Buffer/absorber interface recombination reduction and improvement of back-contact barrier height in CdTe solar cells
- Texas State Univ., San Marcos, TX (United States)
- The Univ. of Toledo, Toledo, OH (United States)
- National Cheng Kung Univ., Tainan (Taiwan)
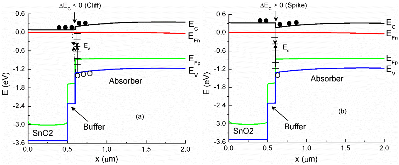
Electronic properties of a CdTe solar cell are reported using temperature-dependent capacitance spectroscopy and current-voltage characteristics, the latter in dark and illuminated conditions. The baseline solar cell material stack investigated is comprised of soda-lime-glass/SnO2:F/SnO2/CdS:O-buffer/CdTe-absorber/Cu/Au. Properties are compared with CdTe solar cells in which the back surface was hydroiodic acid etched, before the back-contact formation, and a CdTe device in which Mg-doped ZnO (MZO) replaces buffer layer CdS. Reduced back-contact barrier height and grain boundary barrier height are observed in the HI treated CdTe cell. As a result, improved device performance in the MZO-based CdTe device is attributed to reduced emitter/absorber interface recombination when using the MZO window layer.
- Research Organization:
- Texas State Univ., San Marcos, TX (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), Renewable Power Office. Solar Energy Technologies Office
- Grant/Contract Number:
- EE0007541
- OSTI ID:
- 1579310
- Journal Information:
- Thin Solid Films, Vol. 685, Issue C; ISSN 0040-6090
- Publisher:
- ElsevierCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
The Effects of Hydrogen Iodide Back Surface Treatment on CdTe Solar Cells
Electrical and optical characterization of CdTe solar cells with CdS and CdSe buffers—A comparative study