Effect of modified periodic waveforms on current-induced spin polarization measurements
Abstract
Applying a voltage to a semiconductor sample generates a current-induced electron spin polarization (CISP). Using an ultrafast mode-locked laser and lock-in detection scheme, we measure CISP on an indium gallium arsenide epilayer via Faraday rotation and extract the spin generation rate. While the measured spin polarization initially increases linearly with electric field as observed in previous work, larger applied voltages lead to a decreasing spin generation rate. Here we show that we can recover the linear dependence of spin generation rate with electric field even at larger applied voltages by modifying the applied voltage waveform to reduce heating and multiplying by an appropriate correction factor. Future CISP studies can utilize this technique to investigate CISP under larger applied electric fields.
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Univ. of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (SC-22). Materials Sciences & Engineering Division; USDOE
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1499031
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1454657
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0016206
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- AIP Advances
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 8; Journal Issue: 6; Journal ID: ISSN 2158-3226
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 72 PHYSICS OF ELEMENTARY PARTICLES AND FIELDS
Citation Formats
Iafrate, Joseph R., Huang, Simon, Del Gaudio, Davide, Goldman, Rachel S., and Sih, Vanessa. Effect of modified periodic waveforms on current-induced spin polarization measurements. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1063/1.5026760.
Iafrate, Joseph R., Huang, Simon, Del Gaudio, Davide, Goldman, Rachel S., & Sih, Vanessa. Effect of modified periodic waveforms on current-induced spin polarization measurements. United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5026760
Iafrate, Joseph R., Huang, Simon, Del Gaudio, Davide, Goldman, Rachel S., and Sih, Vanessa. Mon .
"Effect of modified periodic waveforms on current-induced spin polarization measurements". United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5026760. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1499031.
@article{osti_1499031,
title = {Effect of modified periodic waveforms on current-induced spin polarization measurements},
author = {Iafrate, Joseph R. and Huang, Simon and Del Gaudio, Davide and Goldman, Rachel S. and Sih, Vanessa},
abstractNote = {Applying a voltage to a semiconductor sample generates a current-induced electron spin polarization (CISP). Using an ultrafast mode-locked laser and lock-in detection scheme, we measure CISP on an indium gallium arsenide epilayer via Faraday rotation and extract the spin generation rate. While the measured spin polarization initially increases linearly with electric field as observed in previous work, larger applied voltages lead to a decreasing spin generation rate. Here we show that we can recover the linear dependence of spin generation rate with electric field even at larger applied voltages by modifying the applied voltage waveform to reduce heating and multiplying by an appropriate correction factor. Future CISP studies can utilize this technique to investigate CISP under larger applied electric fields.},
doi = {10.1063/1.5026760},
journal = {AIP Advances},
number = 6,
volume = 8,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Jun 18 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Mon Jun 18 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Figures / Tables:
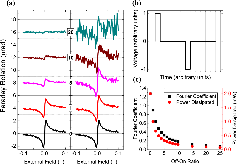 Figure 1: (a) Current-induced spin polarization (CISP) measured under application of a 1 V peak square wave for off/on ratios 0, 1, 5, 10, and 20. A vertical offset between curves has been added for clarity. Left panel: This data has not been corrected for decreasing Fourier coefficient with increasingmore »
Figure 1: (a) Current-induced spin polarization (CISP) measured under application of a 1 V peak square wave for off/on ratios 0, 1, 5, 10, and 20. A vertical offset between curves has been added for clarity. Left panel: This data has not been corrected for decreasing Fourier coefficient with increasingmore »
Works referenced in this record:
All-electrical time-resolved spin generation and spin manipulation in n-InGaAs
journal, February 2014
- Stepanov, I.; Kuhlen, S.; Ersfeld, M.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 104, Issue 6
Spatial imaging of the spin Hall effect and current-induced polarization in two-dimensional electron gases
journal, September 2005
- Sih, V.; Myers, R. C.; Kato, Y. K.
- Nature Physics, Vol. 1, Issue 1
Resonant optical control of the electrically induced spin polarization by periodic excitation
journal, July 2014
- Hernandez, F. G. G.; Gusev, G. M.; Bakarov, A. K.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 90, Issue 4
Spectral Dependence of Spin Photocurrent and Current-Induced Spin Polarization in an Two-Dimensional Electron Gas
journal, May 2006
- Yang, C. L.; He, H. T.; Ding, Lu
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 96, Issue 18
Theory of current-induced spin polarization in an electron gas
journal, May 2017
- Gorini, Cosimo; Maleki Sheikhabadi, Amin; Shen, Ka
- Physical Review B, Vol. 95, Issue 20
Challenges for semiconductor spintronics
journal, March 2007
- Awschalom, David D.; Flatté, Michael E.
- Nature Physics, Vol. 3, Issue 3
Spintronics: A Spin-Based Electronics Vision for the Future
journal, November 2001
- Wolf, S. A.; Awschalom, D. D.; Buhrman, R. A.
- Science, Vol. 294, Issue 5546, p. 1488-1495
Current-Induced Polarization and the Spin Hall Effect at Room Temperature
journal, September 2006
- Stern, N. P.; Ghosh, S.; Xiang, G.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 97, Issue 12
Current-induced spin polarization in InGaAs and GaAs epilayers with varying doping densities
journal, November 2017
- Luengo-Kovac, M.; Huang, S.; Del Gaudio, D.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 96, Issue 19
Current-induced spin polarization at a single heterojunction
journal, December 2004
- Silov, A. Yu.; Blajnov, P. A.; Wolter, J. H.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 85, Issue 24
Evidence for reversible control of magnetization in a ferromagnetic material by means of spin–orbit magnetic field
journal, August 2009
- Chernyshov, Alexandr; Overby, Mason; Liu, Xinyu
- Nature Physics, Vol. 5, Issue 9
Optical spin resonance and transverse spin relaxation in magnetic semiconductor quantum wells
journal, September 1997
- Crooker, S. A.; Awschalom, D. D.; Baumberg, J. J.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 56, Issue 12
Current-induced spin polarization in gallium nitride
journal, August 2009
- Koehl, W. F.; Wong, M. H.; Poblenz, C.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 95, Issue 7
Erratum: Current-Induced Spin Polarization in Anisotropic Spin-Orbit Fields [Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 056601 (2014)]
journal, April 2014
- Norman, B. M.; Trowbridge, C. J.; Awschalom, D. D.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 112, Issue 16
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal