Observation of divertor currents during type-I ELMs on the DIII-D tokamak
Abstract
In DIII-D, large currents flowing into the divertor floor during edge-localized modes (ELMs) have been measured by an array of shunt current resistors before an increase of heat flux is measured by IR thermography. The diagnostic consists of 40 tiles distributed in five concentric circles in the lower divertor with sampling rates range between 50 and 500 kHz. Typically, the current measured by a single tile during an ELM can reach 500 A. This amounts to 5–25 kA flowing in the divertor tiles. The temporal evolution of the ELM currents shows a first phase with large amplitude oscillations, occurring before the heat flux increase measured by infrared thermography at the same location, lasting between 0.05 ms and 0.3 ms. A second phase follows where the time evolution of the divertor current mimics the evolution of the divertor heat flux. These currents could affect the plasma edge stability in the nonlinear ELM phase and provide a mechanism leading to explosive growth of edge stochasticity, the need of which and existence is predicted in contemporary nonlinear ELM simulations.
- Authors:
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- General Atomics, San Diego, CA (United States); Univ. of California, San Diego, CA (United States); Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), Princeton, NJ (United States); Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Fusion Energy Sciences (FES)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1547897
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1502366; OSTI ID: 1570890
- Grant/Contract Number:
- FC02-04ER54698; FG02-07ER54917; FG02-05ER54809; AC05-00OR22725
- Resource Type:
- Published Article
- Journal Name:
- Nuclear Materials and Energy
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: Nuclear Materials and Energy Journal Volume: 18 Journal Issue: C; Journal ID: ISSN 2352-1791
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- Netherlands
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 70 PLASMA PHYSICS AND FUSION TECHNOLOGY
Citation Formats
Knolker, M., Evans, T. E., Wingen, A., Bortolon, A., Chrystal, C., Laggner, F., Moyer, R. A., Nazikian, R., and Zohm, H. Observation of divertor currents during type-I ELMs on the DIII-D tokamak. Netherlands: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.nme.2019.01.003.
Knolker, M., Evans, T. E., Wingen, A., Bortolon, A., Chrystal, C., Laggner, F., Moyer, R. A., Nazikian, R., & Zohm, H. Observation of divertor currents during type-I ELMs on the DIII-D tokamak. Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nme.2019.01.003
Knolker, M., Evans, T. E., Wingen, A., Bortolon, A., Chrystal, C., Laggner, F., Moyer, R. A., Nazikian, R., and Zohm, H. Tue .
"Observation of divertor currents during type-I ELMs on the DIII-D tokamak". Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nme.2019.01.003.
@article{osti_1547897,
title = {Observation of divertor currents during type-I ELMs on the DIII-D tokamak},
author = {Knolker, M. and Evans, T. E. and Wingen, A. and Bortolon, A. and Chrystal, C. and Laggner, F. and Moyer, R. A. and Nazikian, R. and Zohm, H.},
abstractNote = {In DIII-D, large currents flowing into the divertor floor during edge-localized modes (ELMs) have been measured by an array of shunt current resistors before an increase of heat flux is measured by IR thermography. The diagnostic consists of 40 tiles distributed in five concentric circles in the lower divertor with sampling rates range between 50 and 500 kHz. Typically, the current measured by a single tile during an ELM can reach 500 A. This amounts to 5–25 kA flowing in the divertor tiles. The temporal evolution of the ELM currents shows a first phase with large amplitude oscillations, occurring before the heat flux increase measured by infrared thermography at the same location, lasting between 0.05 ms and 0.3 ms. A second phase follows where the time evolution of the divertor current mimics the evolution of the divertor heat flux. These currents could affect the plasma edge stability in the nonlinear ELM phase and provide a mechanism leading to explosive growth of edge stochasticity, the need of which and existence is predicted in contemporary nonlinear ELM simulations.},
doi = {10.1016/j.nme.2019.01.003},
journal = {Nuclear Materials and Energy},
number = C,
volume = 18,
place = {Netherlands},
year = {Tue Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2019},
month = {Tue Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2019}
}
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nme.2019.01.003
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
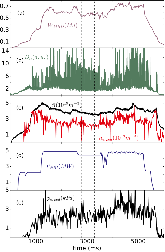 Figure 1: Discharge evolution of 119,434: (a) Stored energy, (b) ELM filterscope, (c) pedestal (red) and line-averaged (black) density (red), (d) NBI power (blue), (e) pedestal electron pressure. The dashed lines mark the H-mode time window most analysis presented here is focused on. (For interpretation of the references to colormore »
Figure 1: Discharge evolution of 119,434: (a) Stored energy, (b) ELM filterscope, (c) pedestal (red) and line-averaged (black) density (red), (d) NBI power (blue), (e) pedestal electron pressure. The dashed lines mark the H-mode time window most analysis presented here is focused on. (For interpretation of the references to colormore »
Works referencing / citing this record:
On the possiblity of direct electrical power extraction from scrape-off layer currents in tokamaks
journal, August 2019
- Komm, M.; Stockel, J.; Adamek, J.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 61, Issue 9
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal