Plasma dynamics near critical density inferred from direct measurements of laser hole boring
- Univ. of California, Los Angeles, CA (United States). Electrical Engineering Dept.
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Menlo Park, CA (United States); Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
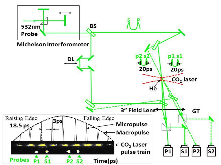
Here, we use multiframe picosecond optical interferometry to make direct measurements of the hole boring velocity, vHB, of the density cavity pushed forward by a train of CO2 laser pulses in a near critical density helium plasma. As the pulse train intensity rises, the increasing radiation pressure of each pulse pushes the density cavity forward and the plasma electrons are strongly heated. After the peak laser intensity, the plasma pressure exerted by the heated electrons strongly impedes the hole boring process and the vHB falls rapidly as the laser pulse intensity falls at the back of the laser pulse train. We present a heuristic theory that allows the estimation of the plasma electron temperature from the measurements of the hole boring velocity. Furthermore, the measured values of vHB, and the estimated values of the heated electron temperature as a function of laser intensity are in reasonable agreement with those obtained from two-dimensional numerical simulations.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Univ. of California, Los Angeles, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344; NA0002950; SC0010064
- OSTI ID:
- 1389949
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1259336; OSTI ID: 1364530
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL-737704; PLEEE8
- Journal Information:
- Physical Review E, Vol. 93, Issue 6; ISSN 2470-0045
- Publisher:
- American Physical Society (APS)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Particle-in-cell simulations of density peak formation and ion heating from short pulse laser-driven ponderomotive steepening
|
journal | December 2019 |
| Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Density Peak Formation and Ion Acceleration from Short Pulse Laser-Driven Ponderomotive Steepening | text | January 2019 |
Similar Records
Final Project Report "Advanced Concept Exploration For Fast Ignition Science Program"
Hole Boring in a DT Pellet and Fast-Ion Ignition with Ultraintense Laser Pulses