Advances in understanding of high- Z material erosion and re-deposition in low-Z wall environment in DIII-D
- Oak Ridge Associated Univ., Oak Ridge, TN (United States); Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Beijing (China). Inst. of Plasma Physics; General Atomics, San Diego, CA (United States)
- Univ. of California, San Diego, CA (United States)
- Univ. of Toronto, ON (Canada). Inst. for Aerospace Studies
- Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States)
- General Atomics, San Diego, CA (United States)
- Julich Research Centre (Germany). Inst. of Energy and Climate Research- Plasma Physics
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Oak Ridge Associated Univ., Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Univ. of Vienna (Austria). Fusion @OAW. Inst. of Applied Physics
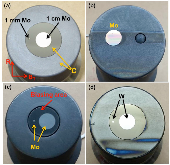
Dedicated DIII-D experiments coupled with modeling reveal that the net erosion rate of high-Z materials, i.e. Mo and W, is strongly affected by carbon concentration in the plasma and the magnetic pre-sheath properties. Different methods such as electrical biasing and local gas injection have been investigated to control high-Z material erosion. The net erosion rate of high-Z materials is significantly reduced due to the high local re-deposition ratio. The ERO modeling shows that the local re-deposition ratio is mainly controlled by the electric field and plasma density within the magnetic pre-sheath. The net erosion can be significantly suppressed by reducing the sheath potential drop. A high carbon impurity concentration in the background plasma is also found to reduce the net erosion rate of high-Z materials. Both DIII-D experiments and modeling show that local 13CH4 injection can create a carbon coating on the metal surface. The profile of 13C deposition provides quantitative information on radial transport due to E×B drift and the cross-field diffusion. The deuterium gas injection upstream of the W sample can reduce W net erosion rate by plasma perturbation. In H-mode plasmas, the measured inter-ELM W erosion rates at different radial locations are well reproduced by ERO modeling taking into account charge-state-resolved carbon ion flux in the background plasma calculated using the OEDGE code.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States); General Atomics, San Diego, CA (United States); Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA); USDOE Office of Science (SC), Fusion Energy Sciences (FES)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344; AC04-94AL85000; GA-DE-SC0008698; AC05-06OR23100; FG02-07ER54917; AC05-00OR22725; FC02-04ER54698
- OSTI ID:
- 1491638
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1357016; OSTI ID: 1374606; OSTI ID: 1374610; OSTI ID: 1503985
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL-736452; SAND-2017-0016J; 836266
- Journal Information:
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 57, Issue 5; ISSN 0029-5515
- Publisher:
- IOP ScienceCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Plasma cleaning of ITER edge Thomson scattering mock-up mirror in the EAST tokamak
|
journal | December 2017 |
Similar Records
Plasma Surface Interactions: Bridging from the Surface to the Micron Frontier through Leadership Class Computing (Final Technical Report)
Modeling of ExB effects on tungsten re-deposition and transport in the DIII-D divertor