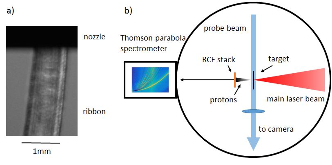
First demonstration of multi-MeV proton acceleration from a cryogenic hydrogen ribbon target
Journal Article
·
· Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion
- Inst. of Radiation Physics, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, Dresden (Germany)
- Inst. of Radiation Physics, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, Dresden (Germany); Dresden Univ. of Technology (Germany)
- Univ. of Grenoble (France).
- Univ. of Grenoble (France)
- National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), Strasbourg (France); Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau (France); ; Univ. Paris-Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette (France); Pierre-and-Marie-Curie Univ., Paris (France); Sorbonne Univ., Paris (France)
- National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), Strasbourg (France); Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau (France); Univ. Paris-Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette (France); Pierre-and-Marie-Curie Univ., Paris (France); Sorbonne Univ., Paris (France)
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Menlo Park, CA (United States). High Energy Density Science Division
We show efficient laser driven proton acceleration up to 14 MeV from a 50 μm thick cryogenic hydrogen ribbon. Pulses of the short pulse laser ELFIE at LULI with a pulse length of ≈ 350 fs at an energy of 8 J per pulse are directed onto the target. The results were then compared to proton spectra from metal and plastic foils with different thicknesses and show a similar good performance both in maximum energy as well as in proton number. Thus, this target type is a promising candidate for experiments with high repetition rate laser systems.
- Research Organization:
- Inst.of Radiation Physics, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, Dresden (Germany)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Fusion Energy Sciences (FES); European Union (EU); Laserlab-Europe, Berlin (Germany); German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF); National Research Agency (ANR); European Consortium for the Development of Fusion Energy (EUROfusion)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-76SF00515; 654148; 03ZIK445; 633053
- OSTI ID:
- 1422027
- Journal Information:
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 60, Issue 4; ISSN 0741-3335
- Publisher:
- IOP ScienceCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Cited by: 15 works
Citation information provided by
Web of Science
Web of Science
Similar Records
Efficient laser-driven proton acceleration from cylindrical and planar cryogenic hydrogen jets
Near monochromatic 20 Me V proton acceleration using fs laser irradiating Au foils in target normal sheath acceleration regime
Three dimensional effects on proton acceleration by intense laser solid target interaction
Journal Article
·
Thu Aug 31 00:00:00 EDT 2017
· Scientific Reports
·
OSTI ID:1422027
+29 more
Near monochromatic 20 Me V proton acceleration using fs laser irradiating Au foils in target normal sheath acceleration regime
Journal Article
·
Fri Apr 15 00:00:00 EDT 2016
· Physics of Plasmas
·
OSTI ID:1422027
+4 more
Three dimensional effects on proton acceleration by intense laser solid target interaction
Journal Article
·
Sat Jun 15 00:00:00 EDT 2013
· Physics of Plasmas
·
OSTI ID:1422027
+2 more