Revealing the beneficial role of K in grain interiors, grain boundaries, and at the buffer interface for highly efficient CuInSe2 solar cells
- Univ. of Florida, Gainesville, FL (United States); National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Univ. of Florida, Gainesville, FL (United States)
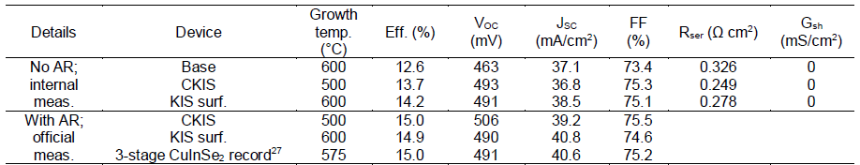
K incorporation within grain boundaries, grain interiors, and interfaces has been studied within CuInSe2 solar cells to better understand the beneficial or detrimental role of K distribution among these regions in chalcopyrite–based solar cells. Solar cells have been fabricated with intentional K introduction into specific regions of the device including the CuInSe2/CdS interface (CuInSe2/KInSe2/CdS) and the grain interiors (Cu0.93K0.07InSe2/CdS). A control CuInSe2/CdS device was also studied to separate effects of K originating from the soda–lime glass substrate from those of intentionally introduced K. The experiment was designed to understand K effects in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells while mitigating complications from multiple elements in the 3+ site. The distribution of all elements within these samples has been directly observed with sub–nm resolution via atom probe tomography. In addition, electron beam–induced current measurements have been performed to correlate the atom probe tomography compositional profiles to the nanoscale carrier collection properties. The experiments show that a large decrease in the Cu/In ratio at the CdS interface can be achieved by forming KInSe2 at the absorber surface, which drastically improves the device efficiency. The results presented here show a direct link between K concentration, Cu depletion, and In accumulation, such that the Cu/In ratio significantly reduces with K incorporation. In conclusion, the findings help clarify the mechanism behind K–induced efficiency enhancement.
- Research Organization:
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), Renewable Power Office. Solar Energy Technologies Office
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC36-08GO28308; DE‐AC36‐08GO28308; AC05-00OR22725
- OSTI ID:
- 1471293
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1441017; OSTI ID: 1454388
- Report Number(s):
- NREL/JA-5K00-71548
- Journal Information:
- Progress in Photovoltaics, Vol. 26, Issue 10; ISSN 1062-7995
- Publisher:
- WileyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Efficiency Improvement of Near‐Stoichiometric CuInSe 2 Solar Cells for Application in Tandem Devices
|
journal | July 2019 |
No Evidence for Passivation Effects of Na and K at Grain Boundaries in Polycrystalline Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 Thin Films for Solar Cells
|
journal | May 2019 |
Similar Records
Understanding the Effect of Na in Improving the Performance of CuInSe2 Based Photovoltaics
Vacuum-Healing of Grain Boundaries in Sodium-Doped CuInSe2 Solar Cell Absorbers