Crumpling of silver nanowires by endolysosomes strongly reduces toxicity
Abstract
Fibrous particles interact with cells and organisms in complex ways that can lead to cellular dysfunction, cell death, inflammation, and disease. The development of conductive transparent networks (CTNs) composed of metallic silver nanowires (AgNWs) for flexible touchscreen displays raises new possibilities for the intimate contact between novel fibers and human skin. Here, we report that a material property, nanowire-bending stiffness that is a function of diameter, controls the cytotoxicity of AgNWs to nonimmune cells from humans, mice, and fish without deterioration of critical CTN performance parameters: electrical conductivity and optical transparency. Both 30- and 90-nm-diameter AgNWs are readily internalized by cells, but thinner NWs are mechanically crumpled by the forces imposed during or after endocytosis, while thicker nanowires puncture the enclosing membrane and release silver ions and lysosomal contents to the cytoplasm, thereby initiating oxidative stress. This finding extends the fiber pathology paradigm and will enable the manufacture of safer products incorporating AgNWs.
- Authors:
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES). Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences Division
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1564566
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1559232
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- Resource Type:
- Published Article
- Journal Name:
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Journal Volume: 116 Journal Issue: 30; Journal ID: ISSN 0027-8424
- Publisher:
- National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC (United States)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 60 APPLIED LIFE SCIENCES; nanotechnology; endocytosis; fiber toxicity
Citation Formats
Lehmann, Sylvia G., Toybou, Djadidi, Pradas del Real, Ana-Elena, Arndt, Devrah, Tagmount, Abderrahmane, Viau, Muriel, Safi, Malak, Pacureanu, Alexandra, Cloetens, Peter, Bohic, Sylvain, Salomé, Murielle, Castillo-Michel, Hiram, Omaña-Sanz, Brenda, Hofmann, Annette, Vulpe, Christopher, Simonato, Jean-Pierre, Celle, Caroline, Charlet, Laurent, and Gilbert, Benjamin. Crumpling of silver nanowires by endolysosomes strongly reduces toxicity. United States: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1073/pnas.1820041116.
Lehmann, Sylvia G., Toybou, Djadidi, Pradas del Real, Ana-Elena, Arndt, Devrah, Tagmount, Abderrahmane, Viau, Muriel, Safi, Malak, Pacureanu, Alexandra, Cloetens, Peter, Bohic, Sylvain, Salomé, Murielle, Castillo-Michel, Hiram, Omaña-Sanz, Brenda, Hofmann, Annette, Vulpe, Christopher, Simonato, Jean-Pierre, Celle, Caroline, Charlet, Laurent, & Gilbert, Benjamin. Crumpling of silver nanowires by endolysosomes strongly reduces toxicity. United States. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820041116
Lehmann, Sylvia G., Toybou, Djadidi, Pradas del Real, Ana-Elena, Arndt, Devrah, Tagmount, Abderrahmane, Viau, Muriel, Safi, Malak, Pacureanu, Alexandra, Cloetens, Peter, Bohic, Sylvain, Salomé, Murielle, Castillo-Michel, Hiram, Omaña-Sanz, Brenda, Hofmann, Annette, Vulpe, Christopher, Simonato, Jean-Pierre, Celle, Caroline, Charlet, Laurent, and Gilbert, Benjamin. Mon .
"Crumpling of silver nanowires by endolysosomes strongly reduces toxicity". United States. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820041116.
