Spatial profiling of stapled α–helical peptide ATSP-7041 in mouse whole-body thin tissue sections using droplet-based liquid microjunction surface sampling-HPLC-ESI–MS/MS
Journal Article
·
· International Journal of Mass Spectrometry
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Merck Research Labs, West Point, PA (United States)
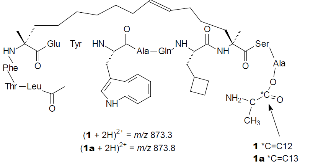
Here, the application of a fully automated autosampler/HPLC-ESI–MS/MS system for spatially resolved quantitative droplet-based liquid extraction surface sampling/profiling of stapled α–helical peptide ATSP-7041 in mouse whole-body thin tissue sections is reported. 20-μm-thick serial tissue sections of an ATSP-7041 dosed mouse were prepared and the absolute concentration of the targeted peptide was first determined in different organs using 2.3-mm diameter tissue punches, standard bulk tissue extraction protocols, and subsequent HPLC separation and tandem mass spectrometric analysis. The same organs/locations were then analyzed in neighboring tissue sections using the droplet-based surface sampling approach. The observed ATSP-7041 concentration using this method was always significantly lower than that measured by the tissue punch workflow at the same tissue location of a serial section. Calculated extraction efficiencies were 10.7 ± 0.5% (brain), 11.0 ± 3.2% (liver spot 1), 10.7 ± 2.6% (liver spot 2), 15.0 ± 0.6% (lung) and 12.9 ± 0.7% (blood). While these extraction efficiency values were low, they were reproducible within a given organ. This suggests that once the extraction efficiency is established for a given tissue type and drug, the reproducibility of the droplet-based approach could provide a non-labor intensive and high-throughput means to acquire spatially resolved quantitative analysis of multiple samples of the same type.
- Research Organization:
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (SC-22)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725
- OSTI ID:
- 1493155
- Journal Information:
- International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, Journal Name: International Journal of Mass Spectrometry Journal Issue: C Vol. 437; ISSN 1387-3806
- Publisher:
- ElsevierCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
Extraction efficiency and implications for absolute quantitation of propranolol in mouse brain, liver and kidney thin tissue sections using droplet-based liquid microjunction surface sampling-HPLC ESI-MS/MS
An enhanced droplet-based liquid microjunction surface sampling system coupled with HPLC-ESI-MS/MS for spatially resolved analysis
Automated Liquid Microjunction Surface Sampling-HPLC-MS/MS Analysis of Drugs and Metabolites in Whole-Body Thin Tissue Sections
Journal Article
·
Tue Jun 21 20:00:00 EDT 2016
· Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry
·
OSTI ID:1259427
An enhanced droplet-based liquid microjunction surface sampling system coupled with HPLC-ESI-MS/MS for spatially resolved analysis
Journal Article
·
Thu Nov 06 19:00:00 EST 2014
· Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry
·
OSTI ID:1185691
Automated Liquid Microjunction Surface Sampling-HPLC-MS/MS Analysis of Drugs and Metabolites in Whole-Body Thin Tissue Sections
Journal Article
·
Mon Dec 31 23:00:00 EST 2012
· Bioanalysis
·
OSTI ID:1092227