High spin polarization in epitaxial Fe4N thin films using Cr and Ag as buffer layers
Abstract
Fe4N thin films with (001) texture were prepared by reactive sputtering on MgO substrates, utilizing either a Cr or Ag buffer layer to facilitate the epitaxial growth. X-ray diffraction, atomic force microscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometry measurements show that the Fe4N thin film grown on the Ag buffer layer is superior to that grown on the Cr buffer layer. The point contact Andreev reflection measurement was then conducted, and the spin polarizations were determined to be 61.1% and 81.3% for Fe4N thin films with Cr and Ag buffer layers, respectively. The 81.3% spin polarization is significantly higher than the ratio reported previously for Fe4N and is comparable with that of state-of-the-art Heusler alloys. This result is in agreement with the theoretical prediction on the discrepancy between the two differently defined spin polarizations for Fe4N. Moreover, our study indicates that an optimized growth process for Fe4N thin films is crucial for achieving a high spin polarization and that true half-metallicity could potentially be realized with Fe4N. Furthermore the high spin polarization of Fe4N combined with its low fabrication temperature and simple composition makes Fe4N a competitive candidate to be a half-metallic ferromagnet in spintronic devices.
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN (United States)
- Arizona State Univ., Tempe, AZ (United States)
- Western Digital Corp., San Jose, CA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (EFRC) (United States). Spins and Heat in Nanoscale Electronic Systems (SHINES); Univ. of California, Riverside, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1503634
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1433574
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012670
- Resource Type:
- Journal Article: Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Applied Physics Letters
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 112; Journal Issue: 16; Journal ID: ISSN 0003-6951
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 36 MATERIALS SCIENCE; 75 CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS, SUPERCONDUCTIVITY AND SUPERFLUIDITY
Citation Formats
Li, Hongshi, Li, Xuan, Kim, Dongrin, Zhao, Gejian, Zhang, Delin, Diao, Zhitao, Chen, Tingyong, and Wang, Jian -Ping. High spin polarization in epitaxial Fe4N thin films using Cr and Ag as buffer layers. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1063/1.5023698.
Li, Hongshi, Li, Xuan, Kim, Dongrin, Zhao, Gejian, Zhang, Delin, Diao, Zhitao, Chen, Tingyong, & Wang, Jian -Ping. High spin polarization in epitaxial Fe4N thin films using Cr and Ag as buffer layers. United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5023698
Li, Hongshi, Li, Xuan, Kim, Dongrin, Zhao, Gejian, Zhang, Delin, Diao, Zhitao, Chen, Tingyong, and Wang, Jian -Ping. 2018.
"High spin polarization in epitaxial Fe4N thin films using Cr and Ag as buffer layers". United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5023698. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1503634.
@article{osti_1503634,
title = {High spin polarization in epitaxial Fe4N thin films using Cr and Ag as buffer layers},
author = {Li, Hongshi and Li, Xuan and Kim, Dongrin and Zhao, Gejian and Zhang, Delin and Diao, Zhitao and Chen, Tingyong and Wang, Jian -Ping},
abstractNote = {Fe4N thin films with (001) texture were prepared by reactive sputtering on MgO substrates, utilizing either a Cr or Ag buffer layer to facilitate the epitaxial growth. X-ray diffraction, atomic force microscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometry measurements show that the Fe4N thin film grown on the Ag buffer layer is superior to that grown on the Cr buffer layer. The point contact Andreev reflection measurement was then conducted, and the spin polarizations were determined to be 61.1% and 81.3% for Fe4N thin films with Cr and Ag buffer layers, respectively. The 81.3% spin polarization is significantly higher than the ratio reported previously for Fe4N and is comparable with that of state-of-the-art Heusler alloys. This result is in agreement with the theoretical prediction on the discrepancy between the two differently defined spin polarizations for Fe4N. Moreover, our study indicates that an optimized growth process for Fe4N thin films is crucial for achieving a high spin polarization and that true half-metallicity could potentially be realized with Fe4N. Furthermore the high spin polarization of Fe4N combined with its low fabrication temperature and simple composition makes Fe4N a competitive candidate to be a half-metallic ferromagnet in spintronic devices.},
doi = {10.1063/1.5023698},
url = {https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1503634},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
issn = {0003-6951},
number = 16,
volume = 112,
place = {United States},
year = {Wed Apr 18 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Wed Apr 18 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
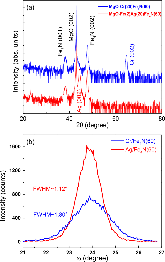 FIG. 1: (a) θ-2θ XRD scans of the Fe4N films grown on Cr and Ag buffer layers. (b) Rocking curve measurement of Fe4N (002) peaks.
FIG. 1: (a) θ-2θ XRD scans of the Fe4N films grown on Cr and Ag buffer layers. (b) Rocking curve measurement of Fe4N (002) peaks.
Works referenced in this record:
Negative spin polarization at the Fermi level in Fe 4 N epitaxial films by spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy
journal, July 2012
- Ito, Keita; Okamoto, Kazuaki; Harada, Kazunori
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 112, Issue 1
Damping constant measurement and inverse giant magnetoresistance in spintronic devices with Fe 4 N
journal, December 2017
- Li, Xuan; Li, Hongshi; Jamali, Mahdi
- AIP Advances, Vol. 7, Issue 12
The calculated electronic and magnetic structures of Fe4N and Mn 4N
journal, January 1988
- Matar, S.; Mohn, P.; Demazeau, G.
- Journal de Physique, Vol. 49, Issue 10
New Class of Materials: Half-Metallic Ferromagnets
journal, June 1983
- de Groot, R. A.; Mueller, F. M.; Engen, P. G. van
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 50, Issue 25
Epitaxial growth and thermal stability of Fe 4 N film on TiN buffered Si(001) substrate
journal, April 2011
- Xiang, H.; Shi, F. -Y.; Rzchowski, M. S.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 109, Issue 7
Anisotropic magnetoresistance in facing-target reactively sputtered epitaxial γ′-Fe4N films
journal, May 2015
- Li, Z. R.; Feng, X. P.; Wang, X. C.
- Materials Research Bulletin, Vol. 65
Anomalous Hall effects in pseudo-single-crystal γ ′-Fe 4 N thin films
journal, May 2016
- Kabara, Kazuki; Tsunoda, Masakiyo; Kokado, Satoshi
- AIP Advances, Vol. 6, Issue 5
Large magnetoresistance in current-perpendicular-to-plane pseudo spin-valves using Co 2 Fe(Ga 0.5 Ge 0.5 ) Heusler alloy and AgZn spacer
journal, September 2015
- Du, Ye; Furubayashi, T.; Sasaki, T. T.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 107, Issue 11
Spin polarization and Gilbert damping of Co2Fe(GaxGe1−x) Heusler alloys
journal, October 2012
- Varaprasad, B. S. D. Ch. S.; Srinivasan, A.; Takahashi, Y. K.
- Acta Materialia, Vol. 60, Issue 18
Negative anisotropic magnetoresistance resulting from minority spin transport in Ni x Fe 4− x N ( x = 1 and 3) epitaxial films
journal, January 2017
- Takata, Fumiya; Kabara, Kazuki; Ito, Keita
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 121, Issue 2
Huge Spin-Polarization of L2 1 -Ordered Co 2 MnSi Epitaxial Heusler Alloy Film
journal, August 2005
- Sakuraba, Yuya; Nakata, Jun; Oogane, Mikihiko
- Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 44, Issue No. 35
Factors affecting surface roughness and coercivity of Ni[sub 80]Fe[sub 20] thin films
journal, January 2002
- Ng, V.; Hu, J. F.; Adeyeye, A. O.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 91, Issue 10
Theoretical analysis of highly spin-polarized transport in the iron nitride
journal, May 2006
- Kokado, Satoshi; Fujima, Nobuhisa; Harigaya, Kikuo
- Physical Review B, Vol. 73, Issue 17
Investigation of γ′-Fe4N thin films deposited on Si(1 0 0) and GaAs(1 0 0) substrates by facing target magnetron sputtering
journal, September 2015
- Na, Yuanyuan; Wang, Cong; Xiang, Jinzhong
- Journal of Crystal Growth, Vol. 426
Deposition and spin polarization study of Fe 4 N thin films with (111) orientation
journal, September 2017
- Li, Xuan; Osofsky, M. S.; Jensen, Kevin L.
- AIP Advances, Vol. 7, Issue 9
Spin polarization of amorphous CoFeB determined by point-contact Andreev reflection
journal, June 2008
- Huang, S. X.; Chen, T. Y.; Chien, C. L.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 92, Issue 24
Perpendicular Magnetic Anisotropy and High Spin Polarization in Tetragonal Heterostructures
journal, December 2016
- Yin, Li; Mi, Wenbo; Wang, Xiaocha
- Physical Review Applied, Vol. 6, Issue 6
Relations of electronic energies and magnetic moments of tetra-3d metal (Mn, Fe, Co and Ni) nitrides calculated using a plane-wave basis method
journal, September 2010
- Imai, Yoji; Takahashi, Yasuhiko; Kumagai, Toshiya
- Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 322, Issue 18
Co2MnSi Heusler alloy as magnetic electrodes in magnetic tunnel junctions
journal, July 2004
- Kämmerer, S.; Thomas, A.; Hütten, A.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 85, Issue 1
Large tunnel magnetoresistance in magnetic tunnel junctions using a Co2MnSi Heusler alloy electrode and a MgO barrier
journal, September 2008
- Tsunegi, Sumito; Sakuraba, Yuya; Oogane, Mikihiko
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 93, Issue 11
Structure and magnetic properties of γ′-Fe4N films grown on MgO-buffered Si (001)
journal, December 2012
- Li, Jing; Jiang, Yinzhu; Ma, Tianyu
- Physica B: Condensed Matter, Vol. 407, Issue 24
Ab initio study of structural and magnetic properties of cubic Fe4N(001) surface
journal, August 2012
- Shi, Y. J.; Du, Y. L.; Chen, G.
- Solid State Communications, Vol. 152, Issue 16
Electric-field tunable perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in tetragonal Fe 4 N/BiFeO 3 heterostructures
journal, July 2017
- Yin, Li; Wang, Xiaocha; Mi, Wenbo
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 111, Issue 3
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and high spin-polarization ratio in epitaxial Fe-N thin films
journal, December 2011
- Ji, Nian; Osofsky, M. S.; Lauter, Valeria
- Physical Review B, Vol. 84, Issue 24
Self-consistent calculations for the electronic structures of iron nitrides, Fe3N, Fe4N and Fe16N2
journal, December 1991
- Sakuma, Akimasa
- Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 102, Issue 1-2
Correlations between structural, electronic transport, and magnetic properties of Heusler alloy epitaxial thin films
journal, August 2015
- Gabor, M. S.; Belmeguenai, M.; Petrisor, T.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 92, Issue 5
Structural and magnetic properties of epitaxially grown full-Heusler alloy Co2MnGe thin films deposited using magnetron sputtering
journal, April 2006
- Ishikawa, Takayuki; Marukame, Takao; Matsuda, Ken-ichi
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 99, Issue 8
Thin film phase diagram of iron nitrides grown by molecular beam epitaxy
journal, January 2017
- Gölden, D.; Hildebrandt, E.; Alff, L.
- Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 422
Measurement of spin polarization of single crystals of and
journal, July 2002
- Ji, Y.; Chien, C. L.; Tomioka, Y.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 66, Issue 1
Structural and magnetic properties of size-controlled Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles and magnetic fluids
journal, October 2009
- Desai, Rucha; Davariya, Vipul; Parekh, Kinnari
- Pramana, Vol. 73, Issue 4
The preparation and ferromagnetism of single crystal ε-Fe3N(111) film on SrTiO3(100) substrate
journal, November 2016
- Qi, Yaping; Liu, Xiangbo; Huang, Weiyi
- Vacuum, Vol. 133
Pronounced effects of additional resistance in Andreev reflection spectroscopy
journal, June 2010
- Chen, T. Y.; Huang, S. X.; Chien, C. L.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 81, Issue 21
Investigation on the structure and magnetic properties at low temperature for nanocrystalline γ′-Fe4N thin films
journal, January 2009
- Wang, L. L.; Zheng, W. T.; Gong, J.
- Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Vol. 467, Issue 1-2
Measuring the Spin Polarization of a Metal with a Superconducting Point Contact
journal, October 1998
- Soulen Jr., R. J.
- Science, Vol. 282, Issue 5386
Fabrication of highly spin-polarized Co 2 FeAl 0.5 Si 0.5 thin-films
journal, April 2014
- Vahidi, M.; Gifford, J. A.; Zhang, S. K.
- APL Materials, Vol. 2, Issue 4
Probing Ferromagnets with Andreev Reflection
journal, October 1998
- Upadhyay, Shashi K.; Palanisami, Akilan; Louie, Richard N.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 81, Issue 15
Determination of the Spin Polarization of Half-Metallic by Point Contact Andreev Reflection
journal, June 2001
- Ji, Y.; Strijkers, G. J.; Yang, F. Y.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 86, Issue 24
Tunneling between ferromagnetic films
journal, September 1975
- Julliere, M.
- Physics Letters A, Vol. 54, Issue 3
75% inverse magnetoresistance at room temperature in Fe4N/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions fabricated on Cu underlayer
journal, April 2009
- Komasaki, Yosuke; Tsunoda, Masakiyo; Isogami, Shinji
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 105, Issue 7
Electronic, magnetic properties and phase diagrams of system with Fe4N compound: An ab initio calculations and Monte Carlo study
journal, May 2018
- Masrour, R.; Jabar, A.; Hlil, E. K.
- Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 453
Near-complete spin polarization in atomically-smooth chromium-dioxide epitaxial films prepared using a CVD liquid precursor
journal, October 2001
- Anguelouch, A.; Gupta, A.; Xiao, Gang
- Physical Review B, Vol. 64, Issue 18
Ab initio studies of magnetic properties of cobalt and tetracobalt nitride
journal, June 2007
- Matar, S. F.; Houari, A.; Belkhir, M. A.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 75, Issue 24
Enhanced half-metallicity of off-stoichiometric quaternary Heusler alloy investigated through saturation magnetization and tunneling magnetoresistance
journal, April 2016
- Moges, Kidist; Honda, Yusuke; Liu, Hong-xi
- Physical Review B, Vol. 93, Issue 13
Reactively sputtered epitaxial γ′-Fe4N films: Surface morphology, microstructure, magnetic and electrical transport properties
journal, October 2013
- Mi, W. B.; Guo, Z. B.; Feng, X. P.
- Acta Materialia, Vol. 61, Issue 17
Spin polarization of Fe4N thin films determined by point-contact Andreev reflection
journal, May 2009
- Narahara, A.; Ito, K.; Suemasu, T.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 94, Issue 20
Mechanism of large magnetoresistance in devices with current perpendicular to the plane
journal, September 2010
- Sakuraba, Y.; Izumi, K.; Iwase, T.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 82, Issue 9
Negative Anisotropic Magnetoresistance in Fe 4 N Film
journal, July 2009
- Tsunoda, Masakiyo; Komasaki, Yosuke; Kokado, Satoshi
- Applied Physics Express, Vol. 2
Diamond-like carbon films prepared by facing-target sputtering
journal, December 2002
- Shi, J. R.; Wang, J. P.
- Thin Solid Films, Vol. 420-421
Works referencing / citing this record:
Strain relaxation in epitaxial γ ′-Fe 4 N ultrathin films
journal, September 2019
- Suzuki, Ippei; Uzuhashi, Jun; Ohkubo, Tadakatsu
- Materials Research Express, Vol. 6, Issue 10
Effect of interfacial interdiffusion on magnetism in epitaxial films on substrates
journal, November 2019
- Pandey, Nidhi; Pütter, S.; Amir, S. M.
- Physical Review Materials, Vol. 3, Issue 11
In-situ growth of iron mononitride thin films studied using x-ray absorption spectroscopy and nuclear resonant scattering
text, January 2019
- Gupta, Mukul; Pandey, Nidhi; Reddy, V. R.
- Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron, DESY, Hamburg
Figures / Tables found in this record: