Reducing variability in the cost of energy of ocean energy arrays
Abstract
Variability in the predicted cost of energy of an ocean energy converter array is more substantial than for other forms of energy generation, due to the combined stochastic action of weather conditions and failures. If the variability is great enough, then this may influence future financial decisions. This paper provides the unique contribution of quantifying variability in the predicted cost of energy and introduces a framework for investigating reduction of variability through investment in components. Following review of existing methodologies for parametric analysis of ocean energy array design, the development of the DTOcean software tool is presented. DTOcean can quantify variability by simulating the design, deployment and operation of arrays with higher complexity than previous models, designing sub-systems at component level. A case study of a theoretical floating wave energy converter array is used to demonstrate that the variability in levelised cost of energy (LCOE) can be greatest for the smallest arrays and that investment in improved component reliability can reduce both the variability and most likely value of LCOE. A hypothetical study of improved electrical cables and connectors shows reductions in LCOE up to 2.51% and reductions in the variability of LCOE of over 50%; these minima occur formore »
- Authors:
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1531034
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1570292
- Report Number(s):
- SAND-2019-10077J
Journal ID: ISSN 1364-0321; S1364032119303454; PII: S1364032119303454
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC04-94AL85000
- Resource Type:
- Published Article
- Journal Name:
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews Journal Volume: 112 Journal Issue: C; Journal ID: ISSN 1364-0321
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- United Kingdom
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 16 TIDAL AND WAVE POWER; Financial; Variability; Energy; Ocean; Wave; Tidal; Arrays
Citation Formats
Topper, Mathew B. R., Nava, Vincenzo, Collin, Adam J., Bould, David, Ferri, Francesco, Olson, Sterling S., Dallman, Ann R., Roberts, Jesse D., Ruiz-Minguela, Pablo, and Jeffrey, Henry F. Reducing variability in the cost of energy of ocean energy arrays. United Kingdom: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.032.
Topper, Mathew B. R., Nava, Vincenzo, Collin, Adam J., Bould, David, Ferri, Francesco, Olson, Sterling S., Dallman, Ann R., Roberts, Jesse D., Ruiz-Minguela, Pablo, & Jeffrey, Henry F. Reducing variability in the cost of energy of ocean energy arrays. United Kingdom. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.032
Topper, Mathew B. R., Nava, Vincenzo, Collin, Adam J., Bould, David, Ferri, Francesco, Olson, Sterling S., Dallman, Ann R., Roberts, Jesse D., Ruiz-Minguela, Pablo, and Jeffrey, Henry F. Sun .
"Reducing variability in the cost of energy of ocean energy arrays". United Kingdom. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.032.
@article{osti_1531034,
title = {Reducing variability in the cost of energy of ocean energy arrays},
author = {Topper, Mathew B. R. and Nava, Vincenzo and Collin, Adam J. and Bould, David and Ferri, Francesco and Olson, Sterling S. and Dallman, Ann R. and Roberts, Jesse D. and Ruiz-Minguela, Pablo and Jeffrey, Henry F.},
abstractNote = {Variability in the predicted cost of energy of an ocean energy converter array is more substantial than for other forms of energy generation, due to the combined stochastic action of weather conditions and failures. If the variability is great enough, then this may influence future financial decisions. This paper provides the unique contribution of quantifying variability in the predicted cost of energy and introduces a framework for investigating reduction of variability through investment in components. Following review of existing methodologies for parametric analysis of ocean energy array design, the development of the DTOcean software tool is presented. DTOcean can quantify variability by simulating the design, deployment and operation of arrays with higher complexity than previous models, designing sub-systems at component level. A case study of a theoretical floating wave energy converter array is used to demonstrate that the variability in levelised cost of energy (LCOE) can be greatest for the smallest arrays and that investment in improved component reliability can reduce both the variability and most likely value of LCOE. A hypothetical study of improved electrical cables and connectors shows reductions in LCOE up to 2.51% and reductions in the variability of LCOE of over 50%; these minima occur for different combinations of components.},
doi = {10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.032},
journal = {Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews},
number = C,
volume = 112,
place = {United Kingdom},
year = {Sun Sep 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019},
month = {Sun Sep 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019}
}
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.032
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
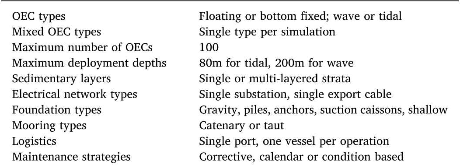 Table 1 : Simulation scope and modelling assumptions of the DTOcean software.
Table 1 : Simulation scope and modelling assumptions of the DTOcean software.
Works referenced in this record:
The offshore wind farm array cable layout problem: a planar open vehicle routing problem
journal, March 2015
- Bauer, Joanna; Lysgaard, Jens
- Journal of the Operational Research Society, Vol. 66, Issue 3
Review of wave energy technologies and the necessary power-equipment
journal, November 2013
- López, Iraide; Andreu, Jon; Ceballos, Salvador
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Vol. 27
Optimising power transmission options for marine energy converter farms
journal, September 2016
- Nambiar, Anup J.; Collin, Adam J.; Karatzounis, Sotirios
- International Journal of Marine Energy, Vol. 15
Techno-economic challenges of tidal energy conversion systems: Current status and trends
journal, September 2017
- Segura, E.; Morales, R.; Somolinos, J. A.
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Vol. 77
A novel method for deriving the diffraction transfer matrix and its application to multi-body interactions in water waves
journal, January 2015
- McNatt, J. Cameron; Venugopal, Vengatesan; Forehand, David
- Ocean Engineering, Vol. 94
A numerical study on the hydrodynamic impact of device slenderness and array size in wave energy farms in realistic wave climates
journal, September 2017
- Penalba, Markel; Touzón, Imanol; Lopez-Mendia, Joseba
- Ocean Engineering, Vol. 142
Wave energy converter array optimization: A genetic algorithm approach and minimum separation distance study
journal, September 2018
- Sharp, Chris; DuPont, Bryony
- Ocean Engineering, Vol. 163
Optimisation of marine energy installation operations
journal, December 2013
- Morandeau, Maxime; Walker, Rich T.; Argall, Richard
- International Journal of Marine Energy, Vol. 3-4
Ocean wave energy in the United States: Current status and future perspectives
journal, July 2017
- Lehmann, Marcus; Karimpour, Farid; Goudey, Clifford A.
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Vol. 74
Maximising value of electrical networks for wave energy converter arrays
journal, April 2013
- Sharkey, Fergus; Bannon, Elva; Conlon, Michael
- International Journal of Marine Energy, Vol. 1
Electrical Components for Marine Renewable Energy Arrays: A Techno-Economic Review
journal, November 2017
- Collin, Adam; Nambiar, Anup; Bould, David
- Energies, Vol. 10, Issue 12
Reliability and O&M sensitivity analysis as a consequence of site specific characteristics for wave energy converters
journal, September 2017
- Gray, Anthony; Dickens, Beth; Bruce, Tom
- Ocean Engineering, Vol. 141
Sensitivity analysis of offshore wind farm operation and maintenance cost and availability
journal, January 2016
- Martin, Rebecca; Lazakis, Iraklis; Barbouchi, Sami
- Renewable Energy, Vol. 85
Productivity and economic assessment of wave energy projects through operational simulations
journal, December 2012
- Teillant, Boris; Costello, Ronan; Weber, Jochem
- Renewable Energy, Vol. 48
Hydrokinetic energy conversion systems: A technology status review
journal, March 2015
- Yuce, M. Ishak; Muratoglu, Abdullah
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Vol. 43
An analytical cost model for co-located floating wind-wave energy arrays
journal, March 2019
- Clark, Caitlyn E.; Miller, Annalise; DuPont, Bryony
- Renewable Energy, Vol. 132
Cost related reliability evaluation of bulk power systems
journal, February 2001
- Billinton, R.; Zhang, W.
- International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, Vol. 23, Issue 2
Why Your Data Won’t Mix: New tools and techniques can help ease the pain of reconciling schemas.
journal, October 2005
- Halevy, Alon
- Queue, Vol. 3, Issue 8
Perspectives on a way forward for ocean renewable energy in Australia
journal, November 2018
- Hemer, Mark A.; Manasseh, Richard; McInnes, Kathleen L.
- Renewable Energy, Vol. 127
Ocean energy development in Europe: Current status and future perspectives
journal, September 2015
- Magagna, Davide; Uihlein, Andreas
- International Journal of Marine Energy, Vol. 11
Energy distance
journal, December 2015
- Rizzo, Maria L.; Székely, Gábor J.
- Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, Vol. 8, Issue 1
Levelised costs of Wave and Tidal energy in the UK: Cost competitiveness and the importance of “banded” Renewables Obligation Certificates
journal, January 2011
- Allan, Grant; Gilmartin, Michelle; McGregor, Peter
- Energy Policy, Vol. 39, Issue 1
Layout Optimisation of Wave Energy Converter Arrays
journal, August 2017
- Ruiz, Pau; Nava, Vincenzo; Topper, Mathew
- Energies, Vol. 10, Issue 9
MATPOWER: Steady-State Operations, Planning, and Analysis Tools for Power Systems Research and Education
journal, February 2011
- Zimmerman, Ray Daniel; Murillo-Sanchez, Carlos Edmundo; Thomas, Robert John
- IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, Vol. 26, Issue 1
Optimal reliability, warranty and price for new products
journal, May 2007
- Huang, Hong-Zhong; Liu, Zhi-Jie; Murthy, D. N. P.
- IIE Transactions, Vol. 39, Issue 8
An experimental investigation simulating flow effects in first generation marine current energy converter arrays
journal, January 2012
- Myers, L. E.; Bahaj, A. S.
- Renewable Energy, Vol. 37, Issue 1
Parametric CAD/CAE integration using a common data model
journal, August 2011
- Gujarathi, G. P.; Ma, Y. -S.
- Journal of Manufacturing Systems, Vol. 30, Issue 3
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal