Free-Energy Landscape of the Dissolution of Gibbsite at High pH
- Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States). Physical Sciences Division. Physical & Computational Sciences Directorate
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States). Chemical Science Division
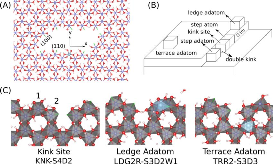
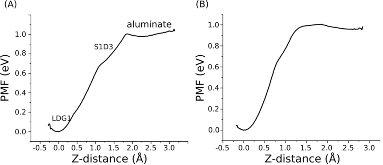
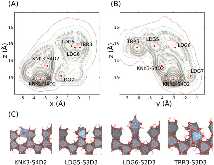
The individual elementary reactions involved in the dissolution of a solid into solution remain mostly speculative due to a lack of direct experimental probes. In this regard, in this paper we have applied atomistic simulations to map the free-energy landscape of the dissolution of gibbsite from a step edge as a model of metal hydroxide dissolution. The overall reaction combines kink formation and kink propagation. Two individual reactions were found to be rate-limiting for kink formation, that is, the displacement of Al from a step site to a ledge adatom site and its detachment from ledge/terrace adatom sites into the solution. Finally, as a result, a pool of mobile and labile adsorbed species, or adatoms, exists before the release of Al into solution. Because of the quasi-hexagonal symmetry of gibbsite, kink site propagation can occur in multiple directions. Overall, our results will enable the development of microscopic mechanistic models of metal oxide dissolution.
- Research Organization:
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (EFRC) (United States). Interfacial Dynamics in Radioactive Environments and Materials (IDREAM); Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (SC-22)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725; AC05-76RL01830
- OSTI ID:
- 1462840
- Journal Information:
- Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, Journal Name: Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters Journal Issue: 7 Vol. 9; ISSN 1948-7185
- Publisher:
- American Chemical SocietyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
Atomistic thermodynamics and kinetics of dicalcium silicate dissolution