Cross-correlation redshift calibration without spectroscopic calibration samples in DES Science Verification Data
- Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, PO Box 2450, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA
- Department of Physics, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA
- Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, PO Box 2450, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA; SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA
- Institute of Space Sciences, IEEC-CSIC, Campus UAB, Carrer de Can Magrans, s/n, E-08193 Barcelona, Spain
- Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637, USA
- Institut de Física d'Altes Energies (IFAE), The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, Campus UAB, E-08193 Bellaterra (Barcelona), Spain
- Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, PO Box 500, Batavia, IL 60510, USA
- Institut de Física d'Altes Energies (IFAE), The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, Campus UAB, E-08193 Bellaterra (Barcelona), Spain; Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avançats, E-08010 Barcelona, Spain
- Center for Cosmology and Astro-Particle Physics, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210, USA; Department of Physics, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210, USA
- Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, National Optical Astronomy Observatory, Casilla 603, La Serena, Chile
- Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK; Department of Physics and Electronics, Rhodes University, PO Box 94, Grahamstown 6140, South Africa
- LSST, 933 North Cherry Avenue, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA
- Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK; CNRS, UMR 7095, Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, F-75014 Paris, France; Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ Paris 06, UMR 7095, Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, F-75014 Paris, France
- CNRS, UMR 7095, Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, F-75014 Paris, France; Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ Paris 06, UMR 7095, Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, F-75014 Paris, France
- Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK
- Laboratório Interinstitucional de e-Astronomia - LIneA, Rua Gal. José Cristino 77, Rio de Janeiro RJ-20921-400, Brazil; Observatório Nacional, Rua Gal. José Cristino 77, Rio de Janeiro RJ-20921-400, Brazil
- Department of Astronomy, University of Illinois, 1002 W. Green Street, Urbana, IL 61801, USA; National Center for Supercomputing Applications, 1205 West Clark St., Urbana, IL 61801, USA
- Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA
- Department of Physics, IIT Hyderabad, Kandi, Telangana 502285, India
- Laboratório Interinstitucional de e-Astronomia - LIneA, Rua Gal. José Cristino 77, Rio de Janeiro RJ-20921-400, Brazil
- Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637, USA; Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, PO Box 500, Batavia, IL 60510, USA
- Instituto de Fisica Teorica UAM/CSIC, Universidad Autonoma de Madrid, E-28049 Madrid, Spain
- Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA; Department of Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
- Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA, UK; Kavli Institute for Cosmology, University of Cambridge, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA, UK; Universitäts-Sternwarte, Fakultät für Physik, Ludwig-Maximilians Universität München, Scheinerstr. 1, D-81679 München, Germany
- Astronomy Department, University of Washington, Box 351580, Seattle, WA 98195, USA; Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, National Optical Astronomy Observatory, Casilla 603, La Serena, Chile
- Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics, Santa Cruz, CA 95064, USA
- Australian Astronomical Observatory, North Ryde, NSW 2113, Australia
- Argonne National Laboratory, 9700 South Cass Avenue, Lemont, IL 60439, USA
- Laboratório Interinstitucional de e-Astronomia - LIneA, Rua Gal. José Cristino 77, Rio de Janeiro RJ-20921-400, Brazil; Departamento de Física Matemática, Instituto de Física, Universidade de São Paulo, CP 66318, São Paulo, SP 05314-970, Brazil
- George P. and Cynthia Woods Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy, and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843, USA
- Center for Cosmology and Astro-Particle Physics, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210, USA; Department of Astronomy, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210, USA
- Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University, Peyton Hall, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA
- Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, 4800 Oak Grove Dr., Pasadena, CA 91109, USA
- Department of Physics and Astronomy, Pevensey Building, University of Sussex, Brighton BN1 9QH, UK
- Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas, Medioambientales y Tecnológicas (CIEMAT), Av. Complutense 40, 28040 Madrid, Spain
- SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA
- Department of Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
- School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Southampton, Southampton SO17 1BJ, UK
- Instituto de Física Gleb Wataghin, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, 13083-859 Campinas, SP, Brazil; Laboratório Interinstitucional de e-Astronomia - LIneA, Rua Gal. José Cristino 77, Rio de Janeiro RJ-20921-400, Brazil
- Computer Science and Mathematics Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37831, USA
- National Center for Supercomputing Applications, 1205 West Clark St., Urbana, IL 61801, USA
- Institute of Cosmology and Gravitation, University of Portsmouth, Portsmouth PO1 3FX, UK
- Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, PO Box 2450, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA; SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA; Department of Physics, Stanford University, 382 Via Pueblo Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, USA
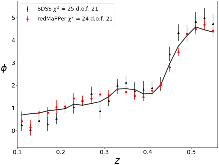
Galaxy cross-correlations with high-fidelity redshift samples hold the potential to precisely calibrate systematic photometric redshift uncertainties arising from the unavailability of complete and representative training and validation samples of galaxies. However, application of this technique in the Dark Energy Survey (DES) is hampered by the relatively low number density, small area, and modest redshift overlap between photometric and spectroscopic samples. We propose instead using photometric catalogues with reliable photometric redshifts for photo-z calibration via cross-correlations. We verify the viability of our proposal using redMaPPer clusters from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) to successfully recover the redshift distribution of SDSS spectroscopic galaxies. We demonstrate how to combine photo-z with cross-correlation data to calibrate photometric redshift biases while marginalizing over possible clustering bias evolution in either the calibration or unknown photometric samples. We apply our method to DES Science Verification (DES SV) data in order to constrain the photometric redshift distribution of a galaxy sample selected for weak lensing studies, constraining the mean of the tomographic redshift distributions to a statistical uncertainty of Δz ~ ±0.01. We forecast that our proposal can, in principle, control photometric redshift uncertainties in DES weak lensing experiments at a level near the intrinsic statistical noise of the experiment over the range of redshifts where redMaPPer clusters are available. Our results provide strong motivation to launch a programme to fully characterize the systematic errors from bias evolution and photo-z shapes in our calibration procedure.
- Research Organization:
- SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (SLAC), Menlo Park, CA (United States); Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL), Batavia, IL (United States); Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), High Energy Physics (HEP); USDOE Office of Science (SC), Advanced Scientific Computing Research (ASCR)
- Contributing Organization:
- DES Collaboration
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-07CH11359; AC05-00OR22725
- OSTI ID:
- 1454415
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1468041
- Report Number(s):
- FERMILAB-PUB-17-284-AE; arXiv:1707.08256; 1611648; TRN: US1901011
- Journal Information:
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 477, Issue 2; ISSN 0035-8711
- Publisher:
- Royal Astronomical SocietyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Dark Energy Survey Year 3 results: calibration of lens sample redshift distributions using clustering redshifts with BOSS/eBOSS
Dark Energy Survey Year 1 results: cross-correlation redshifts – methods and systematics characterization