Effect of Bi substitution on the magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Ni50Mn35In15-xBix Heusler alloys
- Southern Illinois Univ., Carbondale, IL (United States); Department of Physics, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL 62901, USA
- Southern Illinois Univ., Carbondale, IL (United States)
- Louisiana State Univ., Baton Rouge, LA (United States)
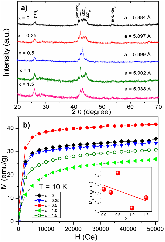
The structural, magnetic, magnetocaloric, and transport properties of Ni50Mn35In15-xBix (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5) compounds has been studied through X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry, and magnetization measurements. A mixture of high temperature austenite phase (AP) and low temperature martensitic phase (MP) was observed from the XRD at room temperature. The saturation magnetization MS at 10 K was found to decrease with increasing Bi content. A shift in the martensitic transition temperature (TM) relative to the parent compound was observed with a maximum shift of ~ 36 K for x = 1.5. Abnormal shifts in TC and TM to higher temperatures were observed at high field for x ≥ 0.5. Large magnetic entropy changes (ΔSM) of about 40 J/kg K (x = 0) and 34 J/kg K (x = 0.25) were observed at TM with H = 5 T, which reduced significantly for higher Bi concentrations. The doping of small amounts of Bi in the In sites increased the peak width of the ΔSM curves at the second order transition, leading to larger values of relative cooling power. A significant magnetoresistance (-30%) was observed near TM with ΔH = 5T for x = 0.5.
- Research Organization:
- Southern Illinois Univ., Carbondale, IL (United States); Louisiana State Univ., Baton Rouge, LA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (SC-22)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- FG02-06ER46291; SC0010521; SC0010521
- OSTI ID:
- 1499381
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1414031
OSTI ID: 1872887
- Journal Information:
- AIP Advances, Journal Name: AIP Advances Journal Issue: 5 Vol. 8; ISSN 2158-3226
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Magnetic field dependence of the martensitic transition and magnetocaloric effects in Ni 49 BiMn 35 In 15
|
journal | January 2020 |
Similar Records
Phase diagram and magnetocaloric effects in Ni{sub 1-x}Cr{sub x}MnGe{sub 1.05}