automation
journal, March 2016
- Nielsen, A. A. K.; Der, B. S.; Shin, J.
- Science, Vol. 352, Issue 6281
Building an Inducible T7 RNA Polymerase/T7 Promoter Circuit in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803
journal, March 2019
- Jin, Haojie; Lindblad, Peter; Bhaya, Devaki
- ACS Synthetic Biology, Vol. 8, Issue 4
Development of Chemical and Metabolite Sensors for Rhodococcus opacus PD630
journal, June 2017
- DeLorenzo, Drew M.; Henson, William R.; Moon, Tae Seok
- ACS Synthetic Biology, Vol. 6, Issue 10
Non-model model organisms
journal, June 2017
- Russell, James J.; Theriot, Julie A.; Sood, Pranidhi
- BMC Biology, Vol. 15, Issue 1
Challenges and Advances for Genetic Engineering of Non-model Bacteria and Uses in Consolidated Bioprocessing
journal, October 2017
- Yan, Qiang; Fong, Stephen S.
- Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol. 8
Rhodococcus opacus strain PD630 as a new source of high-value single-cell oil? Isolation and characterization of triacylglycerols and other storage lipids
journal, May 2000
- Kalscheuer, Rainer; Luftmann, Heinrich; Steinbüchel, Alexander
- Microbiology, Vol. 146, Issue 5
Formation of intracytoplasmic lipid inclusions by Rhodococcus opacus strain PD630
journal, June 1996
- Alvarez, Hector M.; Mayer, Frank; Fabritius, Dirk
- Archives of Microbiology, Vol. 165, Issue 6
Triacylglycerol Production from Corn Stover Using a Xylose-Fermenting Rhodococcus opacus Strain for Lignocellulosic Biofuels
journal, January 2014
- Kurosawa, Kazuhiko
- Journal of Microbial & Biochemical Technology, Vol. 06, Issue 05
Comparative transcriptomics elucidates adaptive phenol tolerance and utilization in lipid-accumulating Rhodococcus opacus PD630
journal, February 2016
- Yoneda, Aki; Henson, William R.; Goldner, Nicholas K.
- Nucleic Acids Research, Vol. 44, Issue 5
Multi-omic elucidation of aromatic catabolism in adaptively evolved Rhodococcus opacus
journal, September 2018
- Henson, William R.; Campbell, Tayte; DeLorenzo, Drew M.
- Metabolic Engineering, Vol. 49
Tolerance and adaptive evolution of triacylglycerol-producing Rhodococcus opacus to lignocellulose-derived inhibitors
journal, January 2015
- Kurosawa, Kazuhiko; Laser, Josephine; Sinskey, Anthony J.
- Biotechnology for Biofuels, Vol. 8, Issue 1
Lipid Production from Dilute Alkali Corn Stover Lignin by Rhodococcus Strains
journal, January 2017
- He, Yucai; Li, Xiaolu; Ben, Haoxi
- ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, Vol. 5, Issue 3
Molecular Toolkit for Gene Expression Control and Genome Modification in Rhodococcus opacus PD630
journal, January 2018
- DeLorenzo, Drew M.; Rottinghaus, Austin G.; Henson, William R.
- ACS Synthetic Biology, Vol. 7, Issue 2
Selection of stable reference genes for RT-qPCR in Rhodococcus opacus PD630
journal, April 2018
- DeLorenzo, Drew M.; Moon, Tae Seok
- Scientific Reports, Vol. 8, Issue 1
The Interrelationship between Promoter Strength, Gene Expression, and Growth Rate
journal, October 2014
- Bienick, Matthew S.; Young, Katherine W.; Klesmith, Justin R.
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 9, Issue 10
Saccharification of Cellulose by Recombinant Rhodococcus opacus PD630 Strains
journal, June 2013
- Hetzler, Stephan; Bröker, Daniel; Steinbüchel, Alexander
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 79, Issue 17
Engineering of a Xylose Metabolic Pathway in Rhodococcus Strains
journal, May 2012
- Xiong, Xiaochao; Wang, Xi; Chen, Shulin
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 78, Issue 16
lac operon induction in Escherichia coli: Systematic comparison of IPTG and TMG induction and influence of the transacetylase LacA
journal, January 2012
- Marbach, Anja; Bettenbrock, Katja
- Journal of Biotechnology, Vol. 157, Issue 1
Minimal length of the lactose operator sequence for the specific recognition by the lactose repressor.
journal, March 1977
- Bahl, C. P.; Wu, R.; Stawinsky, J.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 74, Issue 3
Regulation of ribosomal RNA promoters with a synthetic lac operator.
journal, November 1984
- Brosius, J.; Holy, A.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 81, Issue 22
Use of the Escherichia coli lac repressor and operator to control gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
journal, January 1984
- Yansura, D. G.; Henner, D. J.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 81, Issue 2
Anatomy of Escherichia coli σ 70 promoters
journal, December 2006
- Shultzaberger, Ryan K.; Chen, Zehua; Lewis, Karen A.
- Nucleic Acids Research, Vol. 35, Issue 3
Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes
journal, May 1986
- Studier, F. William; Moffatt, Barbara A.
- Journal of Molecular Biology, Vol. 189, Issue 1, p. 113-130
A Highly Efficient Cell-Free Protein Synthesis System from Escherichia coli
journal, August 1996
- Kim, Dong-Myung; Kigawa, Takanori; Choi, Cha-Yong
- European Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 239, Issue 3
Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli
journal, October 1999
- Baneyx, F.
- Current Opinion in Biotechnology, Vol. 10, Issue 5
Manufacturing of recombinant therapeutic proteins in microbial systems
journal, February 2006
- Graumann, Klaus; Premstaller, Andreas
- Biotechnology Journal, Vol. 1, Issue 2
Directed Evolution of a Panel of Orthogonal T7 RNA Polymerase Variants for in Vivo or in Vitro Synthetic Circuitry
journal, October 2014
- Meyer, Adam J.; Ellefson, Jared W.; Ellington, Andrew D.
- ACS Synthetic Biology, Vol. 4, Issue 10
Kinetic and Thermodynamic Basis of Promoter Strength: Multiple Steps of Transcription Initiation by T7 RNA Polymerase Are Modulated by the Promoter Sequence †
journal, March 2002
- Bandwar, Rajiv P.; Jia, Yiping; Stano, Natalie M.
- Biochemistry, Vol. 41, Issue 11
Library of synthetic transcriptional AND gates built with split T7 RNA polymerase mutants
journal, March 2013
- Shis, D. L.; Bennett, M. R.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 110, Issue 13
Multi-Input Regulation and Logic with T7 Promoters in Cells and Cell-Free Systems
journal, October 2013
- Iyer, Sukanya; Karig, David K.; Norred, S. Elizabeth
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 8, Issue 10
Mechanisms for activating bacterial RNA polymerase
journal, September 2010
- Ghosh, Tamaswati; Bose, Daniel; Zhang, Xiaodong
- FEMS Microbiology Reviews, Vol. 34, Issue 5
Controlling basal expression in an inducible T7 expression system by blocking the target T7 promoter with lac repressor
journal, May 1991
- Dubendorf, John W.; Studier, F. William
- Journal of Molecular Biology, Vol. 219, Issue 1
Genetic programs constructed from layered logic gates in single cells
journal, October 2012
- Moon, Tae Seok; Lou, Chunbo; Tamsir, Alvin
- Nature, Vol. 491, Issue 7423
Isolation and characterization of the Rhodococcus opacus thiostrepton-inducible genes tipAL and tipAS : application for recombinant protein expression in Rhodococcus
journal, August 2004
- Dong, Li; Nakashima, Nobutaka; Tamura, Noriko
- FEMS Microbiology Letters, Vol. 237, Issue 1
The pleiotropic transcriptional regulator NlpR contributes to the modulation of nitrogen metabolism, lipogenesis and triacylglycerol accumulation in oleaginous rhodococci: Regulation of triacylglycerol accumulation in rhodococci
journal, November 2016
- Hernández, Martín A.; Lara, Julia; Gago, Gabriela
- Molecular Microbiology, Vol. 103, Issue 2
NpdR, a Repressor Involved in 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol Degradation in Rhodococcus opacus HL PM-1
journal, January 2004
- Nga, Dang P.; Altenbuchner, Josef; Heiss, Gesche S.
- Journal of Bacteriology, Vol. 186, Issue 1
Construction of a BioBrick™ compatible vector system for Rhodococcus
journal, March 2017
- Ellinger, James; Schmidt-Dannert, Claudia
- Plasmid, Vol. 90
Validation of two ribosomal RNA removal methods for microbial metatranscriptomics
journal, September 2010
- He, Shaomei; Wurtzel, Omri; Singh, Kanwar
- Nature Methods, Vol. 7, Issue 10
Core element characterization of Rhodococcus promoters and development of a promoter-RBS mini-pool with different activity levels for efficient gene expression
journal, September 2018
- Jiao, Song; Yu, Huimin; Shen, Zhongyao
- New Biotechnology, Vol. 44
Synthetic promoter libraries for Corynebacterium glutamicum
journal, January 2014
- Rytter, Jakob Vang; Helmark, Søren; Chen, Jun
- Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 98, Issue 6
Development of a Pseudomonas putida cell-free protein synthesis platform for rapid screening of gene regulatory elements
journal, January 2018
- Wang, He; Li, Jian; Jewett, Michael C.
- Synthetic Biology, Vol. 3, Issue 1
Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases
journal, April 2009
- Gibson, Daniel G.; Young, Lei; Chuang, Ray-Yuan
- Nature Methods, Vol. 6, Issue 5, p. 343-345
Establishment of a gene transfer system for Rhodococcus opacus PD630 based on electroporation and its application for recombinant biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoic acids)
journal, October 1999
- Kalscheuer, R.; Arenskötter, M.; Steinbüchel, A.
- Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 52, Issue 4
Rapid metabolic analysis of Rhodococcus opacus PD630 via parallel 13 C-metabolite fingerprinting
journal, September 2015
- Hollinshead, Whitney D.; Henson, William R.; Abernathy, Mary
- Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Vol. 113, Issue 1
Works referencing / citing this record:
Genetically encoded biosensors for lignocellulose valorization
journal, October 2019
- Alvarez-Gonzalez, Guadalupe; Dixon, Neil
- Biotechnology for Biofuels, Vol. 12, Issue 1
Biosensing in Smart Engineered Probiotics
journal, January 2020
- Rottinghaus, Austin G.; Amrofell, Matthew B.; Moon, Tae Seok
- Biotechnology Journal, Vol. 15, Issue 10
Genetically encoded biosensors for lignocellulose valorization
journal, October 2019
- Alvarez-Gonzalez, Guadalupe; Dixon, Neil
- Biotechnology for Biofuels, Vol. 12, Issue 1
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal