Discovery of Novel Tricyclic Heterocycles as Potent and Selective DPP-4 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Journal Article
·
· ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters
- Merck Research Lab., Kenilworth, NJ (United States). Dept. of Lead Optimization Chemistry
- Merck Research Lab., Kenilworth, NJ (United States). Dept. of Structural Chemistry
- Merck Research Lab., Kenilworth, NJ (United States). Dept. of Structural Chemistry
- Merck Research Lab., Kenilworth, NJ (United States). Dept. of Department of Pharmacology
- Merck Research Lab., Kenilworth, NJ (United States). Dept. of Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Drug Metabolism
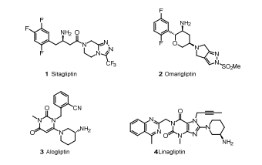
In our efforts to develop second generation DPP-4 inhibitors, we endeavored to identify distinct structures with long-acting (once weekly) potential. Taking advantage of X-ray cocrystal structures of sitagliptin and other DPP-4 inhibitors, such as alogliptin and linagliptin bound to DPP-4, and aided by molecular modeling, we designed several series of heterocyclic compounds as initial targets. During their synthesis, an unexpected chemical transformation provided a novel tricyclic scaffold that was beyond our original design. Capitalizing on this serendipitous discovery, we have elaborated this scaffold into a very potent and selective DPP-4 inhibitor lead series, as highlighted by compound 17c.
- Research Organization:
- Argonne National Laboratory (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States). Advanced Photon Source (APS)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE
- OSTI ID:
- 1404985
- Journal Information:
- ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters, Vol. 7, Issue 5; ISSN 1948-5875
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society (ACS)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- ENGLISH
Cited by: 24 works
Citation information provided by
Web of Science
Web of Science
Emergence of promising novel DPP-4 inhibitory heterocycles as anti-diabetic agents: A review
|
journal | June 2018 |
Palladium nanodendrites uniformly deposited on the surface of polymers as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for direct drug modification via Z -selective semihydrogenation of alkynes
|
journal | January 2018 |
Activity and selectivity cliffs for DPP-IV inhibitors: Lessons we can learn from SAR studies and their application to virtual screening
|
journal | April 2018 |
Gold Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric and Electrochemical Methods for Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Activity Assay and Inhibitor Screening
|
journal | October 2016 |
Similar Records
Trelagliptin (SYR-472, Zafatek), novel once-weekly treatment for type 2 diabetes, inhibits dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) via a non-covalent mechanism
(2R)-4-Oxo-4[3-(Trifluoromethyl)-5,6-diihydro:1,2,4}triazolo[4,3-a}pyrazin-7(8H)-y1]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: A Potent, Orally Active Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Omarigliptin (MK-3102): A Novel Long-Acting DPP-4 Inhibitor for Once-Weekly Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Journal Article
·
Tue Jun 21 00:00:00 EDT 2016
· PLoS ONE
·
OSTI ID:1404985
+9 more
(2R)-4-Oxo-4[3-(Trifluoromethyl)-5,6-diihydro:1,2,4}triazolo[4,3-a}pyrazin-7(8H)-y1]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: A Potent, Orally Active Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Journal Article
·
Wed Nov 10 00:00:00 EST 2010
· J. Med. Chem.
·
OSTI ID:1404985
+20 more
Omarigliptin (MK-3102): A Novel Long-Acting DPP-4 Inhibitor for Once-Weekly Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Journal Article
·
Thu Apr 24 00:00:00 EDT 2014
· Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
·
OSTI ID:1404985
+26 more