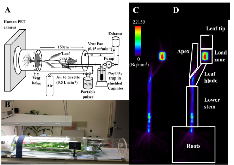
In vivo quantitative imaging of photoassimilate transport dynamics and allocation in large plants using a commercial positron emission tomography (PET) scanner
Although important aspects of whole-plant carbon allocation in crop plants (e.g., to grain) occur late in development when the plants are large, techniques to study carbon transport and allocation processes have not been adapted for large plants. Positron emission tomography (PET), developed for dynamic imaging in medicine, has been applied in plant studies to measure the transport and allocation patterns of carbohydrates, nutrients, and phytohormones labeled with positron-emitting radioisotopes. However, the cost of PET and its limitation to smaller plants has restricted its use in plant biology. Here we describe the adaptation and optimization of a commercial clinical PET scanner to measure transport dynamics and allocation patterns of 11C-photoassimilates in large crops. Based on measurements of a phantom, we optimized instrument settings, including use of 3-D mode and attenuation correction to maximize the accuracy of measurements. To demonstrate the utility of PET, we measured 11C-photoassimilate transport and allocation in Sorghum bicolor, an important staple crop, at vegetative and reproductive stages (40 and 70 days after planting; DAP). The 11C-photoassimilate transport speed did not change over the two developmental stages. However, within a stem, transport speeds were reduced across nodes, likely due to higher 11C-photoassimilate unloading in the nodes. Photosynthesis in leaves and the amount of 11C that was exported to the rest of the plant decreased as plants matured. In young plants, exported 11C was allocated mostly (88 %) to the roots and stem, but in flowering plants (70 DAP) the majority of the exported 11C (64 %) was allocated to the apex. Our results show that commercial PET scanners can be used reliably to measure whole-plant C-allocation in large plants nondestructively including, importantly, allocation to roots in soil. This capability revealed extreme changes in carbon allocation in sorghum plants, as they advanced to maturity. Further, our results suggest that nodes may be important control points for photoassimilate distribution in crops of the family Poaceae. In conclusion, quantifying real-time carbon allocation and photoassimilate transport dynamics, as demonstrated here, will be important for functional genomic studies to unravel the mechanisms controlling phloem transport in large crop plants, which will provide crucial insights for improving yields.
- Research Organization:
- Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02- 98CH10886; MO094; AC02-98CH10886
- OSTI ID:
- 1618602
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1263483
- Journal Information:
- BMC Plant Biology, Journal Name: BMC Plant Biology Vol. 15 Journal Issue: 1; ISSN 1471-2229
- Publisher:
- Springer Science + Business MediaCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United Kingdom
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Photosynthate Regulation of the Root System Architecture Mediated by the Heterotrimeric G Protein Complex in Arabidopsis
|
journal | August 2016 |
Dissecting metabolic flux in C4 plants: experimental and theoretical approaches
|
journal | June 2018 |
How can we harness quantitative genetic variation in crop root systems for agricultural improvement?: Quantifying root architecture for crops
|
journal | March 2016 |
High-Resolution in vivo Imaging of Xylem-Transported CO2 in Leaves Based on Real-Time 11C-Tracing
|
journal | June 2019 |
Similar Records
Stover composition in maize and sorghum reveals remarkable genetic variation and plasticity for carbohydrate accumulation
Identification and analysis of stem‐specific promoters from sugarcane and energy cane for oil accumulation in their stems