Copper/TEMPO Redox Redux: Analysis of PCET Oxidation of TEMPOH by Copper(II) and the Reaction of TEMPO with Copper(I)
Abstract
Copper salts and organic aminoxyls, such as TEMPO (2,2,6,6- tetramethylpiperidine N-oxyl), are versatile catalysts for aerobic alcohol oxidation. Previous reports in the literature contain conflicting proposals concerning the redox interactions that take place between copper(I) and copper(II) salts with the aminoxyl and hydroxylamine species, TEMPO and TEMPOH, respectively. In this work, we reinvestigate these reactions in an effort to resolve the conflicting claims in the literature. Under anaerobic conditions, CuIIX2 salts [X= acetate (OAc), trifluoroacetate (TFA), triflate (OTf)] are shown to promote rapid proton-coupled oxidation of TEMPOH to TEMPO: CuIIX2 + TEMPOH → CuIX + TEMPO + HX. In the reaction with acetate, yet, slow reoxidation of CuIOAc occurs. This process requires both TEMPO and HOAc and coincides with reduction of TEMPO to 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine. Analogous reactivity is not observed with trifluoroacetate and triflate species. As a whole, the facility of proton-coupled oxidation of TEMPOH by CuII salts suggests that this process could contribute to catalyst regeneration under aerobic oxidation conditions.
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison, WI (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison, WI (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES); National Institutes of Health (NIH); National Science Foundation (NSF)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1544423
- Grant/Contract Number:
- FG02-05ER15690; CHE-1048642; CHE-0741901
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 58; Journal Issue: 15; Related Information: Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website at DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01326.; Journal ID: ISSN 0020-1669
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society (ACS)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 37 INORGANIC, ORGANIC, PHYSICAL, AND ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY
Citation Formats
Ryan, Michael C., Whitmire, Lauren D., McCann, Scott D., and Stahl, Shannon S. Copper/TEMPO Redox Redux: Analysis of PCET Oxidation of TEMPOH by Copper(II) and the Reaction of TEMPO with Copper(I). United States: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01326.
Ryan, Michael C., Whitmire, Lauren D., McCann, Scott D., & Stahl, Shannon S. Copper/TEMPO Redox Redux: Analysis of PCET Oxidation of TEMPOH by Copper(II) and the Reaction of TEMPO with Copper(I). United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01326
Ryan, Michael C., Whitmire, Lauren D., McCann, Scott D., and Stahl, Shannon S. Mon .
"Copper/TEMPO Redox Redux: Analysis of PCET Oxidation of TEMPOH by Copper(II) and the Reaction of TEMPO with Copper(I)". United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01326. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1544423.
@article{osti_1544423,
title = {Copper/TEMPO Redox Redux: Analysis of PCET Oxidation of TEMPOH by Copper(II) and the Reaction of TEMPO with Copper(I)},
author = {Ryan, Michael C. and Whitmire, Lauren D. and McCann, Scott D. and Stahl, Shannon S.},
abstractNote = {Copper salts and organic aminoxyls, such as TEMPO (2,2,6,6- tetramethylpiperidine N-oxyl), are versatile catalysts for aerobic alcohol oxidation. Previous reports in the literature contain conflicting proposals concerning the redox interactions that take place between copper(I) and copper(II) salts with the aminoxyl and hydroxylamine species, TEMPO and TEMPOH, respectively. In this work, we reinvestigate these reactions in an effort to resolve the conflicting claims in the literature. Under anaerobic conditions, CuIIX2 salts [X= acetate (OAc), trifluoroacetate (TFA), triflate (OTf)] are shown to promote rapid proton-coupled oxidation of TEMPOH to TEMPO: CuIIX2 + TEMPOH → CuIX + TEMPO + HX. In the reaction with acetate, yet, slow reoxidation of CuIOAc occurs. This process requires both TEMPO and HOAc and coincides with reduction of TEMPO to 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine. Analogous reactivity is not observed with trifluoroacetate and triflate species. As a whole, the facility of proton-coupled oxidation of TEMPOH by CuII salts suggests that this process could contribute to catalyst regeneration under aerobic oxidation conditions.},
doi = {10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01326},
journal = {Inorganic Chemistry},
number = 15,
volume = 58,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Jul 08 00:00:00 EDT 2019},
month = {Mon Jul 08 00:00:00 EDT 2019}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
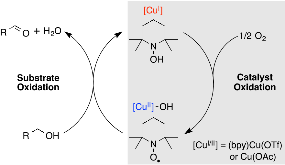 Scheme 1: Simplified Mechanism for Cu/TEMPO-Catalyzed Alcohol Oxidation.
Scheme 1: Simplified Mechanism for Cu/TEMPO-Catalyzed Alcohol Oxidation.
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal