Natural Bacterial Communities Serve as Quantitative Geochemical Biosensors
- Massachusetts Inst. of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, MA (United States)
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Univ. of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN (United States)
- Univ. of Oklahoma, Norman, OK (United States)
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States) ; Northwest Missouri State Univ., Maryville, MO (United States)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States); Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States). Dept. of Bioengineering
- Massachusetts Inst. of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, MA (United States); Univ. of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN (United States)
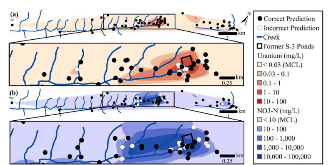
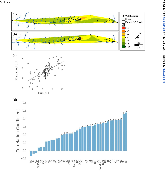
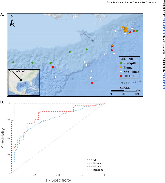
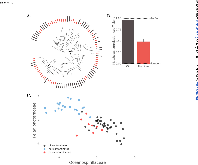
ABSTRACT Biological sensors can be engineered to measure a wide range of environmental conditions. Here we show that statistical analysis of DNA from natural microbial communities can be used to accurately identify environmental contaminants, including uranium and nitrate at a nuclear waste site. In addition to contamination, sequence data from the 16S rRNA gene alone can quantitatively predict a rich catalogue of 26 geochemical features collected from 93 wells with highly differing geochemistry characteristics. We extend this approach to identify sites contaminated with hydrocarbons from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, finding that altered bacterial communities encode a memory of prior contamination, even after the contaminants themselves have been fully degraded. We show that the bacterial strains that are most useful for detecting oil and uranium are known to interact with these substrates, indicating that this statistical approach uncovers ecologically meaningful interactions consistent with previous experimental observations. Future efforts should focus on evaluating the geographical generalizability of these associations. Taken as a whole, these results indicate that ubiquitous, natural bacterial communities can be used asin situenvironmental sensors that respond to and capture perturbations caused by human impacts. Thesein situbiosensors rely on environmental selection rather than directed engineering, and so this approach could be rapidly deployed and scaled as sequencing technology continues to become faster, simpler, and less expensive. IMPORTANCEHere we show that DNA from natural bacterial communities can be used as a quantitative biosensor to accurately distinguish unpolluted sites from those contaminated with uranium, nitrate, or oil. These results indicate that bacterial communities can be used as environmental sensors that respond to and capture perturbations caused by human impacts.
- Research Organization:
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States); Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725; AC02-05CH11231
- OSTI ID:
- 1265499
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1215642; OSTI ID: 1512191
- Journal Information:
- mBio (Online), Vol. 6, Issue 3; ISSN 2150-7511
- Publisher:
- American Society for MicrobiologyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Modeling the Pseudomonas Sulfur Regulome by Quantifying the Storage and Communication of Information
Lateral Gene Transfer in a Heavy Metal-Contaminated-Groundwater Microbial Community