Pulse-resolved intensity measurements at a hard X-ray FEL using semi-transparent diamond detectors
Abstract
Solid-state ionization chambers are presented based on thin diamond crystals that allow pulse-resolved intensity measurements at a hard X-ray free-electron laser (FEL), up to the 4.5 MHz repetition rate that will become available at the European XFEL. Due to the small X-ray absorption of diamond the thin detectors are semi-transparent which eases their use as non-invasive monitoring devices in the beam. FELs are characterized by strong pulse-to-pulse intensity fluctuations due to the self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) process and in many experiments it is mandatory to monitor the intensity of each individual pulse. Two diamond detectors with different electrode materials, beryllium and graphite, were tested as intensity monitors at the XCS endstation of the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) using the pink SASE beam at 9 keV. The performance is compared with LCLS standard monitors that detect X-rays backscattered from thin SiN foils placed in the beam. In conclusion, the graphite detector can also be used as a beam position monitor although with rather coarse resolution.
- Authors:
-
- European X-ray Free-Electron Laser Facility, Schenefeld (Germany); European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble (France)
- European X-ray Free-Electron Laser Facility, Schenefeld (Germany)
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Menlo Park, CA (United States)
- Micron Semiconductors Ltd., Lancing (United Kingdom)
- Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal Univ., Kalinigrad (Russian Federation)
- Univ. Augsburg, Augsburg (Germany)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (SLAC), Menlo Park, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1417650
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-76SF00515
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Journal of Synchrotron Radiation (Online)
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: Journal of Synchrotron Radiation (Online); Journal Volume: 25; Journal Issue: 1; Journal ID: ISSN 1600-5775
- Publisher:
- International Union of Crystallography
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 46 INSTRUMENTATION RELATED TO NUCLEAR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY; XFEL; diamond detector; X-ray intensity measurement
Citation Formats
Roth, Thomas, Freund, Wolfgang, Boesenberg, Ulrike, Carini, Gabriella, Song, Sanghoon, Lefeuvre, Gwenaelle, Goikhman, Alexander, Fischer, Martin, Schreck, Matthias, Grunert, Jan, and Madsen, Anders. Pulse-resolved intensity measurements at a hard X-ray FEL using semi-transparent diamond detectors. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1107/S1600577517015016.
Roth, Thomas, Freund, Wolfgang, Boesenberg, Ulrike, Carini, Gabriella, Song, Sanghoon, Lefeuvre, Gwenaelle, Goikhman, Alexander, Fischer, Martin, Schreck, Matthias, Grunert, Jan, & Madsen, Anders. Pulse-resolved intensity measurements at a hard X-ray FEL using semi-transparent diamond detectors. United States. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600577517015016
Roth, Thomas, Freund, Wolfgang, Boesenberg, Ulrike, Carini, Gabriella, Song, Sanghoon, Lefeuvre, Gwenaelle, Goikhman, Alexander, Fischer, Martin, Schreck, Matthias, Grunert, Jan, and Madsen, Anders. Mon .
"Pulse-resolved intensity measurements at a hard X-ray FEL using semi-transparent diamond detectors". United States. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600577517015016. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1417650.
@article{osti_1417650,
title = {Pulse-resolved intensity measurements at a hard X-ray FEL using semi-transparent diamond detectors},
author = {Roth, Thomas and Freund, Wolfgang and Boesenberg, Ulrike and Carini, Gabriella and Song, Sanghoon and Lefeuvre, Gwenaelle and Goikhman, Alexander and Fischer, Martin and Schreck, Matthias and Grunert, Jan and Madsen, Anders},
abstractNote = {Solid-state ionization chambers are presented based on thin diamond crystals that allow pulse-resolved intensity measurements at a hard X-ray free-electron laser (FEL), up to the 4.5 MHz repetition rate that will become available at the European XFEL. Due to the small X-ray absorption of diamond the thin detectors are semi-transparent which eases their use as non-invasive monitoring devices in the beam. FELs are characterized by strong pulse-to-pulse intensity fluctuations due to the self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) process and in many experiments it is mandatory to monitor the intensity of each individual pulse. Two diamond detectors with different electrode materials, beryllium and graphite, were tested as intensity monitors at the XCS endstation of the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) using the pink SASE beam at 9 keV. The performance is compared with LCLS standard monitors that detect X-rays backscattered from thin SiN foils placed in the beam. In conclusion, the graphite detector can also be used as a beam position monitor although with rather coarse resolution.},
doi = {10.1107/S1600577517015016},
journal = {Journal of Synchrotron Radiation (Online)},
number = 1,
volume = 25,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Mon Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
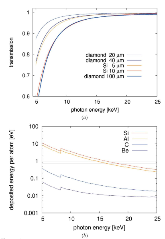 Figure 1: Top: absorption in Si and diamond as a function of photon energy. Bottom: energy deposited per atom and per pulse for different materials, calculated for a detector placed 30 cm upstream of the sample position at the MID station of the European XFEL in a pink SASE beam.more »
Figure 1: Top: absorption in Si and diamond as a function of photon energy. Bottom: energy deposited per atom and per pulse for different materials, calculated for a detector placed 30 cm upstream of the sample position at the MID station of the European XFEL in a pink SASE beam.more »
Works referenced in this record:
The X-ray Correlation Spectroscopy instrument at the Linac Coherent Light Source
journal, April 2015
- Alonso-Mori, Roberto; Caronna, Chiara; Chollet, Matthieu
- Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, Vol. 22, Issue 3
The European X-ray Free-Electron Laser: toward an ultra-bright, high repetition-rate x-ray source
journal, January 2015
- Altarelli, M.
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering, Vol. 3
Fast synchrotron and FEL beam monitors based on single-crystal diamond detectors and InGaAs/InAlAs quantum well devices
journal, December 2013
- Antonelli, M.; Di Fraia, M.; Carrato, S.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 730
Collective instabilities and high-gain regime in a free electron laser
journal, July 1984
- Bonifacio, R.; Pellegrini, C.; Narducci, L. M.
- Optics Communications, Vol. 50, Issue 6
Diamond detectors for synchrotron radiation X-ray applications
journal, July 2007
- De Sio, A.; Pace, E.; Cinque, G.
- Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, Vol. 62, Issue 6-7
Ultra-thin optical grade scCVD diamond as X-ray beam position monitor
journal, October 2014
- Desjardins, Kewin; Pomorski, Michal; Morse, John
- Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, Vol. 21, Issue 6
Demonstration of Diamond-Based Schottky p-i-n Diode With Blocking Voltage > 500 V
journal, September 2016
- Dutta, Maitreya; Koeck, Franz A. M.; Hathwar, Raghuraj
- IEEE Electron Device Letters, Vol. 37, Issue 9
A single-shot intensity-position monitor for hard x-ray FEL sources
conference, September 2011
- Feng, Yiping; Feldkamp, Jan M.; Fritz, David M.
- SPIE Optical Engineering + Applications, SPIE Proceedings
CVD diamond metallization and characterization
journal, February 2017
- Fraimovitch, D.; Adelberd, A.; Marunko, S.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 845
Transmissive x-ray beam position monitors with submicron position- and submillisecond time resolution
journal, June 2008
- Fuchs, Martin R.; Holldack, Karsten; Bullough, Mark
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 79, Issue 6
Photon energy dependence of graphitization threshold for diamond irradiated with an intense XUV FEL pulse
journal, August 2013
- Gaudin, J.; Medvedev, N.; Chalupský, J.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 88, Issue 6
Measurement of x-ray free-electron-laser pulse energies by photoluminescence in nitrogen gas
journal, March 2008
- Hau–Riege, S. P.; Bionta, R. M.; Ryutov, D. D.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 103, Issue 5
Damage threshold of inorganic solids under free-electron-laser irradiation at 32.5nm wavelength
journal, April 2007
- Hau-Riege, S. P.; London, R. A.; Bionta, R. M.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 90, Issue 17
Diode readout electronics for beam intensity and position monitors for FELs
journal, March 2014
- Herrmann, S.; Hart, P.; Freytag, M.
- Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 493
Correlation between breakdown voltage and structural properties of polycrystalline and heteroepitaxial CVD diamond films
journal, April 1994
- Hessmer, R.; Schreck, M.; Geier, S.
- Diamond and Related Materials, Vol. 3, Issue 4-6
High Carrier Mobility in Single-Crystal Plasma-Deposited Diamond
journal, September 2002
- Isberg, Jan; Hammersberg, Johan; Johansson, Erik
- Science, Vol. 297, Issue 5587, p. 1670-1672
Graphitization of diamond by ion impact: Fundamentals and applications
journal, December 1995
- Kalish, R.; Prawer, S.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, Vol. 106, Issue 1-4
Single crystal diamond photodiode for soft X-ray radiometry
journal, July 2009
- Keister, Jeffrey W.; Smedley, John
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 606, Issue 3
Diamond X-ray photodiode for white and monochromatic SR beams
journal, September 2011
- Keister, Jeffrey W.; Smedley, John; Muller, Erik M.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 649, Issue 1
Diamond detectors with laser induced surface graphite electrodes
journal, November 2016
- Komlenok, M.; Bolshakov, A.; Ralchenko, V.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 837
Investigation of ablation thresholds of optical materials using 1-µm-focusing beam at hard X-ray free electron laser
journal, January 2013
- Koyama, Takahisa; Yumoto, Hirokatsu; Senba, Yasunori
- Optics Express, Vol. 21, Issue 13
Damage study of optical substrates using 1-μm-focusing beam of hard X-ray free-electron laser
journal, October 2013
- Koyama, T.; Yumoto, H.; Senba, Y.
- Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 463
A photodiode amplifier system for pulse-by-pulse intensity measurement of an x-ray free electron laser
journal, April 2012
- Kudo, Togo; Tono, Kensuke; Yabashi, Makina
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 83, Issue 4
Computational simulations of high-intensity x-ray matter interaction
conference, December 2001
- London, Richard A.; Bionta, Richard M.; Tatchyn, Roman O.
- International Symposium on Optical Science and Technology, SPIE Proceedings
Nonthermal graphitization of diamond induced by a femtosecond x-ray laser pulse
journal, December 2013
- Medvedev, N.; Jeschke, H. O.; Ziaja, B.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 88, Issue 22
Nonthermal phase transitions in semiconductors induced by a femtosecond extreme ultraviolet laser pulse
journal, January 2013
- Medvedev, Nikita; Jeschke, Harald O.; Ziaja, Beata
- New Journal of Physics, Vol. 15, Issue 1
Thermal and nonthermal melting of silicon under femtosecond x-ray irradiation
journal, February 2015
- Medvedev, Nikita; Li, Zheng; Ziaja, Beata
- Physical Review B, Vol. 91, Issue 5
Single crystal CVD diamond as an X-ray beam monitor
journal, April 2007
- Morse, J.; Salomé, M.; Berdermann, E.
- Diamond and Related Materials, Vol. 16, Issue 4-7
Diamond X-ray beam-position monitoring using signal readout at the synchrotron radiofrequency
journal, May 2010
- Morse, J.; Solar, B.; Graafsma, H.
- Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, Vol. 17, Issue 4
Development of single-crystal CVD-diamond detectors for spectroscopy and timing
journal, September 2006
- Pomorski, M.; Berdermann, E.; Caragheorgheopol, A.
- physica status solidi (a), Vol. 203, Issue 12
Characterisation of single crystal CVD diamond particle detectors for hadron physics experiments
journal, September 2005
- Pomorski, M.; Berdermann, E.; Ciobanu, M.
- physica status solidi (a), Vol. 202, Issue 11
Charge transport properties of single crystal CVD-diamond particle detectors
journal, April 2007
- Pomorski, M.; Berdermann, E.; de Boer, W.
- Diamond and Related Materials, Vol. 16, Issue 4-7
Position-sensitive radiation detectors made of single crystal CVD diamond: Position-sensitive radiation detectors made of single crystal CVD diamond
journal, August 2009
- Pomorski, M.; Ciobanu, M.; Mer, C.
- physica status solidi (a), Vol. 206, Issue 9
The X-ray Correlation Spectroscopy instrument at the Linac Coherent Light Source
journal, March 2013
- Robert, A.; Curtis, R.; Flath, D.
- Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 425, Issue 21
Injection and temperature dependent carrier recombination rate and diffusion length in freestanding CVD diamond: Carrier recombination rate and diffusion length in freestanding CVD diamond
journal, July 2013
- Ščajev, Patrik; Gudelis, Vytautas; Tallaire, Alexandre
- physica status solidi (a), Vol. 210, Issue 10
High-performance diamond radiation detectors produced by lift-off method
journal, March 2016
- Shimaoka, Takehiro; Kaneko, Junichi H.; Tsubota, Masakatsu
- EPL (Europhysics Letters), Vol. 113, Issue 6
Efficiency of dislocation density reduction during heteroepitaxial growth of diamond for detector applications
journal, October 2013
- Stehl, C.; Fischer, M.; Gsell, S.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 103, Issue 15
Soft x-ray induced femtosecond solid-to-solid phase transition
journal, September 2017
- Tavella, Franz; Höppner, Hauke; Tkachenko, Victor
- High Energy Density Physics, Vol. 24
Electric Field Breakdown of Lateral Schottky Diodes of Diamond
journal, February 2007
- Teraji, Tokuyuki; Koizumi, Satoshi; Koide, Yasuo
- Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 46, Issue No. 9
Gas detectors for x-ray lasers
journal, May 2008
- Tiedtke, K.; Feldhaus, J.; Hahn, U.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 103, Issue 9
Single-shot beam-position monitor for x-ray free electron laser
journal, February 2011
- Tono, Kensuke; Kudo, Togo; Yabashi, Makina
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 82, Issue 2
Diamond as an electronic material
journal, January 2008
- Wort, Chris J. H.; Balmer, Richard S.
- Materials Today, Vol. 11, Issue 1-2
Pixelated transmission-mode diamond X-ray detector
journal, September 2015
- Zhou, Tianyi; Ding, Wenxiang; Gaowei, Mengjia
- Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, Vol. 22, Issue 6
Works referencing / citing this record:
Development of a hard X-ray split-and-delay line and performance simulations for two-color pump-probe experiments at the European XFEL
journal, June 2018
- Lu, W.; Friedrich, B.; Noll, T.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 89, Issue 6
Thermomechanical response of thickly tamped targets and diamond anvil cells under pulsed hard x-ray irradiation
journal, May 2020
- Meza-Galvez, J.; Gomez-Perez, N.; Marshall, A. S.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 127, Issue 19
Pulse power measurements and attenuator characterization of the hard X-ray beamline at the Linac Coherent Light Source
conference, May 2019
- Song, Sanghoon; Alonso-Mori, Roberto; Chollet, Matthieu
- X-Ray Free-Electron Lasers: Advances in Source Development and Instrumentation V
Development of a hard X-ray split-and-delay line and performance simulations for two-color pump-probe experiments at the European XFEL
text, January 2018
- Lu, Wei; Friedrich, B.; Noll, Tino
- Technische Universität Berlin
X-ray photon diagnostics at the European XFEL
text, January 2019
- Grünert, Jan; Carbonell, Marc Planas; Dietrich, Florian
- Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron, DESY, Hamburg
Pulse power measurements and attenuator characterization of the hard X-ray beamline at the Linac Coherent Light Source
text, January 2019
- Song, Sanghoon; Alonso-Mori, Roberto; Chollet, Matthieu
- Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron, DESY, Hamburg
Thermomechanical response of thickly tamped targets and diamond anvil cells under pulsed hard x-ray irradiation
text, January 2018
- Meza-Galvez, J.; Gomez-Perez, N.; Marshall, A.
- arXiv

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal