Turbulence, transport, and zonal flows in the Madison symmetric torus reversed-field pinch
Abstract
The robustness and the effect of zonal flows in trapped electron mode (TEM) turbulence and Ion Temperature Gradient (ITG) turbulence in the reversed-field pinch (RFP) are investigated here from numerical solutions of the gyrokinetic equations with and without magnetic external perturbations introduced to model tearing modes. For simulations without external magnetic field perturbations, zonal flows produce a much larger reduction of transport for the density-gradient-driven TEM turbulence than they do for the ITG turbulence. Zonal flows are studied in detail to understand the nature of their strong excitation in the RFP and to gain insight into the key differences between the TEM- and ITG-driven regimes. The zonal flow residuals are significantly larger in the RFP than in tokamak geometry due to the low safety factor. Collisionality is seen to play a significant role in the TEM zonal flow regulation through the different responses of the linear growth rate and the size of the Dimits shift to collisionality, while affecting the ITG only minimally. A secondary instability analysis reveals that the TEM turbulence drives zonal flows at a rate that is twice that of the ITG turbulence. In addition to interfering with zonal flows, the magnetic perturbations are found to obviatemore »
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison, WI (United States). Dept. of Physics
- Jakob-Brucker-Gymnasium, Kaufbeuren (Germany); Max Planck Inst. for Plasma Physics, Garching (Germany)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison, WI (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Fusion Energy Sciences (FES); National Science Foundation (NSF)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1523258
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1414036
- Grant/Contract Number:
- FG02-85ER53212; TG-PHY130027
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Physics of Plasmas
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 24; Journal Issue: 12; Journal ID: ISSN 1070-664X
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 70 PLASMA PHYSICS AND FUSION TECHNOLOGY
Citation Formats
Williams, Z. R., Pueschel, M. J., Terry, P. W., and Hauff, T. Turbulence, transport, and zonal flows in the Madison symmetric torus reversed-field pinch. United States: N. p., 2017.
Web. doi:10.1063/1.5000252.
Williams, Z. R., Pueschel, M. J., Terry, P. W., & Hauff, T. Turbulence, transport, and zonal flows in the Madison symmetric torus reversed-field pinch. United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5000252
Williams, Z. R., Pueschel, M. J., Terry, P. W., and Hauff, T. Tue .
"Turbulence, transport, and zonal flows in the Madison symmetric torus reversed-field pinch". United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5000252. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1523258.
@article{osti_1523258,
title = {Turbulence, transport, and zonal flows in the Madison symmetric torus reversed-field pinch},
author = {Williams, Z. R. and Pueschel, M. J. and Terry, P. W. and Hauff, T.},
abstractNote = {The robustness and the effect of zonal flows in trapped electron mode (TEM) turbulence and Ion Temperature Gradient (ITG) turbulence in the reversed-field pinch (RFP) are investigated here from numerical solutions of the gyrokinetic equations with and without magnetic external perturbations introduced to model tearing modes. For simulations without external magnetic field perturbations, zonal flows produce a much larger reduction of transport for the density-gradient-driven TEM turbulence than they do for the ITG turbulence. Zonal flows are studied in detail to understand the nature of their strong excitation in the RFP and to gain insight into the key differences between the TEM- and ITG-driven regimes. The zonal flow residuals are significantly larger in the RFP than in tokamak geometry due to the low safety factor. Collisionality is seen to play a significant role in the TEM zonal flow regulation through the different responses of the linear growth rate and the size of the Dimits shift to collisionality, while affecting the ITG only minimally. A secondary instability analysis reveals that the TEM turbulence drives zonal flows at a rate that is twice that of the ITG turbulence. In addition to interfering with zonal flows, the magnetic perturbations are found to obviate an energy scaling relation for fast particles.},
doi = {10.1063/1.5000252},
journal = {Physics of Plasmas},
number = 12,
volume = 24,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue Dec 19 00:00:00 EST 2017},
month = {Tue Dec 19 00:00:00 EST 2017}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
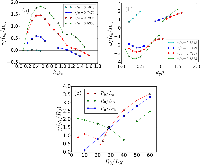 FIG. 1: Linear instability analysis for the low-n, 200 kA PPCD. In (a), growth rates are strongest in the ky ∼ 0.1–1 range. In (b), dominant frequencies are in the electron diamagnetic direction, with positive branches arising from the ubiquitous TEM. In (c), gradient scans at kyρs = 0.5 andmore »
FIG. 1: Linear instability analysis for the low-n, 200 kA PPCD. In (a), growth rates are strongest in the ky ∼ 0.1–1 range. In (b), dominant frequencies are in the electron diamagnetic direction, with positive branches arising from the ubiquitous TEM. In (c), gradient scans at kyρs = 0.5 andmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Evidence for Fast-Ion Transport by Microturbulence
journal, October 2009
- Heidbrink, W. W.; Park, J. M.; Murakami, M.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 103, Issue 17
Reduction of inward momentum flux by damped eigenmodes
journal, December 2009
- Terry, P. W.; Baver, D. A.; Hatch, D. R.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 16, Issue 12
Overview of gyrokinetic studies of finite- β microturbulence
journal, June 2015
- Terry, P. W.; Carmody, D.; Doerk, H.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 55, Issue 10
Advances in stellarator gyrokinetics
journal, April 2015
- Helander, P.; Bird, T.; Jenko, F.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 55, Issue 5
Subdominant Modes in Zonal-Flow-Regulated Turbulence
journal, March 2014
- Makwana, K. D.; Terry, P. W.; Pueschel, M. J.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 112, Issue 9
Microturbulence studies of pulsed poloidal current drive discharges in the reversed field pinch
journal, January 2015
- Carmody, D.; Pueschel, M. J.; Anderson, J. K.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 22, Issue 1
Theory of the ubiquitous mode
journal, October 1977
- Coppi, B.; Pegoraro, F.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 17, Issue 5
On secondary and tertiary instability in electromagnetic plasma microturbulence
journal, October 2013
- Pueschel, M. J.; Görler, T.; Jenko, F.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 10
Zonal flows in plasma—a review
journal, April 2005
- Diamond, P. H.; Itoh, S-I; Itoh, K.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 47, Issue 5
Energetic ion transport by microturbulence is insignificant in tokamaks
journal, May 2013
- Austin, M. E.; Bass, E. M.; Budny, R. V.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 5
Electron temperature gradient driven turbulence
journal, May 2000
- Jenko, F.; Dorland, W.; Kotschenreuther, M.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 7, Issue 5
Considerations of ion‐temperature‐gradient‐driven turbulence
journal, October 1991
- Cowley, S. C.; Kulsrud, R. M.; Sudan, R.
- Physics of Fluids B: Plasma Physics, Vol. 3, Issue 10
Poloidal Flow Driven by Ion-Temperature-Gradient Turbulence in Tokamaks
journal, January 1998
- Rosenbluth, M. N.; Hinton, F. L.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 80, Issue 4
Transport properties of finite-β microturbulence
journal, June 2010
- Pueschel, M. J.; Jenko, F.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 17, Issue 6
A circular equilibrium model for local gyrokinetic simulations of ion temperature gradient fluctuations in reversed field pinches
journal, May 2011
- Tangri, Varun; Terry, P. W.; Waltz, R. E.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 18, Issue 5
Anomalous diffusion of energetic particles: connecting experiment and simulations
journal, September 2012
- Pueschel, M. J.; Jenko, F.; Schneller, M.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 52, Issue 10
On the linear stability of collisionless microtearing modes
journal, April 2013
- Predebon, I.; Sattin, F.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 4
Gyrokinetic studies of trapped electron mode turbulence in the Helically Symmetric eXperiment stellarator
journal, July 2015
- Faber, B. J.; Pueschel, M. J.; Proll, J. H. E.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 22, Issue 7
Toroidal drift modes driven by ion pressure gradients
journal, January 1981
- Horton, Wendell
- Physics of Fluids, Vol. 24, Issue 6
Ion temperature gradient turbulence in helical and axisymmetric RFP plasmas
journal, May 2015
- Predebon, I.; Xanthopoulos, P.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 22, Issue 5
Properties of high-β microturbulence and the non-zonal transition
journal, October 2013
- Pueschel, M. J.; Hatch, D. R.; Görler, T.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 10
Generation and Stability of Zonal Flows in Ion-Temperature-Gradient Mode Turbulence
journal, December 2000
- Rogers, B. N.; Dorland, W.; Kotschenreuther, M.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 85, Issue 25
Energetics of the interaction between electromagnetic ExB turbulence and zonal flows
journal, January 2005
- Scott, Bruce D.
- New Journal of Physics, Vol. 7
Upgrading a high-throughput spectrometer for high-frequency (<400 kHz) measurements
journal, August 2016
- Nishizawa, T.; Nornberg, M. D.; Den Hartog, D. J.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 87, Issue 11
Generation and confinement of hot ions and electrons in a reversed-field pinch plasma
journal, November 2010
- Chapman, B. E.; Almagri, A. F.; Anderson, J. K.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 52, Issue 12
Clarifications to the limitations of the s-α equilibrium model for gyrokinetic computations of turbulence
journal, March 2009
- Lapillonne, X.; Brunner, S.; Dannert, T.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 16, Issue 3
Collisionless damping of zonal flows in helical systems
journal, January 2006
- Sugama, H.; Watanabe, T. -H.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 13, Issue 1
Electrostatic and magnetic transport of energetic ions in turbulent plasmas
journal, February 2009
- Hauff, T.; Pueschel, M. J.; Dannert, T.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 102, Issue 7
Toroidal microinstability studies of high‐temperature tokamaks
journal, January 1990
- Rewoldt, G.; Tang, W. M.
- Physics of Fluids B: Plasma Physics, Vol. 2, Issue 2
Role of trapped electron mode turbulence in internal transport barrier control in the Alcator C-Mod Tokamak
journal, May 2004
- Ernst, D. R.; Bonoli, P. T.; Catto, P. J.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 11, Issue 5
Influence of sheared poloidal rotation on edge turbulence
journal, January 1990
- Biglari, H.; Diamond, P. H.; Terry, P. W.
- Physics of Fluids B: Plasma Physics, Vol. 2, Issue 1
Comparisons and physics basis of tokamak transport models and turbulence simulations
journal, March 2000
- Dimits, A. M.; Bateman, G.; Beer, M. A.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 7, Issue 3
Gyrokinetic simulations in general geometry and applications to collisional damping of zonal flows
journal, May 2000
- Lin, Z.; Hahm, T. S.; Lee, W. W.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 7, Issue 5
The effect of magnetic flutter on residual flow
journal, November 2013
- Terry, P. W.; Pueschel, M. J.; Carmody, D.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 11
Equilibrium reconstruction in the Madison Symmetric Torus reversed field pinch
journal, December 2003
- Anderson, J. K.; Forest, C. B.; Biewer, T. M.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 44, Issue 1
Neutron spectroscopy measurements of tritium beam transport at JET
journal, October 2014
- Nocente, M.; Albergante, M.; Eriksson, J.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 54, Issue 10
Gyrokinetic studies of microinstabilities in the reversed field pinch
journal, May 2013
- Carmody, D.; Pueschel, M. J.; Terry, P. W.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 5
Fast-ion transport and neutral beam current drive in ASDEX upgrade
journal, June 2015
- Geiger, B.; Weiland, M.; Jacobsen, A. S.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 55, Issue 8
Effect of magnetic islands on profiles, flows, turbulence and transport in nonlinear gyrokinetic simulations
journal, February 2017
- Navarro, A. Bañón; Bardóczi, L.; Carter, T. A.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 59, Issue 3
Investigations of the role of nonlinear couplings in structure formation and transport regulation: experiment, simulation, and theory
journal, August 2003
- Holland, C.; Diamond, P. H.; Champeaux, S.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 43, Issue 8
Characterizing turbulent transport in ASDEX Upgrade L-mode plasmas via nonlinear gyrokinetic simulations
journal, December 2013
- Told, D.; Jenko, F.; Görler, T.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 12
Reduction of Turbulent Transport with Zonal Flows Enhanced in Helical Systems
journal, May 2008
- Watanabe, T. -H.; Sugama, H.; Ferrando-Margalet, S.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 100, Issue 19
Fluctuation and transport reduction in a reversed field pinch by inductive poloidal current drive
journal, June 1994
- Sarff, J. S.; Hokin, S. A.; Ji, H.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 72, Issue 23
Role of stable modes in zonal flow regulated turbulence
journal, June 2012
- Makwana, K. D.; Terry, P. W.; Kim, J. -H.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 19, Issue 6
Works referencing / citing this record:
Development of a multi-channel capacitive probe for electric field measurements with fine spatial and high time resolution
journal, October 2018
- Nishizawa, T.; Almagri, A. F.; Goodman, W.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 89, Issue 10
Persistence of Ion Temperature Gradient Turbulent Transport at Finite Normalized Pressure
journal, July 2019
- Ishizawa, A.; Urano, D.; Nakamura, Y.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 123, Issue 2
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal