Contrasts in compliant fault zone properties inferred from geodetic measurements in the San Francisco Bay area
Journal Article
·
· Journal of Geophysical Research. Solid Earth
- Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States). Dept. of Earth and Planetary Sciences
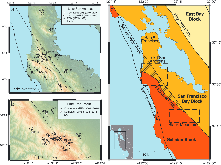
In crustal fault zones, regions of damaged rock characterized by reduced elastic shear modulus can influence patterns of near-field interseismic deformation. In order to study these compliant fault zones (CFZs) and how they might develop over the lifetimes of faults, we compare two fault segments with contrasting fault age and lithology along the San Andreas Fault in the San Francisco Bay Area. New geodetic measurements of the interseismic velocity fields at each location are used to constrain fault zone parameters through a Markov chain Monte Carlo method. At Black Mountain, in the Santa Cruz Mountains of the San Francisco Peninsula, we do not find evidence for a compliant fault zone; instead, we find that the geodetic data are more consistent with a model of a single fault in a homogeneous elastic half-space. At Lake San Andreas, a younger fault segment 35 km farther north, we find evidence for a compliant fault zone about 3.4 +1.1/-1.4 km wide, containing a shear modulus of about 40% of the shear modulus of the surrounding rock. We also find that the best fitting CFZ model at this location, unlike the best fitting homogeneous half-space model, has a locking depth that agrees well with the observed depth of microseismicity. Based on differences in fault age, cumulative displacement, and lithology between Black Mountain and Lake San Andreas, we infer that lithology plays an important and, in this case, perhaps a dominant role in the accumulation of fault zone damage structures and the development of CFZs over the lifetime of a fault.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- OSTI ID:
- 1480732
- Journal Information:
- Journal of Geophysical Research. Solid Earth, Journal Name: Journal of Geophysical Research. Solid Earth Journal Issue: 9 Vol. 121; ISSN 2169-9313
- Publisher:
- American Geophysical UnionCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Buried shallow fault slip from the South Napa earthquake revealed by near-field geodesy
|
journal | July 2017 |
Similar Records
Earthquake travel time tomography of the southern Santa Cruz Mountains: Control of fault rupture by lithological heterogeneity of the San Andreas fault zone
Journal Article
·
Sun Oct 10 00:00:00 EDT 1993
· Journal of Geophysical Research
·
OSTI ID:67988