City-Wide Eco-Routing Navigation Considering Vehicular Communication Impacts
Abstract
Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSs) utilize Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) to collect, disseminate, and share data with the Traffic Management Center (TMC) and different actuators. Consequently, packet drop and delay in VANETs can significantly impact ITS performance. Feedback-based eco-routing (FB-ECO) is a promising ITS technology, which is expected to reduce vehicle fuel/energy consumption and pollutant emissions by routing drivers through the most environmentally friendly routes. To compute these routes, the FB-ECO utilizes VANET communication to update link costs in real-time, based on the experiences of other vehicles in the system. In this paper, we study the impact of vehicular communication on FB-ECO navigation performance in a large-scale real network with realistic calibrated traffic demand data. We conduct this study at different market penetration rates and different congestion levels. We start by conducting a sensitivity analysis of the market penetration rate on the FB-ECO system performance, and its network-wide impacts considering ideal communication. Subsequently, we study the impact of the communication network on system performance for different market penetration levels, considering the communication system. Here, the results demonstrate that, for market penetration levels less than 30%, the eco-routing system performs adequately in both the ideal and realistic communication scenarios. It also showsmore »
- Authors:
-
- Virginia Polytechnic Inst. and State Univ. (Virginia Tech), Blacksburg, VA (United States). Center for Sustainable Mobility
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Virginia Polytechnic Inst. and State Univ. (Virginia Tech), Blacksburg, VA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), Vehicle Technologies Office (EE-3V)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1494834
- Report Number(s):
- DOE-VT-0008209-C03
Journal ID: ISSN 1424-8220; SENSC9
- Grant/Contract Number:
- EE0008209
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Sensors
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 19; Journal Issue: 2; Journal ID: ISSN 1424-8220
- Publisher:
- MDPI AG
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 32 ENERGY CONSERVATION, CONSUMPTION, AND UTILIZATION; 54 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES; 42 ENGINEERING; 97 MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTING; ITS; VANET; eco-routing; large-scale network; smart cities; penetration ratio; connected vehicles, vehicular networks
Citation Formats
Elbery, Ahmed, and Rakha, Hesham. City-Wide Eco-Routing Navigation Considering Vehicular Communication Impacts. United States: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.3390/s19020290.
Elbery, Ahmed, & Rakha, Hesham. City-Wide Eco-Routing Navigation Considering Vehicular Communication Impacts. United States. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020290
Elbery, Ahmed, and Rakha, Hesham. Tue .
"City-Wide Eco-Routing Navigation Considering Vehicular Communication Impacts". United States. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020290. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1494834.
@article{osti_1494834,
title = {City-Wide Eco-Routing Navigation Considering Vehicular Communication Impacts},
author = {Elbery, Ahmed and Rakha, Hesham},
abstractNote = {Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSs) utilize Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) to collect, disseminate, and share data with the Traffic Management Center (TMC) and different actuators. Consequently, packet drop and delay in VANETs can significantly impact ITS performance. Feedback-based eco-routing (FB-ECO) is a promising ITS technology, which is expected to reduce vehicle fuel/energy consumption and pollutant emissions by routing drivers through the most environmentally friendly routes. To compute these routes, the FB-ECO utilizes VANET communication to update link costs in real-time, based on the experiences of other vehicles in the system. In this paper, we study the impact of vehicular communication on FB-ECO navigation performance in a large-scale real network with realistic calibrated traffic demand data. We conduct this study at different market penetration rates and different congestion levels. We start by conducting a sensitivity analysis of the market penetration rate on the FB-ECO system performance, and its network-wide impacts considering ideal communication. Subsequently, we study the impact of the communication network on system performance for different market penetration levels, considering the communication system. Here, the results demonstrate that, for market penetration levels less than 30%, the eco-routing system performs adequately in both the ideal and realistic communication scenarios. It also shows that, for realistic communication, increasing the market penetration rate results in a network-wide degradation of the system performance.},
doi = {10.3390/s19020290},
journal = {Sensors},
number = 2,
volume = 19,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2019},
month = {Tue Jan 01 00:00:00 EST 2019}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
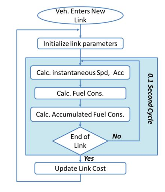 Figure 1: Eco-routing without the Communication modeling
Figure 1: Eco-routing without the Communication modeling
Works referenced in this record:
VANET Communication Impact on a Dynamic Eco-Routing System Performance: Preliminary Results
conference, May 2018
- Elbery, Ahmed; Rakha, Hesham A.
- 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)
Data-driven fuel consumption estimation: A multivariate adaptive regression spline approach
journal, October 2017
- Chen, Yuche; Zhu, Lei; Gonder, Jeffrey
- Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, Vol. 83
INTEGRATION Framework for Modeling Eco-routing Strategies: Logic and Preliminary Results
journal, September 2012
- Rakha, Hesham A.; Ahn, Kyoungho; Moran, Kevin
- International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, Vol. 1, Issue 3
Eco-Routing Navigation System Based on Multisource Historical and Real-Time Traffic Information
journal, December 2012
- Boriboonsomsin, Kanok; Barth, Matthew J.; Zhu, Weihua
- IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Vol. 13, Issue 4
Large-scale Agent-based Multi-modal Modeling of Transportation Networks - System Model and Preliminary Results [Large-scale Agent-based Multi-modal Modeling of Transportation Networks - System Model and Preliminary Results]
conference, March 2018
- Elbery, Ahmed; Dvorak, Filip; Du, Jianhe
- Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
Optimizing route choice for lowest fuel consumption – Potential effects of a new driver support tool
journal, December 2006
- Ericsson, Eva; Larsson, Hanna; Brundell-Freij, Karin
- Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, Vol. 14, Issue 6
Derivation of a fundamental diagram for urban traffic flow
journal, March 2009
- Helbing, D.
- The European Physical Journal B, Vol. 70, Issue 2
Optimizing route choice for lowest fuel consumption – Potential effects of a new driver support tool
journal, December 2006
- Ericsson, Eva; Larsson, Hanna; Brundell-Freij, Karin
- Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, Vol. 14, Issue 6
Data-driven fuel consumption estimation: A multivariate adaptive regression spline approach
journal, October 2017
- Chen, Yuche; Zhu, Lei; Gonder, Jeffrey
- Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, Vol. 83
INTEGRATION Framework for Modeling Eco-routing Strategies: Logic and Preliminary Results
journal, September 2012
- Rakha, Hesham A.; Ahn, Kyoungho; Moran, Kevin
- International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, Vol. 1, Issue 3
Works referencing / citing this record:
Multi-Factor Taxonomy of Eco-Routing Models and Future Outlook
journal, January 2020
- Alfaseeh, Lama; Farooq, Bilal
- Journal of Sensors, Vol. 2020
Multi-Level Taxonomy and Critical Review of Eco-Routing Methods
preprint, January 2019
- Alfaseeh, Lama; Farooq, Bilal
- arXiv
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal