Free-electron laser data for multiple-particle fluctuation scattering analysis
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States); Hit Discovery, Gothenburg (Sweden)
- Max-Planck-Institut fur medizinische Forschung, Heidelberg (Germany); Max Planck Advanced Study Group, Hamburg (Germany)
- Max-Planck-Institut fur medizinische Forschung, Heidelberg (Germany); Univ. of Hamburg, Hamburg (Germany)
- Arizona State Univ., Tempe, AZ (United States); Paul Scherrer Inst. (PSI), Villigen (Switzerland)
- Max-Planck-Institut fur medizinische Forschung, Heidelberg (Germany); Arizona State Univ., Tempe, AZ (United States)
- Arizona State Univ., Tempe, AZ (United States); European XFEL GmbH, Schenefeld (Germany)
- Max Planck Advanced Study Group, Hamburg (Germany); Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg (Germany); Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter, Hamburg (Germany)
- Max-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische Physik, Garching (Germany); Univ. Oldenburg, Oldenburg (Germany)
- Arizona State Univ., Tempe, AZ (United States)
- Max-Planck-Institut fur medizinische Forschung, Heidelberg (Germany)
- PNSensor GmbH, Munchen (Germany)
- Max-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische Physik, Garching (Germany)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States); Univ. of California, Los Angeles, CA (United States)
- Univ. of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI (United States)
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Stanford, CA (United States); California Lutheran Univ., Thousand Oaks, CA (United States)
- Paul Scherrer Inst. (PSI), Villigen (Switzerland)
- Max-Planck-Institut fur medizinische Forschung, Heidelberg (Germany); Max Planck Advanced Study Group, Hamburg (Germany); Kansas State Univ., Manhattan, KS (United States)
- Max Planck Advanced Study Group, Hamburg (Germany); Max-Planck-Institut fur Kernphysik, Heidelberg (Germany); Kansas State Univ., Manhattan, KS (United States)
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Stanford, CA (United States)
- Max-Planck-Institut fur Kernphysik, Heidelberg (Germany)
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Stanford, CA (United States); Traction on Demand, Burnaby, BC (Canada)
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Stanford, CA (United States); Synchrotron SOLEIL, Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex (France)
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Stanford, CA (United States); Northwestern Univ., Evanston, IL (United States); Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States); Michigan State Univ., East Lansing, MI (United States)
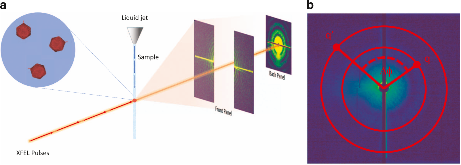
Fluctuation X-ray scattering (FXS) is an emerging experimental technique in which solution scattering data are collected using X-ray exposures below rotational diffusion times, resulting in angularly anisotropic X-ray snapshots that provide several orders of magnitude more information than traditional solution scattering data. Such experiments can be performed using the ultrashort X-ray pulses provided by a free-electron laser source, allowing one to collect a large number of diffraction patterns in a relatively short time. Here, we describe a test data set for FXS, obtained at the Linac Coherent Light Source, consisting of close to 100 000 multi-particle diffraction patterns originating from approximately 50 to 200 Paramecium Bursaria Chlorella virus particles per snapshot. In addition to the raw data, a selection of high-quality pre-processed diffraction patterns and a reference SAXS profile are provided.
- Research Organization:
- SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (SLAC), Menlo Park, CA (United States); Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States); Univ. of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-76SF00515; AC02-05CH11231; SC0002164
- OSTI ID:
- 1490633
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1494082; OSTI ID: 1598178
- Journal Information:
- Scientific Data, Vol. 5; ISSN 2052-4463
- Publisher:
- Nature Publishing GroupCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Design of a liquid cell toward three-dimensional imaging of unidirectionally-aligned particles in solution using X-ray free-electron lasers
|
journal | January 2020 |
Ab initio structure determination from experimental fluctuation X-ray scattering data
|
journal | October 2018 |
Similar Records
Diffraction data from aerosolized Coliphage PR772 virus particles imaged with the Linac Coherent Light Source
Coherent diffraction of single Rice Dwarf virus particles using hard X-rays at the Linac Coherent Light Source