Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Ni-Mn-Cr-Sn Heusler alloys under the effects of hydrostatic pressure
- Southern Illinois Univ., Carbondale, IL (United States)
- Louisiana State Univ., Baton Rouge, LA (United States)
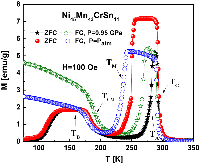
The magnetic, thermal, and magnetocaloric properties of Ni45Mn43CrSn11 Heusler alloy have been investigated using differential scanning calorimetry and magnetization with hydrostatic pressure measurements. A shift in the martensitic transition temperature (TM) to higher temperatures was observed with the application of pressure. The application of pressure stabilizes the martensitic state and demonstrated that pressure can be a parameter used to control and tune the martensitic transition temperature (the temperature where the largest magnetocaloric effect is observed). The magnetic entropy change significantly decreases from 33 J/kg K to 16 J/kg K under the application of a hydrostatic pressure of 0.95 GPa. The critical field of the direct metamagnetic transition increases, whereas the initial susceptibility (dM/dH) in the low magnetic field region drastically decreases with increasing pressure. Thus, the relevant parameters that affect the magnetocaloric properties are discussed.
- Research Organization:
- Southern Illinois Univ., Carbondale, IL (United States); Louisiana State Univ., Baton Rouge, LA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES). Materials Sciences & Engineering Division; USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (SC-22), Material Science Division
- Grant/Contract Number:
- FG02-06ER46291; SC0010521; FG02-13ER46946
- OSTI ID:
- 1499642
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1413826; OSTI ID: 1874687
- Journal Information:
- AIP Advances, Vol. 8, Issue 5; ISSN 2158-3226
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Similar Records
The influence of Au substitution and hydrostatic pressure on the phase transitions and magnetocaloric properties of MnCoGe alloys
Tuning martensitic transitions in (MnNiSi)0.65(Fe2Ge)0.35 through heat treatment and hydrostatic pressure