Tunable stochastic memristors for energy-efficient encryption and computing
Journal Article
·
· Nature Communications
- Seoul National Univ. (Korea, Republic of); Sandia National Lab. (SNL-CA), Livermore, CA (United States); Texas A & M Univ., College Station, TX (United States)
- Seoul National Univ. (Korea, Republic of)
- Texas A & M Univ., College Station, TX (United States)
- Applied Materials Inc., Santa Clara, CA (United States)
- Sandia National Lab. (SNL-CA), Livermore, CA (United States)
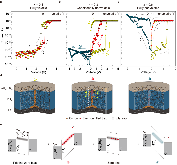
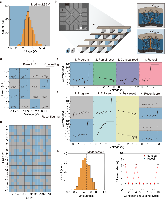
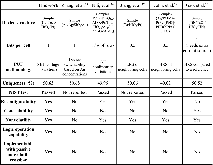
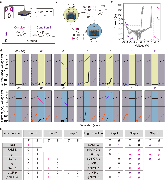
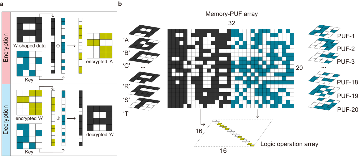
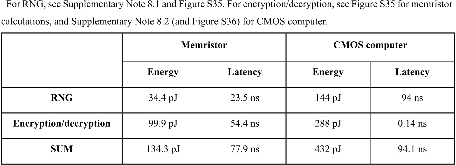
Information security and computing, two critical technological challenges for post-digital computation, pose opposing requirements – security (encryption) requires a source of unpredictability, while computing generally requires predictability. Each of these contrasting requirements presently necessitates distinct conventional Si-based hardware units with power-hungry overheads. This work demonstrates Cu0.3Te0.7/HfO2 (‘CuTeHO’) ion-migration-driven memristors that satisfy the contrasting requirements. Under specific operating biases, CuTeHO memristors generate truly random and physically unclonable functions, while under other biases, they perform universal Boolean logic. Using these computing primitives, this work experimentally demonstrates a single system that performs cryptographic key generation, universal Boolean logic operations, and encryption/decryption. Circuit-based calculations reveal the energy and latency advantages of the CuTeHO memristors in these operations. This work illustrates the functional flexibility of memristors in implementing operations with varying component-level requirements.
- Research Organization:
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (EFRC) (United States). Center for Reconfigurable Electronic Materials Inspired by Nonlinear Neuron Dynamics (reMIND); Sandia National Laboratories (SNL-CA), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF); USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA); USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- NA0003525
- OSTI ID:
- 2341390
- Report Number(s):
- SAND--2024-05027J
- Journal Information:
- Nature Communications, Journal Name: Nature Communications Journal Issue: 1 Vol. 15; ISSN 2041-1723
- Publisher:
- Nature Publishing GroupCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
Fully Homomorphic Encryption
Ultrafast optical message encryption–decryption system using semiconductor optical amplifier based XOR logic gate
Software
·
Thu Jun 19 20:00:00 EDT 2025
·
OSTI ID:code-160029
Ultrafast optical message encryption–decryption system using semiconductor optical amplifier based XOR logic gate
Journal Article
·
Mon Jul 15 00:00:00 EDT 2019
· Optical and Quantum Electronics
·
OSTI ID:22950215