Relationship between lignocellulosic biomass dissolution and physicochemical properties of ionic liquids composed of 3-methylimidazolium cations and carboxylate anions
Journal Article
·
· Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. PCCP
- Univ. of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN (United States). Center for Renewable Carbon. Dept. of Biosystems Engineering and Soil Science
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States). Center for Molecular Biophysics; Univ. of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN (United States). Dept. of Biochemistry and Cellular and Molecular Biology
- Univ. of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN (United States). Center for Renewable Carbon
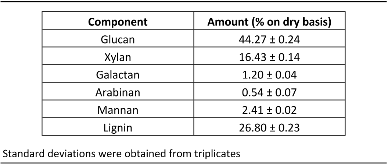
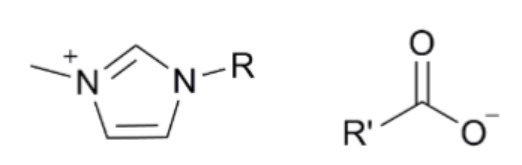
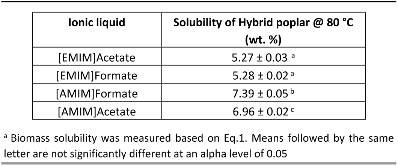
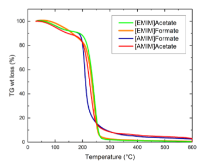
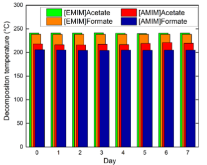
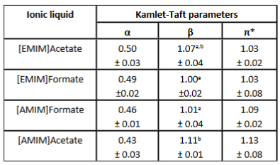
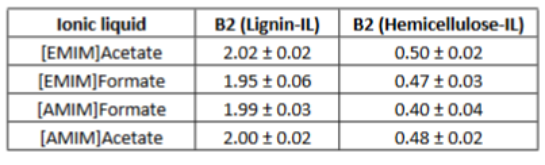
The ionic liquid (IL) 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ([EMIM]Acetate) has been widely used for biomass processing, i.e., to pretreat, activate, or fractionate lignocellulosic biomass to produce soluble sugars and lignin. However, this IL does not achieve high biomass solubility, therefore minimizing the efficiency of biomass processing. In this paper, [EMIM]Acetate and three other ILs composed of different 3-methylimidazolium cations and carboxylate anions ([EMIM]Formate, 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium ([AMIM]) formate, and [AMIM]Acetate) were analyzed to relate their physicochemical properties to their biomass solubility performance. While all four ILs are able to dissolve hybrid poplar under fairly mild process conditions (80 °C and 100 RPM stirring), [AMIM]Formate and [AMIM]Acetate have particularly increased biomass solubility of 40 and 32%, respectively, relative to [EMIM]Acetate. Molecular dynamics simulations suggest that strong interactions between IL and specific plant biopolymers may contribute to this enhanced solubilization, as the calculated second virial coefficients between ILs and hemicellullose are most favorable for [AMIM]Formate, matching the trend of the experimental solubility measurements. The simulations also reveal that the interactions between the ILs and hemicellulose are an important factor in determining the overall biomass solubility, whereas lignin–IL interactions were not found to vary significantly, consistent with literature. Finally, the combined experimental and simulation studies identify [AMIM]Formate as an efficient biomass solvent and explain its efficacy, suggesting a new approach to rationally select ionic liquid solvents for lignocellulosic deconstruction.
- Research Organization:
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States); Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States). Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- National Science Foundation (NSF) (United States); USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER) (SC-23)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725
- OSTI ID:
- 1423012
- Journal Information:
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. PCCP, Journal Name: Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. PCCP Journal Issue: 4 Vol. 20; ISSN 1463-9076
- Publisher:
- Royal Society of ChemistryCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
Prediction of solubility parameters of lignin and ionic liquids using multi-resolution simulation approaches
Physical insight into switchgrass dissolution in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate
Alkyl-methylimidazolium ionic liquids affect the growth and fermentative metabolism of Clostridium sp
Journal Article
·
Thu Dec 02 19:00:00 EST 2021
· Green Chemistry
·
OSTI ID:1960393
Physical insight into switchgrass dissolution in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate
Journal Article
·
Tue Dec 31 23:00:00 EST 2013
· ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering
·
OSTI ID:1131512
Alkyl-methylimidazolium ionic liquids affect the growth and fermentative metabolism of Clostridium sp
Journal Article
·
Wed Jun 01 00:00:00 EDT 2011
· Bioresource Technology
·
OSTI ID:1026772