Upgrading Limiting Peak-Power Analysis Techniques with Modern Validation and Uncertainty Quantification for the Advanced Test Reactor
- Idaho National Lab. (INL), Idaho Falls, ID (United States)
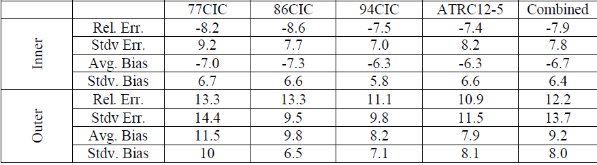
Here, this work demonstrates the acceptability of the 2D deterministic transport code, HELIOS, to replace the legacy diffusion code, PDQ, for computing the peak-power performance parameters of the Advanced Test Reactor (ATR). The 95% Confidence Rule, commonly used in the commercial reactor sector, is explored to develop the so-called “reliability factors” which provide statistical confidence that the peak-power limits within the hottest location along a fuel plate, referred to as the hot-stripe, will not be exceeded. Additionally, an alternative “legacy” methodology was explored that attempts to mimic the exact PDQ analysis process used for defining the peak-power limits. The legacy methodology, involves interpolating power between regions at azimuthal boundaries subtending the regions of interest. In order to apply the 95% Confidence Rule, a statistically significant calculation-to-measurement bias must first be established. Unlike the commercial world where thousands of power observations can be collected every cycle using on-line flux mapping instrumentation, the ATR power distribution must be measured during “depressurized” zero-power measurements using fission wires in polyethylene wands. In 2012, fission wire activation data was collected during a flux run in the Advanced Test Reactor – Critical facility. Also to improve statistical validity, archival data from ATR zero power flux runs from 1977, 1986, and 1994 were digitized from scanned reports and used to create new benchmark models. Borrowing from least-squares adjustment methods commonly used for neutron activation spectroscopy, adjusted fission wire powers were calculated for all four datasets. The mean and standard deviation of the bias between a priori calculated and adjusted wire-powers was then taken as the bias and uncertainty used in the 95% Confidence Rule.
- Research Organization:
- Idaho National Lab. (INL), Idaho Falls, ID (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Nuclear Energy (NE)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC07-05ID14517
- OSTI ID:
- 1473711
- Report Number(s):
- INL/JOU-17-41057-Rev000
- Journal Information:
- Nuclear Technology, Vol. 201, Issue 3; ISSN 0029-5450
- Publisher:
- Taylor & Francis - formerly American Nuclear Society (ANS)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Advanced Test Reactor Core Modeling Update Project Annual Report for Fiscal Year 2012
Validation of HELIOS for ATR Core Follow Analyses