Long-range Doppler lidar measurements of wind turbine wakes and their interaction with turbulent atmospheric boundary-layer flow at Perdigao 2017
- Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., Oberpfaffenhofen (Germany). Inst. of Atmospheric Physics
- Univ. of Colorado, Boulder, CO (United States). Dept. of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
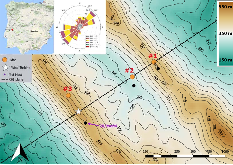
As part of the Perdigão 2017 campaign, vertical RHI (range-height indicator) scans with long-range pulsed Doppler wind lidars were performed aligned with the main wind direction and a wind turbine (WT) located on a mountain ridge. The measurements are used to not only retrieve flow velocities, but also their variance and - by using the turbulent broadening of the Doppler spectrum - also turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) dissipation rate. The study shows that turbulence in the WT wake is dependent on the turbulence of the inflow, but also on atmospheric stability. In stable atmospheric conditions, wakes could be analyzed up to five rotor diameters downstream (D) and showed the maximum turbulence in the wake at 2-3 D, whereas in unstable conditions, the maximum was found at 2 D and the wake could not be detected further than 3 D. A clear dependency of wake turbulence enhancement on inflow turbulence intensity is found, which levels out to no further enhancement at turbulence intensities of 30%.
- Research Organization:
- National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), Renewable Power Office. Wind Energy Technologies Office
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC36-08GO28308
- OSTI ID:
- 1670158
- Report Number(s):
- NREL/JA-5000-77994; MainId:31903; UUID:b9090824-26d0-44c4-abc0-3d53c7b7ed0d; MainAdminID:18620
- Journal Information:
- Journal of Physics. Conference Series, Vol. 1618; ISSN 1742-6588
- Publisher:
- IOP PublishingCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
Estimation of Turbulence Parameters from Scanning Lidars and in-situ Instrumentation in the Perdigao 2017 Campaign
Automated wind turbine wake characterization in complex terrain