The Role of Helium on Ejecta Production in Copper
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
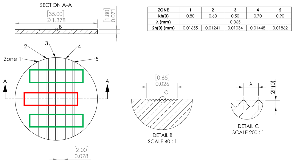
The effect of helium (He) concentration on ejecta production in OFHC-Copper was investigated using Richtmyer–Meshkov Instability (RMI) experiments. The experiments involved complex samples with periodic surface perturbations machined onto the surface. Each of the four target was implanted with a unique helium concentration that varied from 0 to 4000 appm. The perturbation’s wavelengths were $λ ≈$ 65 μ m, and their amplitudes $$h_0$$ were varied to determine the wavenumber $(2 π/ λ)$ amplitude product $$kh_0$$ at which ejecta production beganfor Cu with and without He. The velocity and mass of the ejecta produced was quantified using Photon Doppler Velocimetry (PDV) and Lithium-Niobate (LN) pins, respectively. Our results show that there was an increase of 30% in the velocity at which the ejecta cloud was traveling in Copper with 4000 appm as compared to its unimplanted counterpart. Our work also shows that there was a finer cloud of ejecta particles that was not detected by the PDV probes but was detected by the early arrival of a “signal” at the LN pins. While the LN pins were not able to successfully quantify the mass produced due to it being in the solid state, they did provide information on timing. Our results show that ejecta was produced for a longer time in the 4000 appm copper.
- Research Organization:
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), Office of Defense Programs (DP); USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). Office of Defense Programs (DP)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- 89233218CNA000001; AC52-06NA25396
- OSTI ID:
- 1634977
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1726179
- Report Number(s):
- LA-UR-19-32753; LA-UR-19-30934; MATEG9
- Journal Information:
- Materials, Vol. 13, Issue 6; ISSN 1996-1944
- Publisher:
- MDPICopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Proton radiography measurements and models of ejecta structure in shocked Sn
(U) Physics Validation of the RMI-Based Ejecta Source Model Implementation in FLAG: L2 Milestone #6035 Report