Modification of Carbon Nitride/Reduced Graphene Oxide van der Waals Heterostructure with Copper Nanoparticles To Improve CO2 Sensitivity
- Univ. of Pittsburgh, PA (United States)
- Univ. of Pittsburgh, PA (United States); National Energy Technology Lab. (NETL), Albany, OR (United States)
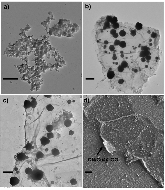
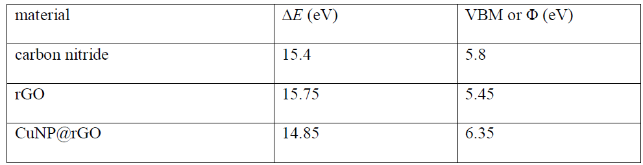
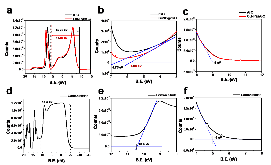
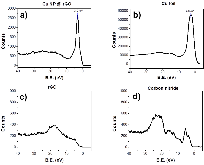
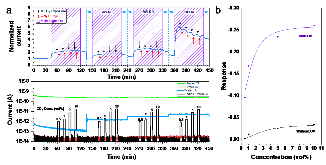
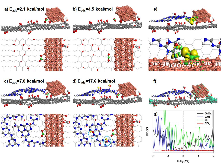
Carbon nitride/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) van der Waals heterostructures (vdWH) have previously shown exceptional oxygen sensitivity via a photoredox mechanism, making it a potential material candidate for various applications such as oxygen reduction reaction catalysis and oxygen sensing. In this work, the electronic structure of a carbon nitride/rGO composite is modified through the introduction of copper nanoparticles (NPs). When incorporated into a chemiresistor device, this vdWH displayed a newfound CO2 sensitivity. The effects of humidity and light were investigated and found to be crucial components for the CO2 sensitivity. Density functional theory calculations performed on a carbon nitride/copper NP@rGO model system found an enhanced stabilization of CO2 caused by H-bonds between the carbon nitride layer and chemisorbed CO2 on copper, pointing to the important role played by humidity. The synergetic effect between the carbon nitride layer interfaced with CuNP@rGO, in combination with humidity and light (395 nm) irradiation, is found to be responsible for the newfound sensitivity toward CO2.
- Research Organization:
- National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL), Pittsburgh, PA, Morgantown, WV, and Albany, OR (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Fossil Energy (FE)
- OSTI ID:
- 1607763
- Journal Information:
- ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, Journal Name: ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces Journal Issue: 44 Vol. 11; ISSN 1944-8244
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society (ACS)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English