Impact of Fluorination on Phase Stability, Crystal Chemistry, and Capacity of LiCoMnO4 High Voltage Spinels
- Forschungszentrum Julich GmbH, Julich (Germany); Julich Aachen Research Alliance: JARA-Energy, Julich (Germany)
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
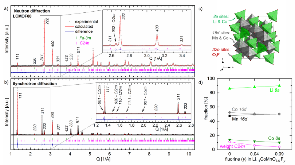
In this paper, fluorinated LiCoMnO4–yFy (y = 0, 0.05, 0.1) spinel electrodes, electrochemically active at 5–5.3 V versus Li/Li+, show enhanced phase purity and enhanced capacity with increasing y. We disclose the impact of fluorination on the phase purity and reversible capacity of LiCoMnO4 via joint Rietveld refinement of neutron and synchrotron powder diffraction data, combined with micro-Raman spectroscopy. It is found that fluorination stabilizes the spinel phase and hinders precipitation of Li2MnO3 as a secondary phase, which controls the cation distribution on tetrahedral and octahedral sites in spinel. That is to say, for higher fluorine content the cobalt occupancy at the tetrahedral site in spinel decreases, and the lithium occupancy increases. Accordingly, the number of lithium sites that are available for electrochemical extraction and insertion of lithium ions is raised so that the capacity is increased. Further investigation of the lithium ion diffusion by means of cyclic voltammetry at different scan rates and the application of the Randles–Sevcik equation were carried out to investigate the extent of capacity enhancement due to faster lithium ion diffusion in the high voltage region.
- Research Organization:
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (SC-22)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725
- OSTI ID:
- 1494020
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1436800
- Journal Information:
- ACS Applied Energy Materials, Journal Name: ACS Applied Energy Materials Journal Issue: 2 Vol. 1; ISSN 2574-0962
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society (ACS)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
Electrochemical properties of spinel Li{sub x}CoO{sub 2}: A first-principles investigation
Low-Temperature Synthesis, Structural Characterization, and Electrochemistry of Ni-Rich Spinel-like LiNi2–yMnyO4 (0.4 ≤ y ≤ 1)