New Ligand Design Provides Delocalization and Promotes Strong Absorption throughout the Visible Region in a Ru(II) Complex
Journal Article
·
· Journal of the American Chemical Society
- The Ohio State Univ., Columbus, OH (United States). Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry; The Ohio State University
- The Ohio State Univ., Columbus, OH (United States). Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
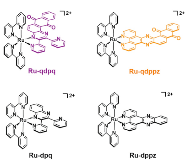
The new Ru(II)–anthraquinone complex [Ru(bpy)2(qdpq)](PF6)2 (Ru-qdpq; bpy = 2,2'-bipyridine; qdpq = 2,3-di(2-pyridyl)naphtho[2,3-f]quinoxaline-7,12-quinone) possesses a strong 1MLCT Ru → qdpq absorption with a maximum at 546 nm that tails into the near-IR and is significantly red-shifted relative to that of the related complex [Ru(bpy)2(qdppz)](PF6)2 (Ru-qdppz; qdppz = naphtho[2,3-a]dipyrido[3,2-h:2',3'-f]phenazine-5,18-dione), with λmax = 450 nm. Ru-qdppz possesses electronically isolated proximal and distal qdppz-based excited states; the former is initially generated and decays to the latter, which repopulates the ground state with τ = 362 ps. In contrast, excitation of Ru-qdpq results in the population of a relatively long-lived (τ = 19 ns) Ru(dπ) → qdpq(π*) 3MLCT excited state where the promoted electron is delocalized throughout the qdpq ligand. Ultrafast spectroscopy, used together with steady-state absorption, electrochemistry, and DFT calculations, indicates that the unique coordination modes of the qdpq and qdppz ligands impart substantially different electronic communication throughout the quinone-containing ligand, affecting the excited state and electron transfer properties of these molecules. As a result, these observations create a pathway to synthesize complexes with red-shifted absorptions that possess long-lived, redox-active excited states that are useful for various applications, including solar energy conversion and photochemotherapy.
- Research Organization:
- The Ohio State Univ., Columbus, OH (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (SC-22)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0010542
- OSTI ID:
- 1430217
- Journal Information:
- Journal of the American Chemical Society, Journal Name: Journal of the American Chemical Society Journal Issue: 1 Vol. 140; ISSN 0002-7863
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society (ACS)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
Revealing Parallel Inter‐ and Intra‐Ligand Charge Transfer Dynamics in [Ru(L)2(dppz)]2+ Molecular Lightswitch with N K‐Edge X‐Ray Absorption Spectroscopy
Application of resonance Raman spectroscopy to electronic structure in metal complex excited states. Excited-state ordering and electron delocalization in dipyrido[3,2-a: 2`,3`-c] phenazine (dppz): Complexes of Re(I) and Ru(II)
Spectroscopic, electrochemical, and spectroelectrochemical investigations of mixed-metal osmium(II)/ruthenium(II) bimetallic complexes incorporating polypyridyl bridging ligands
Journal Article
·
Wed Jul 09 20:00:00 EDT 2025
· Angewandte Chemie (International Edition)
·
OSTI ID:2583411
Application of resonance Raman spectroscopy to electronic structure in metal complex excited states. Excited-state ordering and electron delocalization in dipyrido[3,2-a: 2`,3`-c] phenazine (dppz): Complexes of Re(I) and Ru(II)
Journal Article
·
Tue Dec 19 23:00:00 EST 1995
· Inorganic Chemistry
·
OSTI ID:274010
Spectroscopic, electrochemical, and spectroelectrochemical investigations of mixed-metal osmium(II)/ruthenium(II) bimetallic complexes incorporating polypyridyl bridging ligands
Journal Article
·
Wed Apr 29 00:00:00 EDT 1992
· Inorganic Chemistry; (United States)
·
OSTI ID:6915650