Effects of MEA Fabrication and Ionomer Composition on Fuel Cell Performance of PGM-Free ORR Catalyst
Journal Article
·
· ECS Transactions (Online)
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
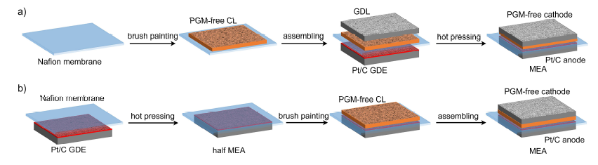
Carbon-based platinum group metal-free (PGM-free) catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) have received increasing attention as potential candidates for low-cost fuel cell cathode catalysts. Mass-transport within the very thick catalyst layer (CL) presents a major challenge to further improve the fuel cell performance of PGM-free catalysts, which may be realized through the optimization of CL structure. Herein, we demonstrate that membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs) with not hot-pressed PGM-free cathode showed improved H2-air fuel cell performance in mass transport region when compared to MEAs prepared via hot-pressing technique. Further, the effects of the ionomer content and equivalent weight (EW) on fuel cell performance were systematically explored. We observed that an increase in ionomer content resulted in performance improvement in the kinetic region, while negatively affecting the performance in the mass transport region. The overall optimum fuel cell performance was achieved with an ionomer EW of 830 g mol-1.
- Research Organization:
- Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE). Fuel Cell Technologies Program (EE-3F)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-06NA25396
- OSTI ID:
- 1463547
- Report Number(s):
- LA-UR-17-24947
- Journal Information:
- ECS Transactions (Online), Journal Name: ECS Transactions (Online) Journal Issue: 11 Vol. 77; ISSN 1938-6737
- Publisher:
- Electrochemical SocietyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Integrating PGM‐Free Catalysts into Catalyst Layers and Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Devices
|
journal | December 2018 |
Progress in the Development of Fe‐Based PGM‐Free Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction
|
journal | December 2018 |
Molecular Design of Single‐Atom Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
|
journal | February 2020 |
A Structure and Durability Comparison of Membrane Electrode Assembly Fabrication Methods: Self-Assembled Versus Hot-Pressed
|
journal | January 2018 |
Similar Records
Active and Durable PGM-free Cathodic Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cell
Application
Influence of ionomer content on the structure and performance of PEFC membrane electrode assemblies
Technical Report
·
Sun Oct 30 00:00:00 EDT 2022
·
OSTI ID:2371586
Influence of ionomer content on the structure and performance of PEFC membrane electrode assemblies
Journal Article
·
Thu Dec 31 23:00:00 EST 2009
· Electrochimica Acta
·
OSTI ID:1023340