Using Discrete Event Simulation to Model Attacker Interactions with Cyber and Physical Security Systems
Abstract
The number of connections between physical and cyber security systems is rapidly increasing due to centralized control from automated and remotely connected means. As the number of interfaces between systems continues to grow, the interactions and interdependencies between them cannot be ignored. Historically, physical and cyber vulnerability assessments have been performed independently. This independent evaluation omits important aspects of the integrated system, where the impacts resulting from malicious or opportunistic attacks are not easily known or understood. Here, we describe a discrete event simulation model that uses information about integrated physical and cyber security systems, attacker characteristics and simple response rules to identify key safeguards that limit an attacker's likelihood of success. Key features of the proposed model include comprehensive data generation to support a variety of sophisticated analyses, and full parameterization of safeguard performance characteristics and attacker behaviours to evaluate a range of scenarios. Lastly, we also describe the core data requirements and the network of networks that serves as the underlying simulation structure.
- Authors:
-
- Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1347710
- Report Number(s):
- PNNL-24335
Journal ID: ISSN 1877-0509; PII: S187705091503029X
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC0576RL01830
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Procedia Computer Science
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 61; Journal Issue: C; Journal ID: ISSN 1877-0509
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 97 MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTING; 98 NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT, SAFEGUARDS, AND PHYSICAL PROTECTION; Cyber-physical systems; vulnerability assessment; discrete event simulation; risk analysis
Citation Formats
Perkins, Casey, and Muller, George. Using Discrete Event Simulation to Model Attacker Interactions with Cyber and Physical Security Systems. United States: N. p., 2015.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2015.09.199.
Perkins, Casey, & Muller, George. Using Discrete Event Simulation to Model Attacker Interactions with Cyber and Physical Security Systems. United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.09.199
Perkins, Casey, and Muller, George. Thu .
"Using Discrete Event Simulation to Model Attacker Interactions with Cyber and Physical Security Systems". United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.09.199. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1347710.
@article{osti_1347710,
title = {Using Discrete Event Simulation to Model Attacker Interactions with Cyber and Physical Security Systems},
author = {Perkins, Casey and Muller, George},
abstractNote = {The number of connections between physical and cyber security systems is rapidly increasing due to centralized control from automated and remotely connected means. As the number of interfaces between systems continues to grow, the interactions and interdependencies between them cannot be ignored. Historically, physical and cyber vulnerability assessments have been performed independently. This independent evaluation omits important aspects of the integrated system, where the impacts resulting from malicious or opportunistic attacks are not easily known or understood. Here, we describe a discrete event simulation model that uses information about integrated physical and cyber security systems, attacker characteristics and simple response rules to identify key safeguards that limit an attacker's likelihood of success. Key features of the proposed model include comprehensive data generation to support a variety of sophisticated analyses, and full parameterization of safeguard performance characteristics and attacker behaviours to evaluate a range of scenarios. Lastly, we also describe the core data requirements and the network of networks that serves as the underlying simulation structure.},
doi = {10.1016/j.procs.2015.09.199},
journal = {Procedia Computer Science},
number = C,
volume = 61,
place = {United States},
year = {Thu Oct 08 00:00:00 EDT 2015},
month = {Thu Oct 08 00:00:00 EDT 2015}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
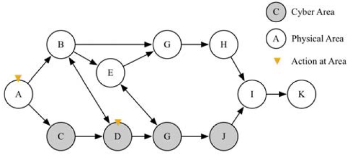 Figure 1: Graph representation of integrated cyber-physical system.
Figure 1: Graph representation of integrated cyber-physical system.
Works referenced in this record:
On the Definition of Vulnerabilities in Measuring Risks to Infrastructures
journal, April 2006
- Haimes, Yacov Y.
- Risk Analysis, Vol. 26, Issue 2
Infrastructure Vulnerability Assessment Model (I-VAM)
journal, June 2007
- Ezell, Barry Charles
- Risk Analysis, Vol. 27, Issue 3
Discrete-event simulation for the design and evaluation of physical protection systems
conference, January 1998
- Jordan, S. E.; Snell, M. K.; Madsen, M. M.
- IEEE Winter Simulation Conference, 1998 Winter Simulation Conference. Proceedings (Cat. No.98CH36274)
A survey of Cyber-Physical Systems
conference, November 2011
- Shi, Jianhua; Wan, Jiafu; Yan, Hehua
- Signal Processing (WCSP 2011), 2011 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP)
Petri Net Modeling of Cyber-Physical Attacks on Smart Grid
journal, December 2011
- Chen, Thomas M.; Sanchez-Aarnoutse, Juan Carlos; Buford, John
- IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, Vol. 2, Issue 4
Cyber–Physical System Security for the Electric Power Grid
journal, January 2012
- Sridhar, Siddharth; Hahn, Adam; Govindarasu, Manimaran
- Proceedings of the IEEE, Vol. 100, Issue 1
Modeling cyber and physical interdependencies - Application in ICT and power grids
conference, March 2009
- HadjSaid, N.; Tranchita, C.; Rozel, B.
- 2009 IEEE/PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition (PSCE)
On the Definition of Vulnerabilities in Measuring Risks to Infrastructures
journal, April 2006
- Haimes, Yacov Y.
- Risk Analysis, Vol. 26, Issue 2
Infrastructure Vulnerability Assessment Model (I-VAM)
journal, June 2007
- Ezell, Barry Charles
- Risk Analysis, Vol. 27, Issue 3
Works referencing / citing this record:
Literature review of Industry 4.0 and related technologies
journal, July 2018
- Oztemel, Ercan; Gursev, Samet
- Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, Vol. 31, Issue 1
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal