Controllable protein phase separation and modular recruitment to form responsive membraneless organelles
Abstract
Abstract Many intrinsically disordered proteins self-assemble into liquid droplets that function as membraneless organelles. Because of their biological importance and ability to colocalize molecules at high concentrations, these protein compartments represent a compelling target for bio-inspired materials engineering. Here we manipulated the intrinsically disordered, arginine/glycine-rich RGG domain from the P granule protein LAF-1 to generate synthetic membraneless organelles with controllable phase separation and cargo recruitment. First, we demonstrate enzymatically triggered droplet assembly and disassembly, whereby miscibility and RGG domain valency are tuned by protease activity. Second, we control droplet composition by selectively recruiting cargo molecules via protein interaction motifs. We then demonstrate protease-triggered controlled release of cargo. Droplet assembly and cargo recruitment are robust, occurring in cytoplasmic extracts and in living mammalian cells. This versatile system, which generates dynamic membraneless organelles with programmable phase behavior and composition, has important applications for compartmentalizing collections of proteins in engineered cells and protocells.
- Authors:
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Univ. of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1461590
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1511484
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0007063
- Resource Type:
- Published Article
- Journal Name:
- Nature Communications
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: Nature Communications Journal Volume: 9 Journal Issue: 1; Journal ID: ISSN 2041-1723
- Publisher:
- Nature Publishing Group
- Country of Publication:
- United Kingdom
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 59 BASIC BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES
Citation Formats
Schuster, Benjamin S., Reed, Ellen H., Parthasarathy, Ranganath, Jahnke, Craig N., Caldwell, Reese M., Bermudez, Jessica G., Ramage, Holly, Good, Matthew C., and Hammer, Daniel A. Controllable protein phase separation and modular recruitment to form responsive membraneless organelles. United Kingdom: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-05403-1.
Schuster, Benjamin S., Reed, Ellen H., Parthasarathy, Ranganath, Jahnke, Craig N., Caldwell, Reese M., Bermudez, Jessica G., Ramage, Holly, Good, Matthew C., & Hammer, Daniel A. Controllable protein phase separation and modular recruitment to form responsive membraneless organelles. United Kingdom. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05403-1
Schuster, Benjamin S., Reed, Ellen H., Parthasarathy, Ranganath, Jahnke, Craig N., Caldwell, Reese M., Bermudez, Jessica G., Ramage, Holly, Good, Matthew C., and Hammer, Daniel A. Mon .
"Controllable protein phase separation and modular recruitment to form responsive membraneless organelles". United Kingdom. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05403-1.
@article{osti_1461590,
title = {Controllable protein phase separation and modular recruitment to form responsive membraneless organelles},
author = {Schuster, Benjamin S. and Reed, Ellen H. and Parthasarathy, Ranganath and Jahnke, Craig N. and Caldwell, Reese M. and Bermudez, Jessica G. and Ramage, Holly and Good, Matthew C. and Hammer, Daniel A.},
abstractNote = {Abstract Many intrinsically disordered proteins self-assemble into liquid droplets that function as membraneless organelles. Because of their biological importance and ability to colocalize molecules at high concentrations, these protein compartments represent a compelling target for bio-inspired materials engineering. Here we manipulated the intrinsically disordered, arginine/glycine-rich RGG domain from the P granule protein LAF-1 to generate synthetic membraneless organelles with controllable phase separation and cargo recruitment. First, we demonstrate enzymatically triggered droplet assembly and disassembly, whereby miscibility and RGG domain valency are tuned by protease activity. Second, we control droplet composition by selectively recruiting cargo molecules via protein interaction motifs. We then demonstrate protease-triggered controlled release of cargo. Droplet assembly and cargo recruitment are robust, occurring in cytoplasmic extracts and in living mammalian cells. This versatile system, which generates dynamic membraneless organelles with programmable phase behavior and composition, has important applications for compartmentalizing collections of proteins in engineered cells and protocells.},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-018-05403-1},
journal = {Nature Communications},
number = 1,
volume = 9,
place = {United Kingdom},
year = {Mon Jul 30 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Mon Jul 30 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05403-1
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
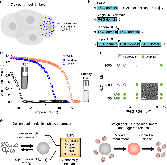 Fig. 1: Phase separation of RGG-based IDP constructs. a Illustration of four-cell C. elegans embryo. LAF-1 is present in P granules, which contribute to germline specification. b Domain organization of LAF-1, RGG, RGG-RGG, and RGG-RGG-RGG. c Representative turbidity measurements show temperaturedependent phase behavior of RGG, RGG-RGG, and RGG-RGG-RGG at proteinmore »
Fig. 1: Phase separation of RGG-based IDP constructs. a Illustration of four-cell C. elegans embryo. LAF-1 is present in P granules, which contribute to germline specification. b Domain organization of LAF-1, RGG, RGG-RGG, and RGG-RGG-RGG. c Representative turbidity measurements show temperaturedependent phase behavior of RGG, RGG-RGG, and RGG-RGG-RGG at proteinmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Phase Separation by Low Complexity Domains Promotes Stress Granule Assembly and Drives Pathological Fibrillization
journal, September 2015
- Molliex, Amandine; Temirov, Jamshid; Lee, Jihun
- Cell, Vol. 163, Issue 1
Formation and Maturation of Phase-Separated Liquid Droplets by RNA-Binding Proteins
journal, October 2015
- Lin, Yuan; Protter, David S. W.; Rosen, Michael K.
- Molecular Cell, Vol. 60, Issue 2
Novel Split-Luciferase-Based Genetically Encoded Biosensors for Noninvasive Visualization of Rho GTPases
journal, April 2013
- Leng, Weibing; Pang, Xiaohui; Xia, Hongwei
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 8, Issue 4
Cascade Reactions in Multicompartmentalized Polymersomes
journal, November 2013
- Peters, Ruud J. R. W.; Marguet, Maïté; Marais, Sébastien
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Vol. 53, Issue 1
Spatiotemporal Control of Supramolecular Self-Assembly and Function
journal, March 2017
- Zhan, Jie; Cai, Yanbin; Ji, Shenglu
- ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, Vol. 9, Issue 11
Enzyme-Instructed Intracellular Molecular Self-Assembly to Boost Activity of Cisplatin against Drug-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cells
journal, September 2015
- Li, Jie; Kuang, Yi; Shi, Junfeng
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Vol. 54, Issue 45
Vesicle-based artificial cells as chemical microreactors with spatially segregated reaction pathways
journal, October 2014
- Elani, Yuval; Law, Robert V.; Ces, Oscar
- Nature Communications, Vol. 5, Issue 1
Enzymatic Formation of Supramolecular Hydrogels
journal, August 2004
- Yang, Z.; Gu, H.; Fu, D.
- Advanced Materials, Vol. 16, Issue 16
An overview of enzymatic reagents for the removal of affinity tags
journal, December 2011
- Waugh, David S.
- Protein Expression and Purification, Vol. 80, Issue 2
Phase separation in biology; functional organization of a higher order
journal, January 2016
- Mitrea, Diana M.; Kriwacki, Richard W.
- Cell Communication and Signaling, Vol. 14, Issue 1
Stimuli-sensitive intrinsically disordered protein brushes
journal, October 2014
- Srinivasan, Nithya; Bhagawati, Maniraj; Ananthanarayanan, Badriprasad
- Nature Communications, Vol. 5, Issue 1
Phase behaviour of disordered proteins underlying low density and high permeability of liquid organelles
journal, June 2017
- Wei, Ming-Tzo; Elbaum-Garfinkle, Shana; Holehouse, Alex S.
- Nature Chemistry, Vol. 9, Issue 11
Light-cleavable rapamycin dimer as an optical trigger for protein dimerization
journal, January 2015
- Brown, Kalyn A.; Zou, Yan; Shirvanyants, David
- Chemical Communications, Vol. 51, Issue 26
Compositional Control of Phase-Separated Cellular Bodies
journal, July 2016
- Banani, Salman F.; Rice, Allyson M.; Peeples, William B.
- Cell, Vol. 166, Issue 3
Two-Step Protein Self-Assembly in the Extracellular Matrix
journal, June 2013
- Park, Won Min; Champion, Julie A.
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Vol. 52, Issue 31
Active liquid-like behavior of nucleoli determines their size and shape in Xenopus laevis oocytes
journal, February 2011
- Brangwynne, C. P.; Mitchison, T. J.; Hyman, A. A.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 108, Issue 11
Rational design of functional and tunable oscillating enzymatic networks
journal, January 2015
- Semenov, Sergey N.; Wong, Albert S. Y.; van der Made, R. Martijn
- Nature Chemistry, Vol. 7, Issue 2
Sequence heuristics to encode phase behaviour in intrinsically disordered protein polymers
journal, September 2015
- Quiroz, Felipe García; Chilkoti, Ashutosh
- Nature Materials, Vol. 14, Issue 11
Organization of Intracellular Reactions with Rationally Designed RNA Assemblies
journal, June 2011
- Delebecque, C. J.; Lindner, A. B.; Silver, P. A.
- Science, Vol. 333, Issue 6041
Phosphorylation-mediated RNA/peptide complex coacervation as a model for intracellular liquid organelles
journal, December 2015
- Aumiller, William M.; Keating, Christine D.
- Nature Chemistry, Vol. 8, Issue 2
Synthetic protein scaffolds provide modular control over metabolic flux
journal, August 2009
- Dueber, John E.; Wu, Gabriel C.; Malmirchegini, G. Reza
- Nature Biotechnology, Vol. 27, Issue 8, p. 753-759
Harnessing yeast organelles for metabolic engineering
journal, July 2017
- Hammer, Sarah K.; Avalos, José L.
- Nature Chemical Biology, Vol. 13, Issue 8
Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Biology
journal, October 2014
- Hyman, Anthony A.; Weber, Christoph A.; Jülicher, Frank
- Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vol. 30, Issue 1
Monitoring regulated protein-protein interactions using split TEV
journal, October 2006
- Wehr, Michael C.; Laage, Rico; Bolz, Ulrike
- Nature Methods, Vol. 3, Issue 12
Beyond Stereospecificity: Liquids and Mesoscale Organization of Cytoplasm
journal, July 2011
- Hyman, Anthony A.; Brangwynne, Clifford P.
- Developmental Cell, Vol. 21, Issue 1
Modularity of a carbon-fixing protein organelle
journal, December 2011
- Bonacci, W.; Teng, P. K.; Afonso, B.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 109, Issue 2
Investigating mitotic spindle assembly and function in vitro using Xenopus laevis egg extracts
journal, December 2006
- Hannak, Eva; Heald, Rebecca
- Nature Protocols, Vol. 1, Issue 5
Phase transitions in the assembly of multivalent signalling proteins
journal, March 2012
- Li, Pilong; Banjade, Sudeep; Cheng, Hui-Chun
- Nature, Vol. 483, Issue 7389
Photoactivatable fluorescent probes reveal heterogeneous nanoparticle permeation through biological gels at multiple scales
journal, August 2017
- Schuster, Benjamin S.; Allan, Daniel B.; Kays, Joshua C.
- Journal of Controlled Release, Vol. 260
Injectable protease-operated depots of glucagon-like peptide-1 provide extended and tunable glucose control
journal, January 2013
- Amiram, M.; Luginbuhl, K. M.; Li, X.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 110, Issue 8
Germline P Granules Are Liquid Droplets That Localize by Controlled Dissolution/Condensation
journal, May 2009
- Brangwynne, C. P.; Eckmann, C. R.; Courson, D. S.
- Science, Vol. 324, Issue 5935
Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease
journal, September 2017
- Shin, Yongdae; Brangwynne, Clifford P.
- Science, Vol. 357, Issue 6357
Phase Transition of a Disordered Nuage Protein Generates Environmentally Responsive Membraneless Organelles
journal, March 2015
- Nott, Timothy J.; Petsalaki, Evangelia; Farber, Patrick
- Molecular Cell, Vol. 57, Issue 5
SYNZIP Protein Interaction Toolbox: in Vitro and in Vivo Specifications of Heterospecific Coiled-Coil Interaction Domains
journal, February 2012
- Thompson, Kenneth Evan; Bashor, Caleb J.; Lim, Wendell A.
- ACS Synthetic Biology, Vol. 1, Issue 4
Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression by Protease-Alleviated Spatial Sequestration (PASS)
journal, April 2015
- Pitner, Ragan A.; Scarpelli, Andrew H.; Leonard, Joshua N.
- ACS Synthetic Biology, Vol. 4, Issue 9
Spatiotemporal Control of Intracellular Phase Transitions Using Light-Activated optoDroplets
journal, January 2017
- Shin, Yongdae; Berry, Joel; Pannucci, Nicole
- Cell, Vol. 168, Issue 1-2
Particle tracking in drug and gene delivery research: State-of-the-art applications and methods
journal, August 2015
- Schuster, Benjamin S.; Ensign, Laura M.; Allan, Daniel B.
- Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, Vol. 91
Designer amphiphilic proteins as building blocks for the intracellular formation of organelle-like compartments
journal, November 2014
- Huber, Matthias C.; Schreiber, Andreas; von Olshausen, Philipp
- Nature Materials, Vol. 14, Issue 1
Engineered Protein Nano-Compartments for Targeted Enzyme Localization
journal, March 2012
- Choudhary, Swati; Quin, Maureen B.; Sanders, Mark A.
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 7, Issue 3
Coexisting Liquid Phases Underlie Nucleolar Subcompartments
journal, June 2016
- Feric, Marina; Vaidya, Nilesh; Harmon, Tyler S.
- Cell, Vol. 165, Issue 7
Intracellular production of hydrogels and synthetic RNA granules by multivalent molecular interactions
journal, November 2017
- Nakamura, Hideki; Lee, Albert A.; Afshar, Ali Sobhi
- Nature Materials, Vol. 17, Issue 1
Towards repurposing the yeast peroxisome for compartmentalizing heterologous metabolic pathways
journal, March 2016
- DeLoache, William C.; Russ, Zachary N.; Dueber, John E.
- Nature Communications, Vol. 7, Issue 1
Phase separation of signaling molecules promotes T cell receptor signal transduction
journal, April 2016
- Su, Xiaolei; Ditlev, Jonathon A.; Hui, Enfu
- Science, Vol. 352, Issue 6285
Tobacco etch virus protease: mechanism of autolysis and rational design of stable mutants with wild-type catalytic proficiency
journal, December 2001
- Kapust, Rachel B.; Tözsér, József; Fox, Jeffrey D.
- Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, Vol. 14, Issue 12
Protein sequestration generates a flexible ultrasensitive response in a genetic network
journal, January 2009
- Buchler, Nicolas E.; Cross, Frederick R.
- Molecular Systems Biology, Vol. 5, Issue 1
The disordered P granule protein LAF-1 drives phase separation into droplets with tunable viscosity and dynamics
journal, May 2015
- Elbaum-Garfinkle, Shana; Kim, Younghoon; Szczepaniak, Krzysztof
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 112, Issue 23
RNA catalysis through compartmentalization
journal, October 2012
- Strulson, Christopher A.; Molden, Rosalynn C.; Keating, Christine D.
- Nature Chemistry, Vol. 4, Issue 11
Residue-by-Residue View of In Vitro FUS Granules that Bind the C-Terminal Domain of RNA Polymerase II
journal, October 2015
- Burke, Kathleen A.; Janke, Abigail M.; Rhine, Christy L.
- Molecular Cell, Vol. 60, Issue 2
Biomolecular condensates: organizers of cellular biochemistry
journal, February 2017
- Banani, Salman F.; Lee, Hyun O.; Hyman, Anthony A.
- Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, Vol. 18, Issue 5
Compartmentalization of metabolic pathways in yeast mitochondria improves the production of branched-chain alcohols
journal, February 2013
- Avalos, José L.; Fink, Gerald R.; Stephanopoulos, Gregory
- Nature Biotechnology, Vol. 31, Issue 4
Membraneless organelles can melt nucleic acid duplexes and act as biomolecular filters
journal, May 2016
- Nott, Timothy J.; Craggs, Timothy D.; Baldwin, Andrew J.
- Nature Chemistry, Vol. 8, Issue 6
Programming molecular self-assembly of intrinsically disordered proteins containing sequences of low complexity
journal, January 2017
- Simon, Joseph R.; Carroll, Nick J.; Rubinstein, Michael
- Nature Chemistry, Vol. 9, Issue 6
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal