Fast computation of synthetic seismograms within a medium containing remote localized perturbations: a numerical solution to the scattering problem
- Inst. de Physique du Globe, Paris (France)
- Inst. de Physique du Globe, Paris (France); College de France, Paris (France); Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States). Berkeley Siesmological Laboratory
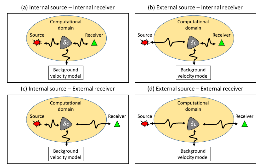
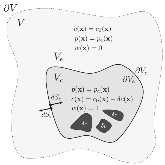
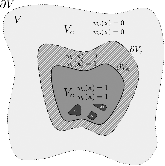
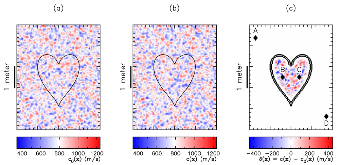
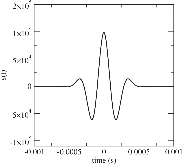
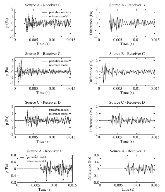
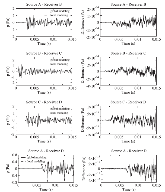
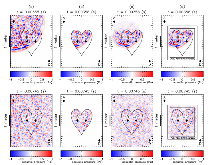
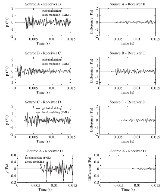
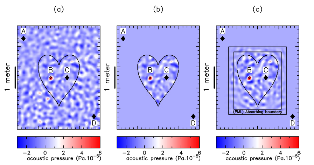
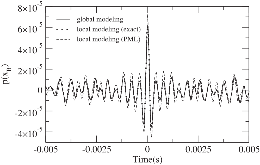
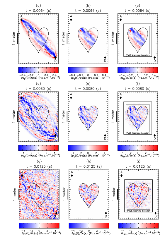
We derive a fast discrete solution to the scattering problem. This solution allows us to compute accurate synthetic seismograms or waveforms for arbitrary locations of sources and receivers within a medium containing localized perturbations. The key to efficiency is that wave propagation modelling does not need to be carried out in the entire volume that encompasses the sources and the receivers but only within the subvolume containing the perturbations or scatterers. The proposed solution has important applications, for example, it permits the imaging of remote targets located in regions where no sources or receivers are present. Our solution relies on domain decomposition: within a small volume that contains the scatterers, wave propagation is modelled numerically, while in the surrounding volume, where the medium isn't perturbed, the response is obtained through wavefield extrapolation. The originality of this work is the derivation of discrete formulas for representation theorems and Kirchhof–Helmholtz integrals that naturally adapt to the numerical scheme employed for modelling wave propagation. Our solution applies, for example, to finite difference methods or finite/spectral elements methods. The synthetic seismograms obtained with our solution can be considered ‘exact’ as the total numerical error is comparable to that of the method employed for modelling wave propagation. We detail a basic implementation of our solution in the acoustic case using the finite difference method and present numerical examples that demonstrate the accuracy of the method. We show that ignoring some terms accounting for higher order scattering effects in our solution has a limited effect on the computed seismograms and significantly reduces the computational effort. Finally, we show that our solution can be used to compute localized sensitivity kernels and we discuss applications to target oriented imaging. Extension to the elastic case is straightforward and summarized in a dedicated section.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States). National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- OSTI ID:
- 1526206
- Journal Information:
- Geophysical Journal International, Journal Name: Geophysical Journal International Journal Issue: 2 Vol. 208; ISSN 0956-540X
- Publisher:
- Oxford University PressCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Enabling numerically exact local solver for waveform inversion—a low-rank approach
|
journal | June 2019 |
High-frequency seismic wave modelling of the deep Earth based on hybrid methods and spectral-element simulations: a conceptual study
|
journal | September 2019 |
Similar Records
Numerical-analytical interfacing in two dimensions with applications to modeling NTS seismograms