Development and performance of a HemeLB GPU code for human-scale blood flow simulation
- Univ. College London (United Kingdom)
- Univ. College London (United Kingdom); Univ. of Amsterdam (Netherlands)
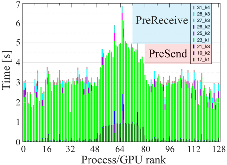
In recent years, it has become increasingly common for high performance computers (HPC) to possess some level of heterogeneous architecture - typically in the form of GPU accelerators. In some machines these are isolated within a dedicated partition, whilst in others they are integral to all compute nodes - often with multiple GPUs per node - and provide the majority of a machine's compute performance. In light of this trend, it is becoming essential that codes deployed on HPC are updated to execute on accelerator hardware. Here, in this paper, we introduce a GPU implementation of the 3D blood flow simulation code HemeLB that has been developed using CUDA C++. We demonstrate how taking advantage of NVIDIA GPU hardware can achieve significant performance improvements compared to the equivalent CPU only code on which it has been built whilst retaining the excellent strong scaling characteristics that have been repeatedly demonstrated by the CPU version. With HPC positioned on the brink of the exascale era, we use HemeLB as a motivation to provide a discussion on some of the challenges that many users will face when deploying their own applications on upcoming exascale machines.
- Research Organization:
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States). Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Advanced Scientific Computing Research (ASCR)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725
- OSTI ID:
- 2424007
- Journal Information:
- Computer Physics Communications, Journal Name: Computer Physics Communications Vol. 282; ISSN 0010-4655
- Publisher:
- ElsevierCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
Evaluating performance and portability of high-level programming models: Julia, Python/Numba, and Kokkos on exascale nodes
Experiences with High-Level Programming Directives for Porting Applications to GPUs. In: Facing the Multicore--Challenge II, Lecture Notes in Computer Science.