Roughness effects in uncompensated antiferromagnets
- Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States). Dept. of Physics; Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States). Materials Science Division; Federal Inst. of Technology, Zurich (Switzerland). Lab. of Metal Physics and Technology
- Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States). Dept. of Physics; Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States). Materials Science Division
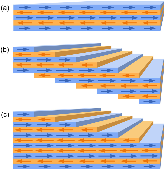
Monte Carlo simulations show that roughness in uncompensated antiferromagnets decreases not just the surface magnetization but also the net magnetization and particularly strongly affects the temperature dependence. In films with step-type roughness, each step creates a new compensation front that decreases the global net magnetization. The saturation magnetization decreases non-monotonically with increasing roughness and does not scale with the surface area. Roughness in the form of surface vacancies changes the temperature-dependence of the magnetization; when only one surface has vacancies, the saturation magnetization will decrease linearly with surface occupancy, whereas when both surfaces have vacancies, the magnetization is negative and exhibits a compensation point at finite temperature, which can be tuned by controlling the occupancy. Roughness also affects the spin-texture of the surfaces due to long-range dipolar interactions and generates non-collinear spin configurations that could be used in devices to produce locally modified exchange bias. Lastly, these results explain the strongly reduced magnetization found in magnetometry experiments and furthers our understanding of the temperature-dependence of exchange bias.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- OSTI ID:
- 1512172
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1228199
- Journal Information:
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 117, Issue 8; ISSN 0021-8979
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Magnetocaloric effect in cubically anisotropic magnets
|
journal | January 2019 |
Influence of atomic roughness at the uncompensated Fe/CoO(111) interface on the exchange-bias effect
|
journal | January 2020 |
Imaging uncompensated moments and exchange-biased emergent ferromagnetism in FeRh thin films
|
journal | December 2019 |
Influence of atomic roughness at the uncompensated Fe/CoO(111) interface on the exchange-bias effect
|
text | January 2020 |
| Imaging uncompensated moments and exchange-biased emergent ferromagnetism in FeRh thin films | text | January 2019 |
| Influence of Atomic Roughness at The Uncompensated Fe/CoO (111) Interface on Exchange Bias Effect | text | January 2020 |
Similar Records
Magnetoresistive detection of strongly pinned uncompensated magnetization in antiferromagnetic FeMn
Anomalous magnetic thermodynamics in uncompensated collinear antiferromagnets