@article{osti_1564566,
title = {Crumpling of silver nanowires by endolysosomes strongly reduces toxicity},
author = {Lehmann, Sylvia G. and Toybou, Djadidi and Pradas del Real, Ana-Elena and Arndt, Devrah and Tagmount, Abderrahmane and Viau, Muriel and Safi, Malak and Pacureanu, Alexandra and Cloetens, Peter and Bohic, Sylvain and Salomé, Murielle and Castillo-Michel, Hiram and Omaña-Sanz, Brenda and Hofmann, Annette and Vulpe, Christopher and Simonato, Jean-Pierre and Celle, Caroline and Charlet, Laurent and Gilbert, Benjamin},
abstractNote = {Fibrous particles interact with cells and organisms in complex ways that can lead to cellular dysfunction, cell death, inflammation, and disease. The development of conductive transparent networks (CTNs) composed of metallic silver nanowires (AgNWs) for flexible touchscreen displays raises new possibilities for the intimate contact between novel fibers and human skin. Here, we report that a material property, nanowire-bending stiffness that is a function of diameter, controls the cytotoxicity of AgNWs to nonimmune cells from humans, mice, and fish without deterioration of critical CTN performance parameters: electrical conductivity and optical transparency. Both 30- and 90-nm-diameter AgNWs are readily internalized by cells, but thinner NWs are mechanically crumpled by the forces imposed during or after endocytosis, while thicker nanowires puncture the enclosing membrane and release silver ions and lysosomal contents to the cytoplasm, thereby initiating oxidative stress. This finding extends the fiber pathology paradigm and will enable the manufacture of safer products incorporating AgNWs.},
doi = {10.1073/pnas.1820041116},
journal = {Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America},
number = 30,
volume = 116,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Jul 08 00:00:00 EDT 2019},
month = {Mon Jul 08 00:00:00 EDT 2019}
}
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820041116
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
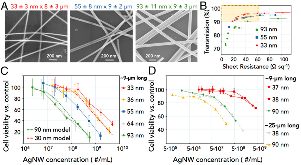 Fig. 1: Diameter-dependent performance and cytotoxicity of AgNWs. (A) Scanning-electron microscopy images of 8- to 9-μm long AgNW with 3 mean diameters. (B) Relationship between optical transparency and sheet resistance for CTNs fabricated by ∼9-μm-long AgNWs with three different diameters. Each data point represents a spray-coated network at a differentmore »
Fig. 1: Diameter-dependent performance and cytotoxicity of AgNWs. (A) Scanning-electron microscopy images of 8- to 9-μm long AgNW with 3 mean diameters. (B) Relationship between optical transparency and sheet resistance for CTNs fabricated by ∼9-μm-long AgNWs with three different diameters. Each data point represents a spray-coated network at a differentmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Flexible transparent conductive materials based on silver nanowire networks: a review
journal, October 2013
- Langley, Daniel; Giusti, Gaël; Mayousse, Céline
- Nanotechnology, Vol. 24, Issue 45
The effect of nanowire length and diameter on the properties of transparent, conducting nanowire films
journal, January 2012
- Bergin, Stephen M.; Chen, Yu-Hui; Rathmell, Aaron R.
- Nanoscale, Vol. 4, Issue 6
Co-Percolating Graphene-Wrapped Silver Nanowire Network for High Performance, Highly Stable, Transparent Conducting Electrodes
journal, April 2013
- Chen, Ruiyi; Das, Suprem R.; Jeong, Changwook
- Advanced Functional Materials, Vol. 23, Issue 41
The effect of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on mammalian and plant cells in vitro
journal, October 2016
- Jiravova, Jana; Tomankova, Katerina Barton; Harvanova, Monika
- Food and Chemical Toxicology, Vol. 96
NADPH Oxidase-Dependent NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and its Important Role in Lung Fibrosis by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes
journal, January 2015
- Sun, Bingbing; Wang, Xiang; Ji, Zhaoxia
- Small, Vol. 11, Issue 17
Shape matters: effects of silver nanospheres and wires on human alveolar epithelial cells
journal, January 2011
- Stoehr, Linda C.; Gonzalez, Edgar; Stampfl, Andreas
- Particle and Fibre Toxicology, Vol. 8, Issue 1
Use of silver nanowires to determine thresholds for fibre length-dependent pulmonary inflammation and inhibition of macrophage migration in vitro
journal, January 2012
- Schinwald, Anja; Chernova, Tanya; Donaldson, Ken
- Particle and Fibre Toxicology, Vol. 9, Issue 1
Diameter and rigidity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes are critical factors in mesothelial injury and carcinogenesis
journal, November 2011
- Nagai, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Chew, S. H.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 108, Issue 49
Mechanics of Microtubule-Based Membrane Extension
journal, December 1997
- Fygenson, Deborah Kuchnir; Marko, John F.; Libchaber, Albert
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 79, Issue 22
Silver Nanowire Exposure Results in Internalization and Toxicity to Daphnia magna
journal, November 2013
- Scanlan, Leona D.; Reed, Robert B.; Loguinov, Alexandre V.
- ACS Nano, Vol. 7, Issue 12
Mechanisms of Nanoparticle-Induced Oxidative Stress and Toxicity
journal, January 2013
- Manke, Amruta; Wang, Liying; Rojanasakul, Yon
- BioMed Research International, Vol. 2013
Silver Wire Amplifies the Signaling Mechanism for IL-1beta Production More Than Silver Submicroparticles in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells
journal, November 2014
- Jung, Hye Jin; Pak, Pyo June; Park, Sung Hyo
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 9, Issue 11
Crystalline Silver Nanowires by Soft Solution Processing
journal, February 2002
- Sun, Yugang; Gates, Byron; Mayers, Brian
- Nano Letters, Vol. 2, Issue 2
Toxic Potential of Materials at the Nanolevel
journal, February 2006
- Nel, A.
- Science, Vol. 311, Issue 5761
Antioxidant and Cell-Signaling Functions of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Central Nervous System
journal, January 2018
- Shefa, Ulfuara; Kim, Min-Sik; Jeong, Na Young
- Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, Vol. 2018
In Vitro Dermal Safety Assessment of Silver Nanowires after Acute Exposure: Tissue vs. Cell Models
journal, April 2018
- Lehmann, Sylvia; Gilbert, Benjamin; Maffeis, Thierry
- Nanomaterials, Vol. 8, Issue 4
High performance transparent multi-touch sensors based on silver nanowires
journal, June 2016
- Cann, Maria; Large, Matthew J.; Henley, Simon J.
- Materials Today Communications, Vol. 7
The dependence of the optoelectrical properties of silver nanowire networks on nanowire length and diameter
journal, April 2012
- Sorel, Sophie; Lyons, Philip E.; De, Sukanta
- Nanotechnology, Vol. 23, Issue 18
Metallic Nanowire-Based Transparent Electrodes for Next Generation Flexible Devices: a Review
journal, October 2016
- Sannicolo, Thomas; Lagrange, Mélanie; Cabos, Anthony
- Small, Vol. 12, Issue 44
Strategies for the intracellular delivery of nanoparticles
journal, January 2011
- Chou, Leo Y. T.; Ming, Kevin; Chan, Warren C. W.
- Chem. Soc. Rev., Vol. 40, Issue 1
Silver Nanowire Particle Reactivity with Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophage Cells: Intracellular Availability of Silver Governs Their Cytotoxicity
journal, September 2017
- Theodorou, Ioannis G.; Müller, Karin H.; Chen, Shu
- ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, Vol. 3, Issue 10
GM1 structure determines SV40-induced membrane invagination and infection
journal, December 2009
- Ewers, Helge; Römer, Winfried; Smith, Alicia E.
- Nature Cell Biology, Vol. 12, Issue 1
Asbestos, carbon nanotubes and the pleural mesothelium: a review and the hypothesis regarding the role of long fibre retention in the parietal pleura, inflammation and mesothelioma
journal, January 2010
- Donaldson, Ken; Murphy, Fiona A.; Duffin, Rodger
- Particle and Fibre Toxicology, Vol. 7, Issue 1
Engineered nanomaterial-induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization and anti-cathepsin agents
journal, May 2017
- Bunderson-Schelvan, Melisa; Holian, Andrij; Hamilton, Raymond F.
- Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B, Vol. 20, Issue 4
Environmental Transformations of Silver Nanoparticles: Impact on Stability and Toxicity
journal, February 2012
- Levard, Clément; Hotze, E. Matt; Lowry, Gregory V.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 46, Issue 13
Autophagy induction by silver nanowires: A new aspect in the biocompatibility assessment of nanocomposite thin films
journal, November 2012
- Verma, Navin K.; Conroy, Jennifer; Lyons, Philip E.
- Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, Vol. 264, Issue 3
Early Combination of Material Characteristics and Toxicology Is Useful in the Design of Low Toxicity Carbon Nanofiber
journal, September 2012
- Jensen, Ellen K.; Larsen, Sten Y.; Nygaard, Unni C.
- Materials, Vol. 5, Issue 9
SimpleElastix: A User-Friendly, Multi-lingual Library for Medical Image Registration
conference, June 2016
- Marstal, Kasper; Berendsen, Floris; Staring, Marius
- 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)
Particle length-dependent titanium dioxide nanomaterials toxicity and bioactivity
journal, January 2009
- Hamilton, Raymond F.; Wu, Nianqiang; Porter, Dale
- Particle and Fibre Toxicology, Vol. 6, Issue 1
Cell entry of one-dimensional nanomaterials occurs by tip recognition and rotation
journal, September 2011
- Shi, Xinghua; von dem Bussche, Annette; Hurt, Robert H.
- Nature Nanotechnology, Vol. 6, Issue 11
Nanomechanical mechanism for lipid bilayer damage induced by carbon nanotubes confined in intracellular vesicles
journal, October 2016
- Zhu, Wenpeng; von dem Bussche, Annette; Yi, Xin
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 113, Issue 44
Surface Interactions with Compartmentalized Cellular Phosphates Explain Rare Earth Oxide Nanoparticle Hazard and Provide Opportunities for Safer Design
journal, January 2014
- Li, Ruibin; Ji, Zhaoxia; Chang, Chong Hyun
- ACS Nano, Vol. 8, Issue 2
Efficient correction of wavefront inhomogeneities in X-ray holographic nanotomography by random sample displacement
journal, May 2018
- Hubert, Maxime; Pacureanu, Alexandra; Guilloud, Cyril
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 112, Issue 20
Use of back-scatter electron signals to visualise cell/nanowires interactions in vitro and in vivo; frustrated phagocytosis of long fibres in macrophages and compartmentalisation in mesothelial cells in vivo
journal, January 2012
- Schinwald, Anja; Donaldson, Ken
- Particle and Fibre Toxicology, Vol. 9, Issue 1
Kinks, rings, and rackets in filamentous structures
journal, October 2003
- Cohen, A. E.; Mahadevan, L.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 100, Issue 21
Short versus long silver nanowires: a comparison of in vivo pulmonary effects post instillation
journal, October 2014
- Silva, Rona M.; Xu, Jingyi; Saiki, Clare
- Particle and Fibre Toxicology, Vol. 11, Issue 1
A multiplatform code for the analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectra
journal, January 2007
- Solé, V. A.; Papillon, E.; Cotte, M.
- Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, Vol. 62, Issue 1
Silver nanowires as prospective carriers for drug delivery in cancer treatment: an in vitro biocompatibility study on lung adenocarcinoma cells and fibroblasts
journal, January 2013
- Singh, Manisha; Movia, Dania; Mahfoud, Omar K.
- European Journal of Nanomedicine, Vol. 5, Issue 4
Efficient concentration of high-energy x-rays for diffraction-limited imaging resolution
journal, January 2017
- Cesar da Silva, Julio; Pacureanu, Alexandra; Yang, Yang
- Optica, Vol. 4, Issue 5
Holotomography: Quantitative phase tomography with micrometer resolution using hard synchrotron radiation x rays
journal, November 1999
- Cloetens, P.; Ludwig, W.; Baruchel, J.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 75, Issue 19
The asbestos analogy revisited
journal, July 2008
- Kane, Agnes B.; Hurt, Robert H.
- Nature Nanotechnology, Vol. 3, Issue 7
Sulfidation of silver nanowires inside human alveolar epithelial cells: a potential detoxification mechanism
journal, January 2013
- Chen, Shu; Goode, Angela E.; Sweeney, Sinbad
- Nanoscale, Vol. 5, Issue 20
Designed Synthesis of CeO 2 Nanorods and Nanowires for Studying Toxicological Effects of High Aspect Ratio Nanomaterials
journal, May 2012
- Ji, Zhaoxia; Wang, Xiang; Zhang, Haiyuan
- ACS Nano, Vol. 6, Issue 6
An introduction to the short-term toxicology of respirable industrial fibres
journal, September 2004
- Donaldson, Ken; Tran, C. Lang
- Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, Vol. 553, Issue 1-2
Improvements in purification of silver nanowires by decantation and fabrication of flexible transparent electrodes. Application to capacitive touch sensors
journal, April 2013
- Mayousse, Céline; Celle, Caroline; Moreau, Eléonore
- Nanotechnology, Vol. 24, Issue 21
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal