Nano-Oxide-Dispersed Ferritic Steel for Fusion Energy Systems
Abstract
ABSTRACT The role of oxide nanoparticles in cavity formation of a nano-oxide-dispersed ferritic steel subjected to (Fe + He) dual-ion and (Fe + He + H) triple-ion irradiations has been studied using transmission electron microscopy to elucidate the synergistic effects of helium and hydrogen on radiation tolerance of nano-oxide-dispersed ferritic steel for fusion energy systems. The effect of oxide nanoparticles on suppressing radiation-induced void swelling is clearly revealed from the observation of preferred trapping of helium bubbles at oxide nanoparticles, which results in a unimodal distribution of cavities in the (Fe + He) dual-ion irradiatedspecimen. An adverse effect of hydrogen implantation, however, is revealed from the observation of a bimodal distribution of cavities with large and facetted voids in association with the formation of HFe5O8-based hydroxide in local regions of the (Fe + He + H) triple-ion irradiated specimen.
- Authors:
-
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1458650
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1471885
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL-742960
Journal ID: ISSN 2059-8521; applab; 897866
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344; AC05-00OR22725
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- MRS Advances
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 3; Journal Issue: 31; Journal ID: ISSN 2059-8521
- Publisher:
- Materials Research Society (MRS)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 70 PLASMA PHYSICS AND FUSION TECHNOLOGY
Citation Formats
Hsiung, L. L., Tumey, S. J., Hoelzer, D. T., and Fluss, M. J. Nano-Oxide-Dispersed Ferritic Steel for Fusion Energy Systems. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1557/adv.2018.202.
Hsiung, L. L., Tumey, S. J., Hoelzer, D. T., & Fluss, M. J. Nano-Oxide-Dispersed Ferritic Steel for Fusion Energy Systems. United States. https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.202
Hsiung, L. L., Tumey, S. J., Hoelzer, D. T., and Fluss, M. J. Mon .
"Nano-Oxide-Dispersed Ferritic Steel for Fusion Energy Systems". United States. https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.202. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1458650.
@article{osti_1458650,
title = {Nano-Oxide-Dispersed Ferritic Steel for Fusion Energy Systems},
author = {Hsiung, L. L. and Tumey, S. J. and Hoelzer, D. T. and Fluss, M. J.},
abstractNote = {ABSTRACT The role of oxide nanoparticles in cavity formation of a nano-oxide-dispersed ferritic steel subjected to (Fe + He) dual-ion and (Fe + He + H) triple-ion irradiations has been studied using transmission electron microscopy to elucidate the synergistic effects of helium and hydrogen on radiation tolerance of nano-oxide-dispersed ferritic steel for fusion energy systems. The effect of oxide nanoparticles on suppressing radiation-induced void swelling is clearly revealed from the observation of preferred trapping of helium bubbles at oxide nanoparticles, which results in a unimodal distribution of cavities in the (Fe + He) dual-ion irradiatedspecimen. An adverse effect of hydrogen implantation, however, is revealed from the observation of a bimodal distribution of cavities with large and facetted voids in association with the formation of HFe5O8-based hydroxide in local regions of the (Fe + He + H) triple-ion irradiated specimen.},
doi = {10.1557/adv.2018.202},
journal = {MRS Advances},
number = 31,
volume = 3,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Feb 19 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Mon Feb 19 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Figures / Tables:
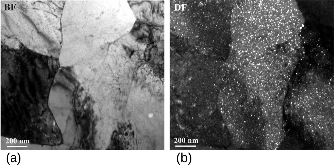 Figure 1: (a) Bright-field (BF) and (b) dark-field (DF) TEM images show high-density oxide nanoparticles formed within several grains.
Figure 1: (a) Bright-field (BF) and (b) dark-field (DF) TEM images show high-density oxide nanoparticles formed within several grains.
Works referenced in this record:
Correlation of neutron and heavy-ion damage
journal, November 1978
- Packan, N. H.; Farrell, K.; Stiegler, J. O.
- Journal of Nuclear Materials, Vol. 78, Issue 1
Mechanisms of helium interaction with radiation effects in metals and alloys: A review
journal, November 1983
- Mansur, L. K.; Coghlan, W. A.
- Journal of Nuclear Materials, Vol. 119, Issue 1
Density Functional Theory Study of Ferrihydrite and Related Fe-Oxyhydroxides
journal, December 2009
- Pinney, Nathan; Kubicki, James D.; Middlemiss, Derek S.
- Chemistry of Materials, Vol. 21, Issue 24
Defect and void evolution in oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic steels under 3.2 MeV Fe+ ion irradiation with simultaneous helium injection
journal, August 2000
- Kim, I. -S; Hunn, J. D.; Hashimoto, N.
- Journal of Nuclear Materials, Vol. 280, Issue 3
Development of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Ferritic Steels for FBR Core Application, (I): Improvement of Mechanical Properties by Recrystallization Processing
journal, March 1997
- Ukai, Shigeharu; Nishida, Toshio; Okada, Hirokazu
- Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, Vol. 34, Issue 3
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal