Hot Spots and Hot Moments of Nitrogen in a Riparian Corridor
Abstract
Abstract We use 3‐D high‐resolution reactive transport modeling to investigate whether the spatial distribution of organic‐carbon‐rich and chemically reduced sediments located in the riparian zone and temporal variability in groundwater flow direction impact the formation and distribution of nitrogen hot spots (regions that exhibit higher reaction rates when compared to other locations nearby) and hot moments (times that exhibit high reaction rates as compared to longer intervening time periods) within the Rifle floodplain in Colorado. Groundwater flows primarily toward the Colorado River from the floodplain but changes direction at times of high river stage. The result is that oxic river water infiltrates the Rifle floodplain during these relatively short‐term events. Simulation results indicate that episodic rainfall in the summer season leads to the formation of nitrogen hot moments associated with Colorado River rise and resulting river infiltration into the floodplain. The results further demonstrate that the naturally reduced zones (NRZs) present in sediments of the Rifle floodplain have a higher potential for nitrate removal, approximately 70% greater than non‐NRZs for typical hydrological conditions. During river water infiltration, nitrate reduction capacity remains the same within the NRZs, however, these conditions impact non‐NRZs to a greater extent (approximately 95% less nitrate removal).more »
- Authors:
-
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States). Energy Geosciences Division
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States). Climate and Ecosystem Sciences
- Subsurface Insights, LLC, Hanover NH (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1476595
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1417061
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231; DE‐SC0009732; DE‐AC02‐05CH11231
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Water Resources Research
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 54; Journal Issue: 1; Journal ID: ISSN 0043-1397
- Publisher:
- American Geophysical Union (AGU)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 54 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Citation Formats
Dwivedi, Dipankar, Arora, Bhavna, Steefel, Carl I., Dafflon, Baptiste, and Versteeg, Roelof. Hot Spots and Hot Moments of Nitrogen in a Riparian Corridor. United States: N. p., 2017.
Web. doi:10.1002/2017WR022346.
Dwivedi, Dipankar, Arora, Bhavna, Steefel, Carl I., Dafflon, Baptiste, & Versteeg, Roelof. Hot Spots and Hot Moments of Nitrogen in a Riparian Corridor. United States. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR022346
Dwivedi, Dipankar, Arora, Bhavna, Steefel, Carl I., Dafflon, Baptiste, and Versteeg, Roelof. Thu .
"Hot Spots and Hot Moments of Nitrogen in a Riparian Corridor". United States. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR022346. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1476595.
@article{osti_1476595,
title = {Hot Spots and Hot Moments of Nitrogen in a Riparian Corridor},
author = {Dwivedi, Dipankar and Arora, Bhavna and Steefel, Carl I. and Dafflon, Baptiste and Versteeg, Roelof},
abstractNote = {Abstract We use 3‐D high‐resolution reactive transport modeling to investigate whether the spatial distribution of organic‐carbon‐rich and chemically reduced sediments located in the riparian zone and temporal variability in groundwater flow direction impact the formation and distribution of nitrogen hot spots (regions that exhibit higher reaction rates when compared to other locations nearby) and hot moments (times that exhibit high reaction rates as compared to longer intervening time periods) within the Rifle floodplain in Colorado. Groundwater flows primarily toward the Colorado River from the floodplain but changes direction at times of high river stage. The result is that oxic river water infiltrates the Rifle floodplain during these relatively short‐term events. Simulation results indicate that episodic rainfall in the summer season leads to the formation of nitrogen hot moments associated with Colorado River rise and resulting river infiltration into the floodplain. The results further demonstrate that the naturally reduced zones (NRZs) present in sediments of the Rifle floodplain have a higher potential for nitrate removal, approximately 70% greater than non‐NRZs for typical hydrological conditions. During river water infiltration, nitrate reduction capacity remains the same within the NRZs, however, these conditions impact non‐NRZs to a greater extent (approximately 95% less nitrate removal). Model simulations indicate chemolithoautotrophs are primarily responsible for the removal of nitrate in the Rifle floodplain. These nitrogen hot spots and hot moments are sustained by microbial respiration and the chemolithoautotrophic oxidation of reduced minerals in the riparian zone.},
doi = {10.1002/2017WR022346},
journal = {Water Resources Research},
number = 1,
volume = 54,
place = {United States},
year = {Thu Dec 28 00:00:00 EST 2017},
month = {Thu Dec 28 00:00:00 EST 2017}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
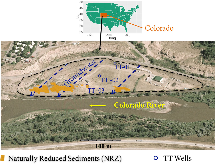 Figure 1: Rifle floodplain is located in western Colorado. Previous studies have identified naturally reduced zones (NRZs; shown in orange) in the saturated alluvium using induced polarization imaging (see, Wainwright et al., 2016). NRZs are linked with elevated organic carbon, Fe(II), sulfide, and U(IV).
Figure 1: Rifle floodplain is located in western Colorado. Previous studies have identified naturally reduced zones (NRZs; shown in orange) in the saturated alluvium using induced polarization imaging (see, Wainwright et al., 2016). NRZs are linked with elevated organic carbon, Fe(II), sulfide, and U(IV).
Works referenced in this record:
Multicomponent reactive transport modeling of uranium bioremediation field experiments
journal, October 2009
- Fang, Yilin; Yabusaki, Steven B.; Morrison, Stan J.
- Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 73, Issue 20
Stimulating the In Situ Activity of Geobacter Species To Remove Uranium from the Groundwater of a Uranium-Contaminated Aquifer
journal, October 2003
- Anderson, R. T.; Vrionis, H. A.; Ortiz-Bernad, I.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 69, Issue 10
Seasonal biogeochemical hotspots in the streambed around restoration structures
journal, August 2008
- Lautz, L. K.; Fanelli, R. M.
- Biogeochemistry, Vol. 91, Issue 1
Effects of physical and geochemical heterogeneities on mineral transformation and biomass accumulation during biostimulation experiments at Rifle, Colorado
journal, March 2010
- Li, Li; Steefel, Carl I.; Kowalsky, Michael B.
- Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, Vol. 112, Issue 1-4
Landscape controls on nitrate removal in stream riparian zones: LANDSCAPE CONTROLS ON NITRATE REMOVAL
journal, March 2004
- Vidon, Philippe G. F.; Hill, Alan R.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 40, Issue 3
A numerical transport model for oxygen- and nitrate-based respiration linked to substrate and nutrient availability in porous media
journal, September 1988
- Widdowson, Mark A.; Molz, Fred J.; Benefield, Larry D.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 24, Issue 9
Evaluating the performance of parallel subsurface simulators: An illustrative example with PFLOTRAN: Evaluating the Parallel Performance of Pflotran
journal, January 2014
- Hammond, G. E.; Lichtner, P. C.; Mills, R. T.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 50, Issue 1
Physico-Chemical Heterogeneity of Organic-Rich Sediments in the Rifle Aquifer, CO: Impact on Uranium Biogeochemistry
journal, December 2015
- Janot, Noémie; Lezama Pacheco, Juan S.; Pham, Don Q.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 50, Issue 1
Microbiological regulation of the biogeochemical nitrogen cycle
journal, February 1982
- Rosswall, T.
- Plant and Soil, Vol. 67, Issue 1-3
Metatranscriptomic evidence of pervasive and diverse chemolithoautotrophy relevant to C, S, N and Fe cycling in a shallow alluvial aquifer
journal, March 2016
- Jewell, Talia N. M.; Karaoz, Ulas; Brodie, Eoin L.
- The ISME Journal, Vol. 10, Issue 9
Rate-limited U(VI) desorption during a small-scale tracer test in a heterogeneous uranium-contaminated aquifer: RATE-LIMITED U(VI) DESORPTION IN A U-CONTAMINATED AQUIFER
journal, May 2012
- Fox, Patricia M.; Davis, James A.; Hay, Michael B.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 48, Issue 5
Oxidative Uranium Release from Anoxic Sediments under Diffusion-Limited Conditions
journal, September 2017
- Bone, Sharon E.; Cahill, Melanie R.; Jones, Morris E.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 51, Issue 19
Residence time control on hot moments of net nitrate production and uptake in the hyporheic zone: RESIDENCE TIME CONTROL ON TEMPORAL HYPORHEIC NITRATE CYCLING
journal, June 2013
- Briggs, Martin A.; Lautz, Laura K.; Hare, Danielle K.
- Hydrological Processes, Vol. 28, Issue 11
Multicomponent reactive transport modeling in variably saturated porous media using a generalized formulation for kinetically controlled reactions: REACTIVE TRANSPORT MODELING IN VARIABLY SATURATED MEDIA
journal, September 2002
- Mayer, K. Ulrich; Frind, Emil O.; Blowes, David W.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 38, Issue 9
Control Points in Ecosystems: Moving Beyond the Hot Spot Hot Moment Concept
journal, January 2017
- Bernhardt, Emily S.; Blaszczak, Joanna R.; Ficken, Cari D.
- Ecosystems, Vol. 20, Issue 4
Geochemical, mineralogical and microbiological characteristics of sediment from a naturally reduced zone in a uranium-contaminated aquifer
journal, August 2012
- Campbell, K. M.; Kukkadapu, R. K.; Qafoku, N. P.
- Applied Geochemistry, Vol. 27, Issue 8
Uranium Bioreduction Rates across Scales: Biogeochemical Hot Moments and Hot Spots during a Biostimulation Experiment at Rifle, Colorado
journal, August 2014
- Bao, Chen; Wu, Hongfei; Li, Li
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 48, Issue 17
Riparian biogeochemical hot moments induced by stream fluctuations: HYDROLOGICALLY DRIVEN RIPARIAN BUFFERING EFFECTS
journal, September 2012
- Gu, Chuanhui; Anderson, William; Maggi, Federico
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 48, Issue 9
Association of Novel and Highly Diverse Acid-Tolerant Denitrifiers with N2O Fluxes of an Acidic Fen
journal, December 2009
- Palmer, K.; Drake, H. L.; Horn, M. A.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 76, Issue 4
Mineral Transformation and Biomass Accumulation Associated With Uranium Bioremediation at Rifle, Colorado
journal, July 2009
- Li, Li; Steefel, Carl I.; Williams, Kenneth H.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 43, Issue 14
Identification and mitigation of nitrate leaching hot spots using NLEAP-GIS technology
journal, December 1995
- Shaffer, M. J.; Wylie, B. K.; Hall, M. D.
- Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, Vol. 20, Issue 3-4
Deep Vadose Zone Respiration Contributions to Carbon Dioxide Fluxes from a Semiarid Floodplain
journal, January 2016
- Tokunaga, Tetsu K.; Kim, Yongman; Conrad, Mark E.
- Vadose Zone Journal, Vol. 15, Issue 7
Water Table Dynamics and Biogeochemical Cycling in a Shallow, Variably-Saturated Floodplain
journal, March 2017
- Yabusaki, Steven B.; Wilkins, Michael J.; Fang, Yilin
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 51, Issue 6
Mineral properties, microbes, transport, and plant-input profiles control vertical distribution and age of soil carbon stocks
journal, April 2017
- Dwivedi, D.; Riley, W. J.; Torn, M. S.
- Soil Biology and Biochemistry, Vol. 107
Biogeochemical Hot Spots and Hot Moments at the Interface of Terrestrial and Aquatic Ecosystems
journal, June 2003
- McClain, Michael E.; Boyer, Elizabeth W.; Dent, C. Lisa
- Ecosystems, Vol. 6, Issue 4
A mechanistic treatment of the dominant soil nitrogen cycling processes: Model development, testing, and application: NITROGEN CYCLE MODELING
journal, April 2008
- Maggi, F.; Gu, C.; Riley, W. J.
- Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, Vol. 113, Issue G2
Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Sulfide Oxidation by Oxygen: A Look at Inorganically Controlled Reactions and Biologically Mediated Processes in the Environment
journal, January 2011
- Luther, George W.; Findlay, Alyssa J.; MacDonald, Daniel J.
- Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol. 2
Microbiological and Geochemical Heterogeneity in an In Situ Uranium Bioremediation Field Site
journal, October 2005
- Vrionis, H. A.; Anderson, R. T.; Ortiz-Bernad, I.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 71, Issue 10
Acetate Availability and its Influence on Sustainable Bioremediation of Uranium-Contaminated Groundwater
journal, June 2011
- Williams, Kenneth H.; Long, Philip E.; Davis, James A.
- Geomicrobiology Journal, Vol. 28, Issue 5-6
A multiple-continuum model for simulating single-phase and multiphase flow in naturally fractured vuggy reservoirs
journal, July 2011
- Wu, Yu-Shu; Di, Yuan; Kang, Zhijiang
- Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, Vol. 78, Issue 1
Field evidence of selenium bioreduction in a uranium-contaminated aquifer: Field evidence of selenium bioreduction
journal, February 2013
- Williams, Kenneth H.; Wilkins, Michael J.; N'Guessan, A. Lucie
- Environmental Microbiology Reports, Vol. 5, Issue 3
Uranium in Framboidal Pyrite from a Naturally Bioreduced Alluvial Sediment
journal, November 2009
- Qafoku, Nikolla P.; Kukkadapu, Ravi K.; McKinley, James P.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 43, Issue 22
Identifying geochemical hot moments and their controls on a contaminated river floodplain system using wavelet and entropy approaches
journal, November 2016
- Arora, Bhavna; Dwivedi, Dipankar; Hubbard, Susan S.
- Environmental Modelling & Software, Vol. 85
Influence of hydrological, biogeochemical and temperature transients on subsurface carbon fluxes in a flood plain environment
journal, February 2016
- Arora, Bhavna; Spycher, Nicolas F.; Steefel, Carl I.
- Biogeochemistry, Vol. 127, Issue 2-3
Denitrification in the Mississippi River network controlled by flow through river bedforms
journal, October 2015
- Gomez-Velez, Jesus D.; Harvey, Judson W.; Cardenas, M. Bayani
- Nature Geoscience, Vol. 8, Issue 12
Hot spots and hot moments of carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a semiarid riparian zone: RIPARIAN HOT SPOTS AND HOT MOMENTS
journal, March 2008
- Harms, Tamara K.; Grimm, Nancy B.
- Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, Vol. 113, Issue G1
Modern marine sediments as a natural analog to the chemically stressed environment of a landfill
journal, October 1979
- Baedecker, Mary Jo; Back, William
- Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 43, Issue 1-4
No Measurable Changes in 238 U/ 235 U due to Desorption–Adsorption of U(VI) from Groundwater at the Rifle, Colorado, Integrated Field Research Challenge Site
journal, February 2013
- Shiel, Alyssa E.; Laubach, Parker G.; Johnson, Thomas M.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 47, Issue 6
Biostimulation induces syntrophic interactions that impact C, S and N cycling in a sediment microbial community
journal, November 2012
- Handley, Kim M.; VerBerkmoes, Nathan C.; Steefel, Carl I.
- The ISME Journal, Vol. 7, Issue 4
Kinetic modeling of microbially-driven redox chemistry of subsurface environments: coupling transport, microbial metabolism and geochemistry
journal, August 1998
- Hunter, Kimberley S.; Wang, Yifeng; Van Cappellen, Philippe
- Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 209, Issue 1-4
Hierarchical Bayesian method for mapping biogeochemical hot spots using induced polarization imaging
journal, January 2016
- Wainwright, Haruko M.; Flores Orozco, Adrian; Bücker, Matthias
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 52, Issue 1
Thousands of microbial genomes shed light on interconnected biogeochemical processes in an aquifer system
journal, October 2016
- Anantharaman, Karthik; Brown, Christopher T.; Hug, Laura A.
- Nature Communications, Vol. 7, Issue 1
Upscaling Nitrogen Removal Capacity from Local Hotspots to Low Stream Orders’ Drainage Basins
journal, May 2015
- Pinay, Gilles; Peiffer, Stefan; De Dreuzy, Jean-Raynald
- Ecosystems, Vol. 18, Issue 6
Direct and Indirect Hydrological Controls on Concentration and Loading in Midwestern Streams
journal, January 2008
- Vidon, P.; Tedesco, L. P.; Wilson, J.
- Journal of Environment Quality, Vol. 37, Issue 5
Variably saturated flow and multicomponent biogeochemical reactive transport modeling of a uranium bioremediation field experiment
journal, November 2011
- Yabusaki, Steven B.; Fang, Yilin; Williams, Kenneth H.
- Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, Vol. 126, Issue 3-4
Timing the Onset of Sulfate Reduction over Multiple Subsurface Acetate Amendments by Measurement and Modeling of Sulfur Isotope Fractionation
journal, August 2012
- Druhan, Jennifer L.; Steefel, Carl I.; Molins, Sergi
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 46, Issue 16
Surface micro-topography causes hot spots of biogeochemical activity in wetland systems: A virtual modeling experiment: MICRO-TOPOGRAPHY AND HOT SPOT FORMATION
journal, October 2012
- Frei, S.; Knorr, K. H.; Peiffer, S.
- Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, Vol. 117, Issue G4
Challenges to incorporating spatially and temporally explicit phenomena (hotspots and hot moments) in denitrification models
journal, January 2009
- Groffman, Peter M.; Butterbach-Bahl, Klaus; Fulweiler, Robinson W.
- Biogeochemistry, Vol. 93, Issue 1-2
Geochemical and mineralogical investigation of uranium in multi-element contaminated, organic-rich subsurface sediment
journal, March 2014
- Qafoku, Nikolla P.; Gartman, Brandy N.; Kukkadapu, Ravi K.
- Applied Geochemistry, Vol. 42
Hot Spots and Persistence of Nitrate in Aquifers Across Scales
journal, January 2016
- Dwivedi, Dipankar; Mohanty, Binayak
- Entropy, Vol. 18, Issue 1
Prenatal Nitrate Intake from Drinking Water and Selected Birth Defects in Offspring of Participants in the National Birth Defects Prevention Study
journal, September 2013
- Brender, Jean D.; Weyer, Peter J.; Romitti, Paul A.
- Environmental Health Perspectives, Vol. 121, Issue 9
Works referencing / citing this record:
Development of a Fully Coupled Biogeochemical Reactive Transport Model to Simulate Microbial Oxidation of Organic Carbon and Pyrite Under Nitrate‐Reducing Conditions
journal, November 2018
- Knabe, Dustin; Kludt, Christoph; Jacques, Diederik
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 54, Issue 11
Morphogenesis of a Floodplain as a Criterion for Assessing the Susceptibility to Water Pollution in an Agriculturally Rich Valley of a Lowland River
journal, March 2018
- Sieczka, Anna; Bujakowski, Filip; Falkowski, Tomasz
- Water, Vol. 10, Issue 4
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal