The Future Prospects of Muon Colliders and Neutrino Factories
Abstract
The potential of muon beams for high energy physics applications is described along with the challenges of producing high quality muon beams. Two proposed approaches for delivering high intensity muon beams, a proton driver source and a positron driver source, are described and compared. The proton driver concepts are based on the studies from the Muon Accelerator Program (MAP). Here, the MAP effort focused on a path to deliver muon-based facilities, ranging from neutrino factories to muon colliders, that could span research needs at both the intensity and energy frontiers. The Low EMittance Muon Accelerator (LEMMA) concept, which uses a positron-driven source, provides an attractive path to very high energy lepton colliders with improved particle backgrounds. The recent study of a 14-TeV muon collider in the LHC tunnel, which could leverage the existing CERN injectors and infrastructure and provide physics reach comparable to the 100[Formula: see text]TeV FCC-hh, at lower cost and with cleaner physics conditions, is also discussed. The present status of the design and R&D efforts towards each of these sources is described. A summary of important R&D required to establish a facility path for each concept is also presented.
- Authors:
-
- Istituto Nazionale Fisica Nucleare, Frascati (Rome) (Italy)
- CERN, Geneva (Switzerland)
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), High Energy Physics (HEP)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1572287
- Report Number(s):
- BNL-212265-2019-JAAM
Journal ID: ISSN 1793-6268; TRN: US2100299
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012704
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 10; Journal Issue: 01; Journal ID: ISSN 1793-6268
- Publisher:
- World Scientific
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 43 PARTICLE ACCELERATORS; muon; collider; neutrino factory; high energy physics
Citation Formats
Boscolo, Manuela, Delahaye, Jean-Pierre, and Palmer, Mark. The Future Prospects of Muon Colliders and Neutrino Factories. United States: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1142/S179362681930010X.
Boscolo, Manuela, Delahaye, Jean-Pierre, & Palmer, Mark. The Future Prospects of Muon Colliders and Neutrino Factories. United States. https://doi.org/10.1142/S179362681930010X
Boscolo, Manuela, Delahaye, Jean-Pierre, and Palmer, Mark. Thu .
"The Future Prospects of Muon Colliders and Neutrino Factories". United States. https://doi.org/10.1142/S179362681930010X. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1572287.
@article{osti_1572287,
title = {The Future Prospects of Muon Colliders and Neutrino Factories},
author = {Boscolo, Manuela and Delahaye, Jean-Pierre and Palmer, Mark},
abstractNote = {The potential of muon beams for high energy physics applications is described along with the challenges of producing high quality muon beams. Two proposed approaches for delivering high intensity muon beams, a proton driver source and a positron driver source, are described and compared. The proton driver concepts are based on the studies from the Muon Accelerator Program (MAP). Here, the MAP effort focused on a path to deliver muon-based facilities, ranging from neutrino factories to muon colliders, that could span research needs at both the intensity and energy frontiers. The Low EMittance Muon Accelerator (LEMMA) concept, which uses a positron-driven source, provides an attractive path to very high energy lepton colliders with improved particle backgrounds. The recent study of a 14-TeV muon collider in the LHC tunnel, which could leverage the existing CERN injectors and infrastructure and provide physics reach comparable to the 100[Formula: see text]TeV FCC-hh, at lower cost and with cleaner physics conditions, is also discussed. The present status of the design and R&D efforts towards each of these sources is described. A summary of important R&D required to establish a facility path for each concept is also presented.},
doi = {10.1142/S179362681930010X},
journal = {Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology},
number = 01,
volume = 10,
place = {United States},
year = {Thu Aug 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019},
month = {Thu Aug 01 00:00:00 EDT 2019}
}
Figures / Tables:
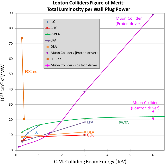 Fig. 1: Figure of merit (defined as the luminosity per wall plug power) of various lepton collider technologies [1, 2].
Fig. 1: Figure of merit (defined as the luminosity per wall plug power) of various lepton collider technologies [1, 2].
Works referenced in this record:
Design of a 6 TeV muon collider
journal, September 2016
- Wang, M-H.; Nosochkov, Y.; Cai, Y.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 11, Issue 09
Fixed field circular accelerator designs
conference, January 1999
- Johnstone, C.; Wan, W.; Garren, A.
- Proceedings of the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference (Cat. No.99CH36366)
Optimization of an hybrid positron source using channeling
journal, July 2017
- Chaikovska, I.; Chehab, R.; Guler, H.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, Vol. 402
A FODO racetrack ring for nuSTORM: design and optimization
journal, July 2017
- Liu, A.; Bross, A.; Neuffer, D.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 12, Issue 07
Muon Colliders
journal, January 2014
- Palmer, R. B.
- Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology, Vol. 07
A study of muon collider background rejection criteria in silicon vertex and tracker detectors
journal, September 2018
- Benedetto, V. Di; Gatto, C.; Mazzacane, A.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 13, Issue 09
Helical six-dimensional muon ionization cooling channel with gas-filled RF cavities
journal, September 2018
- Yonehara, K.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 13, Issue 09
Detector Backgrounds at Muon Colliders
journal, January 2012
- Mokhov, N. V.; Striganov, S. I.
- Physics Procedia, Vol. 37, p. 2015-2022
A Low-Emittance Lattice for the ESRF
journal, November 2014
- Biasci, J. C.; Bouteille, J. F.; Carmignani, N.
- Synchrotron Radiation News, Vol. 27, Issue 6
Final cooling for a high-energy high-luminosity lepton collider
journal, July 2017
- Neuffer, D.; Sayed, H.; Acosta, J.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 12, Issue 07
Novel proposal for a low emittance muon beam using positron beam on target
journal, January 2016
- Antonelli, M.; Boscolo, M.; Di Nardo, R.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 807
The NuMAX Long Baseline Neutrino Factory concept
journal, June 2018
- Delahaye, J-P.; Ankenbrandt, C. M.; Bogacz, S. A.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 13, Issue 06
Rectilinear six-dimensional ionization cooling channel for a muon collider: A theoretical and numerical study
journal, March 2015
- Stratakis, Diktys; Palmer, Robert B.
- Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 18, Issue 3
Pulsed synchrotrons for very rapid acceleration
conference, January 2016
- Berg, J. Scott; Witte, Holger
- ADVANCED ACCELERATOR CONCEPTS 2016: 16th Advanced Accelerator Concepts Workshop, AIP Conference Proceedings
A hybrid six-dimensional muon cooling channel using gas filled rf cavities
journal, September 2017
- Stratakis, D.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 12, Issue 09
The experimental program for high pressure gas filled radio frequency cavities for muon cooling channels
journal, January 2018
- Freemire, B.; Chung, M.; Hanlet, P. M.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 13, Issue 01
Angular collection using solenoids
journal, August 2000
- Chehab, Robert
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 451, Issue 1
Simulation of plasma loading of high-pressure RF cavities
journal, January 2018
- Yu, K.; Samulyak, R.; Yonehara, K.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 13, Issue 01
Front End for a neutrino factory or muon collider
journal, November 2017
- Neuffer, D.; Snopok, P.; Alexahin, Y.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 12, Issue 11
Muon Acceleration Concepts for NuMAX: “Dual-use” Linac and “Dogbone” RLA
journal, February 2018
- Bogacz, S. A.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 13, Issue 02
On the feasibility of a pulsed 14 TeV c.m.e. muon collider in the LHC tunnel
journal, October 2018
- Neuffer, D.; Shiltsev, V.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 13, Issue 10
Tapered channel for six-dimensional muon cooling towards micron-scale emittances
journal, September 2013
- Stratakis, Diktys; Fernow, Richard C.; Berg, J. Scott
- Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 16, Issue 9
High field – low energy muon ionization cooling channel
journal, September 2015
- Kamal Sayed, Hisham; Palmer, Robert B.; Neuffer, David
- Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 18, Issue 9
Muon Collider lattice concepts
journal, November 2018
- Alexahin, Y.; Gianfelice-Wendt, E.; Kapin, V.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 13, Issue 11
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal