Sputtered NiOx Films for Stabilization of p+n-InP Photoanodes for Solar-Driven Water Oxidation
Journal Article
·
· Advanced Energy Materials
- California Institute of Technology (CalTech), Pasadena, CA (United States); California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA
- Univ. of California, San Diego, CA (United States)
- California Institute of Technology (CalTech), Pasadena, CA (United States)
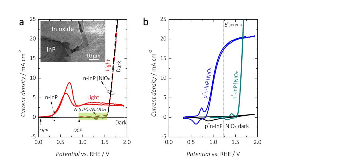
A reactively sputtered NiOx film has been used here to stabilize a buried-junction p+n-InP photoanode from anodic dissolution/corrosion for > 48 h of continuous light-driven evolution of O2(g) in 1.0 M KOH(aq) as well as in an aqueous electrolyte buffered at near-neutral pH. Under 1-Sun Air Mass (AM) 1.5G simulated solar illumination, NiOx-protected p+n-InP photoanodes produced photocurrent-onset potentials of -370 ± 10 mV referenced to the equilibrium potential for evolution of O2(g), light-limited photocurrent densities of 20.5 ± 0.3 mA cm-2, and photocurrent densities of 17.5 ± 0.4 mA cm-2 at the equilibrium potential for evolution of O2(g), while evolving O2(g) from 1.0 M KOH(aq) with 100% Faradaic yield. Furthermore, during 48 h of continuous operation, the total charge passed through the electrode, ~4600 C cm-2, exceeded by a factor of at least 10 the amount of charge required to anodically dissolve or oxidize the entire InP substrate.
- Research Organization:
- California Institute of Technology (CalTech), Pasadena, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR); Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation; National Science Foundation (NSF); USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (SC-22)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0004993
- OSTI ID:
- 1633791
- Journal Information:
- Advanced Energy Materials, Journal Name: Advanced Energy Materials Journal Issue: 11 Vol. 5; ISSN 1614-6832
- Publisher:
- WileyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English