Experimental Evidence of the Lorentz-like Effective Medium Resonance in Semiconductor Hyperbolic Metamaterials using Strong Coupling to Plasmonic Metasurfaces
Abstract
The Lorentz-like effective medium resonance (LEMR) exhibited by the longitudinal effective permittivity of semiconductor hyperbolic metamaterials (SHMs) has been known for some time. However, direct observation of this resonance proved to be difficult. Here we experimentally demonstrate its existence by strongly coupling SHMs to plasmonic metasurfaces. We consider four strong coupling implementations of SHMs that exhibit different LEMR absorption profiles (both in frequency and strength) to validate our approach.
- Authors:
-
- Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States)
- Northern Arizona Univ., Flagstaff, AZ (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1559488
- Report Number(s):
- SAND-2019-7174J
Journal ID: ISSN 0018-926X; 676760; TRN: US2000347
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC04-94AL85000
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 68; Journal Issue: 3; Journal ID: ISSN 0018-926X
- Publisher:
- IEEE
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 42 ENGINEERING; hyperbolic metamaterials; plasmonic metasurfaces; strong coupling; effective medium resonance
Citation Formats
Campione, Salvatore, Klem, John F., Liu, Sheng, Montano, Ines, Sinclair, Michael B., and Luk, Ting S. Experimental Evidence of the Lorentz-like Effective Medium Resonance in Semiconductor Hyperbolic Metamaterials using Strong Coupling to Plasmonic Metasurfaces. United States: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1109/TAP.2019.2930154.
Campione, Salvatore, Klem, John F., Liu, Sheng, Montano, Ines, Sinclair, Michael B., & Luk, Ting S. Experimental Evidence of the Lorentz-like Effective Medium Resonance in Semiconductor Hyperbolic Metamaterials using Strong Coupling to Plasmonic Metasurfaces. United States. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2019.2930154
Campione, Salvatore, Klem, John F., Liu, Sheng, Montano, Ines, Sinclair, Michael B., and Luk, Ting S. Fri .
"Experimental Evidence of the Lorentz-like Effective Medium Resonance in Semiconductor Hyperbolic Metamaterials using Strong Coupling to Plasmonic Metasurfaces". United States. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2019.2930154. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1559488.
@article{osti_1559488,
title = {Experimental Evidence of the Lorentz-like Effective Medium Resonance in Semiconductor Hyperbolic Metamaterials using Strong Coupling to Plasmonic Metasurfaces},
author = {Campione, Salvatore and Klem, John F. and Liu, Sheng and Montano, Ines and Sinclair, Michael B. and Luk, Ting S.},
abstractNote = {The Lorentz-like effective medium resonance (LEMR) exhibited by the longitudinal effective permittivity of semiconductor hyperbolic metamaterials (SHMs) has been known for some time. However, direct observation of this resonance proved to be difficult. Here we experimentally demonstrate its existence by strongly coupling SHMs to plasmonic metasurfaces. We consider four strong coupling implementations of SHMs that exhibit different LEMR absorption profiles (both in frequency and strength) to validate our approach.},
doi = {10.1109/TAP.2019.2930154},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation},
number = 3,
volume = 68,
place = {United States},
year = {Fri Jul 26 00:00:00 EDT 2019},
month = {Fri Jul 26 00:00:00 EDT 2019}
}
Free Publicly Available Full Text
Publisher's Version of Record
Other availability
Cited by: 3 works
Citation information provided by
Web of Science
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
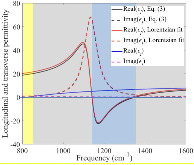 Fig. 1: Longitudinal effective medium permittivity εl from Eq. (3) compared to a Lorentzian oscillator fit of Design 4 in Fig. 4. The transverse effective medium permittivity εt is also reported. The yellow region indicates type-II hyperbolic, grey anisotropic dielectric, and blue type-I hyperbolic.
Fig. 1: Longitudinal effective medium permittivity εl from Eq. (3) compared to a Lorentzian oscillator fit of Design 4 in Fig. 4. The transverse effective medium permittivity εt is also reported. The yellow region indicates type-II hyperbolic, grey anisotropic dielectric, and blue type-I hyperbolic.
All figures and tables
(13 total)
Save to My Library
You must Sign In or Create an Account in order to save documents to your library.
Figures / Tables found in this record:
Figures/Tables have been extracted from DOE-funded journal article accepted manuscripts.

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal