A rule-based expert system applied to moisture durability of building envelopes
Abstract
The moisture durability of an envelope component such as a wall or roof is difficult to predict. Moisture durability depends on all the construction materials used, as well as the climate, orientation, air tightness, and indoor conditions. Modern building codes require more insulation and tighter construction but provide little guidance about how to ensure these energy-efficient assemblies remain moisture durable. Furthermore, as new products and materials are introduced, builders are increasingly uncertain about the long-term durability of their building envelope designs. Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the US Department of Energy’s Building America Program are applying a rule-based expert system methodology in a web tool to help designers determine whether a given wall design is likely to be moisture durable and provide expert guidance on moisture risk management specific to a wall design and climate. Finally, the expert system is populated with knowledge from both expert judgment and probabilistic hygrothermal simulation results.
- Authors:
-
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
- Embry-Riddle Aeronautical Univ., Prescott, AZ (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), Energy Efficiency Office. Building Technologies Office
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1429214
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Journal of Building Physics
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 42; Journal Issue: 3; Journal ID: ISSN 1744-2591
- Publisher:
- SAGE
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 42 ENGINEERING; Moisture durability; building envelopes; walls, residential buildings; rule-based expert system
Citation Formats
Boudreaux, Philip R., Pallin, Simon B., Accawi, Gina K., Desjarlais, Andre Omer, Jackson, Roderick K., and Senecal, David R. A rule-based expert system applied to moisture durability of building envelopes. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1177/1744259117750370.
Boudreaux, Philip R., Pallin, Simon B., Accawi, Gina K., Desjarlais, Andre Omer, Jackson, Roderick K., & Senecal, David R. A rule-based expert system applied to moisture durability of building envelopes. United States. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744259117750370
Boudreaux, Philip R., Pallin, Simon B., Accawi, Gina K., Desjarlais, Andre Omer, Jackson, Roderick K., and Senecal, David R. Tue .
"A rule-based expert system applied to moisture durability of building envelopes". United States. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744259117750370. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1429214.
@article{osti_1429214,
title = {A rule-based expert system applied to moisture durability of building envelopes},
author = {Boudreaux, Philip R. and Pallin, Simon B. and Accawi, Gina K. and Desjarlais, Andre Omer and Jackson, Roderick K. and Senecal, David R.},
abstractNote = {The moisture durability of an envelope component such as a wall or roof is difficult to predict. Moisture durability depends on all the construction materials used, as well as the climate, orientation, air tightness, and indoor conditions. Modern building codes require more insulation and tighter construction but provide little guidance about how to ensure these energy-efficient assemblies remain moisture durable. Furthermore, as new products and materials are introduced, builders are increasingly uncertain about the long-term durability of their building envelope designs. Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the US Department of Energy’s Building America Program are applying a rule-based expert system methodology in a web tool to help designers determine whether a given wall design is likely to be moisture durable and provide expert guidance on moisture risk management specific to a wall design and climate. Finally, the expert system is populated with knowledge from both expert judgment and probabilistic hygrothermal simulation results.},
doi = {10.1177/1744259117750370},
journal = {Journal of Building Physics},
number = 3,
volume = 42,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue Jan 09 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Tue Jan 09 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
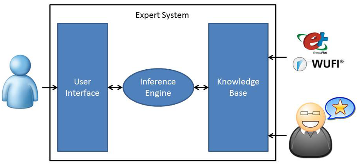 Figure 1: The expert system connects users to expert knowledge, which requires three parts: a user interface, an inference engine, and a knowledge base. The knowledge base is populated with information from expert building scientists and probabilistic hygrothermal simulation results.
Figure 1: The expert system connects users to expert knowledge, which requires three parts: a user interface, an inference engine, and a knowledge base. The knowledge base is populated with information from expert building scientists and probabilistic hygrothermal simulation results.
Works referenced in this record:
The integration of environmental variables in the process of architectural design
journal, September 2001
- Mazouz, S.; Zerouala, M. S.
- Energy and Buildings, Vol. 33, Issue 7
An interactive expert system for daylighting design exploration
journal, November 2011
- Gagne, Jaime M. L.; Andersen, Marilyne; Norford, Leslie K.
- Building and Environment, Vol. 46, Issue 11
HYPEREX—A generic expert system to assist architects in the design of routine building types
journal, April 1995
- Lutton, Linley
- Building and Environment, Vol. 30, Issue 2
Probabilistic modeling of the indoor climates of residential buildings using EnergyPlus
journal, April 2017
- Buechler, Elizabeth; Pallin, Simon; Boudreaux, Philip
- Journal of Building Physics, Vol. 41, Issue 3
Moisture Performance of Energy-Efficient and Conventional Wood-Frame Wall Assemblies in a Mixed-Humid Climate
journal, July 2015
- Glass, Samuel; Kochkin, Vladimir; Drumheller, S.
- Buildings, Vol. 5, Issue 3
Development of an outdoor lighting control system using expert system
journal, October 2016
- Atis, Selcuk; Ekren, Nazmi
- Energy and Buildings, Vol. 130
Application of expert systems to building design analysis and evaluation
journal, January 1990
- Rosenman, M. A.
- Building and Environment, Vol. 25, Issue 3
Experimental investigation of the wetting and drying potentials of wood frame walls subjected to vapor diffusion and wind-driven rain loads
journal, October 2015
- Tariku, Fitsum; Simpson, Ying; Iffa, Emishaw
- Building and Environment, Vol. 92
Intelligent systems in the automotive industry: applications and trends
journal, February 2007
- Gusikhin, Oleg; Rychtyckyj, Nestor; Filev, Dimitar
- Knowledge and Information Systems, Vol. 12, Issue 2
An expert system for the humidity and temperature control in HVAC systems using ANFIS and optimization with Fuzzy Modeling Approach
journal, August 2009
- Soyguder, Servet; Alli, Hasan
- Energy and Buildings, Vol. 41, Issue 8
U.S. Department of Energy Commercial Reference Building Models of the National Building Stock
report, February 2011
- Deru, M.; Field, K.; Studer, D.
Foreward: Knowledge-based expert systems in building
journal, January 1990
- Maher, Mary Lou; Gero, John S.
- Building and Environment, Vol. 25, Issue 3
Works referencing / citing this record:
Evaluation of design faults in HVAC systems in housing: A study based on thermohygrometric variables
journal, June 2019
- Carretero-Ayuso, Manuel J.; Moreno-Cansado, Alberto; García-Sanz-Calcedo, Justo
- Science and Technology for the Built Environment, Vol. 26, Issue 2
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal