Representing lateral groundwater flow from land to river in Earth system models
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
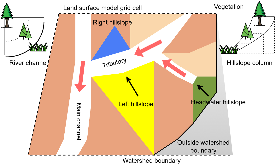
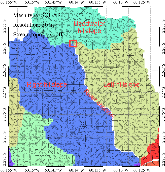
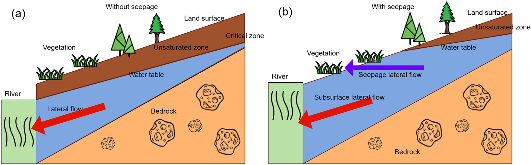
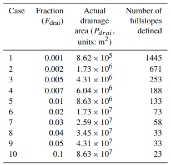
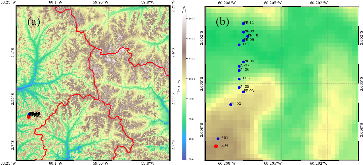
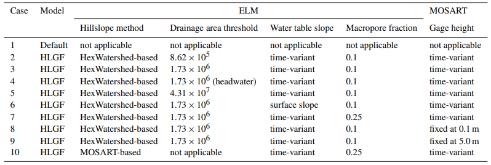
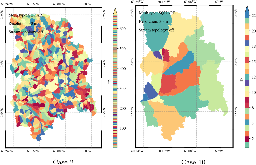
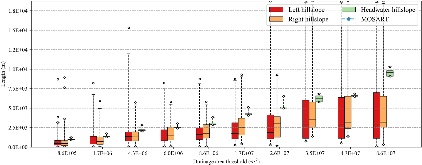
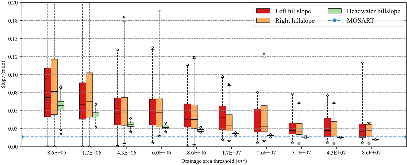
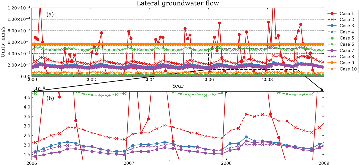
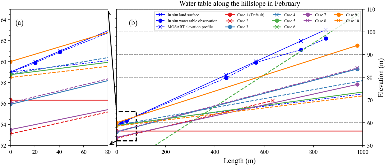
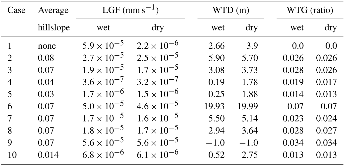
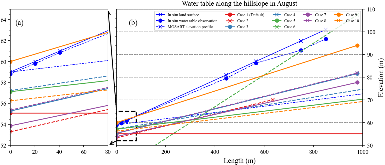
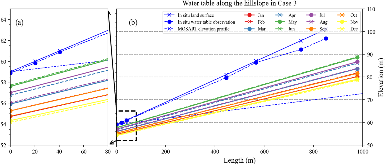
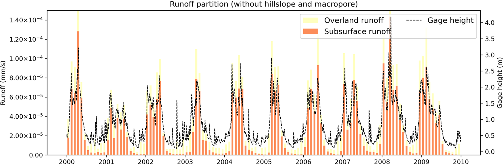
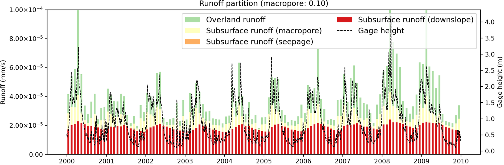
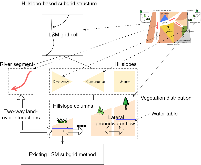
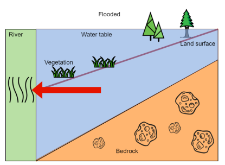
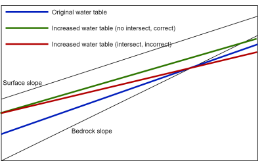
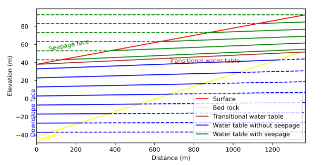
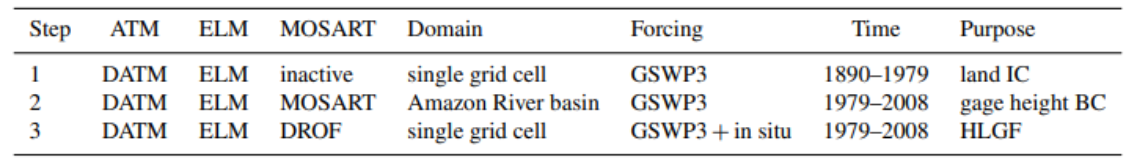
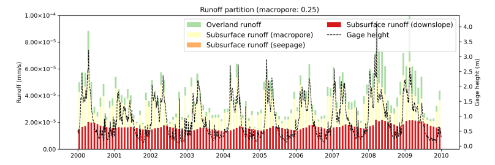
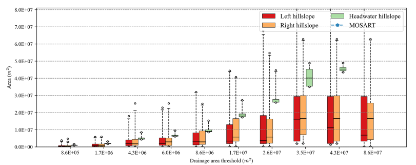
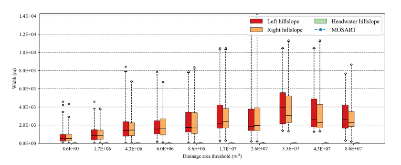
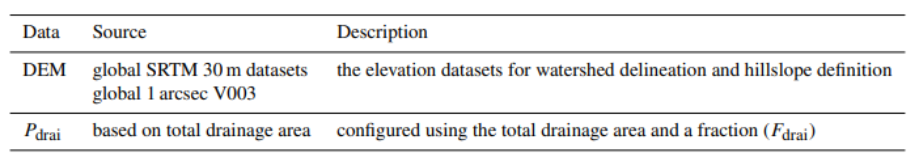
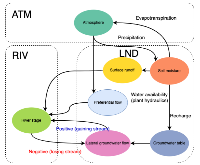
Lateral groundwater flow (LGF) is an important hydrologic process in controlling water table dynamics. Due to the relatively coarse spatial resolutions of land surface models, the representation of this process is often overlooked or overly simplified. In this study, we developed a hillslope-based lateral groundwater flow model. Specifically, we first developed a hillslope definition model based on an existing watershed delineation model to represent the subgrid spatial variability in topography. Building upon this hillslope definition, we then developed a physical-based lateral groundwater flow using Darcy’s equation. This model explicitly considers the relationships between the groundwater table along the hillslope and the river water table levels. We coupled this intra-grid model to the land component (E3SM Land Model: ELM) and river component (MOdel for Scale Adaptive River Transport: MOSART) of the Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM). We tested both the hillslope definition model and the lateral groundwater flow model and performed sensitivity experiments using different configurations. Simulations for a single grid cell at 0.5°×0.5° within the Amazon basin show that the definition of hillslope is the key to modeling lateral flow processes and the runoff partition between surface and subsurface can be dramatically changed using the hillslope approach. Although our method provides a pathway to improve the lateral flow process, future improvements are needed to better capture the subgrid structure to account for the spatial variability in hillslopes within the simulated grid of land surface models.
- Research Organization:
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-76RL01830
- OSTI ID:
- 2574249
- Report Number(s):
- PNNL-SA--204015
- Journal Information:
- Geoscientific Model Development (Online), Journal Name: Geoscientific Model Development (Online) Journal Issue: 14 Vol. 18; ISSN 1991-9603
- Publisher:
- Copernicus Publications, EGUCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English