Advanced geophysical underground coal gasification monitoring
Journal Article
·
· Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
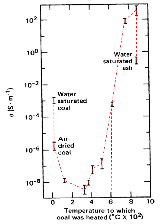
Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) produces less surface impact, atmospheric pollutants and greenhouse gas than traditional surface mining and combustion. Therefore, it may be useful in mitigating global change caused by anthropogenic activities. Careful monitoring of the UCG process is essential in minimizing environmental impact. In this paper, we first summarize monitoring methods that have been used in previous UCG field trials. We then discuss in more detail a number of promising advanced geophysical techniques. These methods – seismic, electromagnetic, and remote sensing techniques – may provide improved and cost-effective ways to image both the subsurface cavity growth and surface subsidence effects. Active and passive seismic data have the promise to monitor the burn front, cavity growth, and observe cavity collapse events. Electrical resistance tomography (ERT) produces near real time tomographic images autonomously, monitors the burn front and images the cavity using low-cost sensors, typically running within boreholes. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) is a remote sensing technique that has the capability to monitor surface subsidence over the wide area of a commercial-scale UCG operation at a low cost. It may be possible to infer cavity geometry from InSAR (or other surface topography) data using geomechanical modeling. The expected signals from these monitoring methods are described along with interpretive modeling for typical UCG cavities. They are illustrated using field results from UCG trials and other relevant subsurface operations.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Livermore, CA
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344
- OSTI ID:
- 1366915
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL--641052
- Journal Information:
- Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, Journal Name: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change Journal Issue: 4 Vol. 21; ISSN 1381-2386
- Publisher:
- SpringerCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Thermo-mechanical coupling numerical simulation method under high temperature heterogeneous rock and application in underground coal gasification
|
journal | January 2020 |
Monitoring and Control in Underground Coal Gasification: Current Research Status and Future Perspective
|
journal | January 2019 |
Similar Records
Monitoring of Underground Coal Gasification
Detecting and monitoring UCG subsidence with InSAR
Use of high-frequency electromagnetic waves for mapping an in situ coal gasification burn front
Technical Report
·
Fri Aug 31 00:00:00 EDT 2012
·
OSTI ID:1345326
Detecting and monitoring UCG subsidence with InSAR
Technical Report
·
Thu Mar 22 20:00:00 EDT 2012
·
OSTI ID:1047778
Use of high-frequency electromagnetic waves for mapping an in situ coal gasification burn front
Journal Article
·
Sun Dec 31 23:00:00 EST 1978
· In Situ; (United States)
·
OSTI ID:6056946