The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria
Abstract
As mercury (Hg) biosensors are sensitive to only intracellular Hg, they are useful in the investigation of Hg uptake mechanisms and the effects of speciation on Hg bioavailability to microbes. In this study, bacterial biosensors were used to evaluate the roles that several transporters such as the glutathione, cystine/cysteine, and Mer transporters play in the uptake of Hg from Hg-thiol complexes by comparing uptake rates in strains with functioning transport systems to strains where these transporters had been knocked out by deletion of key genes. The Hg uptake into the biosensors was quantified based on the intracellular conversion of inorganic mercury (Hg(II)) to elemental mercury (Hg(0)) by the enzyme MerA. It was found that uptake of Hg from Hg-cysteine (Hg(CYS)2) and Hg-glutathione (Hg(GSH)2) complexes occurred at the same rate as that of inorganic complexes of Hg(II) into Escherichia coli strains with and without intact Mer transport systems. However, higher rates of Hg uptake were observed in the strain with a functioning Mer transport system. These results demonstrate that thiol-bound Hg is bioavailable to E. coli and that this bioavailability is higher in Hg-resistant bacteria with a complete Mer system than in non-resistant strains. No difference in the uptake rate ofmore »
- Authors:
-
- Rutgers Univ., New Brunswick, NJ (United States); Duke Univ., Durham, NC (United States)
- Rutgers Univ., New Brunswick, NJ (United States)
- Univ. of Connecticut, Groton, CT (United States)
- Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA (United States)
- King Abdul-Aziz Univ., Jeddah (Saudi Arabia)
- Cornell Univ., Ithaca, NY (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Rutgers Univ., New Brunswick, NJ (United States); Rutgers Univ., Piscataway, NJ (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1324975
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1454700
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0007051; sc0007051
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- PLoS ONE
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 10; Journal Issue: 9; Journal ID: ISSN 1932-6203
- Publisher:
- Public Library of Science
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 59 BASIC BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES; bacillus stubtilis; glutathione; cysteine; thiols; biosensors; biological transport; synport proteins; cell membranes
Citation Formats
Ndu, Udonna, Barkay, Tamar, Mason, Robert P., Schartup, Amina Traore, Al-Farawati, Radwan, Liu, Jie, Reinfelder, John R., and Chang, Yung -Fu. The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria. United States: N. p., 2015.
Web. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0138333.
Ndu, Udonna, Barkay, Tamar, Mason, Robert P., Schartup, Amina Traore, Al-Farawati, Radwan, Liu, Jie, Reinfelder, John R., & Chang, Yung -Fu. The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria. United States. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138333
Ndu, Udonna, Barkay, Tamar, Mason, Robert P., Schartup, Amina Traore, Al-Farawati, Radwan, Liu, Jie, Reinfelder, John R., and Chang, Yung -Fu. Tue .
"The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria". United States. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138333. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1324975.
@article{osti_1324975,
title = {The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria},
author = {Ndu, Udonna and Barkay, Tamar and Mason, Robert P. and Schartup, Amina Traore and Al-Farawati, Radwan and Liu, Jie and Reinfelder, John R. and Chang, Yung -Fu},
abstractNote = {As mercury (Hg) biosensors are sensitive to only intracellular Hg, they are useful in the investigation of Hg uptake mechanisms and the effects of speciation on Hg bioavailability to microbes. In this study, bacterial biosensors were used to evaluate the roles that several transporters such as the glutathione, cystine/cysteine, and Mer transporters play in the uptake of Hg from Hg-thiol complexes by comparing uptake rates in strains with functioning transport systems to strains where these transporters had been knocked out by deletion of key genes. The Hg uptake into the biosensors was quantified based on the intracellular conversion of inorganic mercury (Hg(II)) to elemental mercury (Hg(0)) by the enzyme MerA. It was found that uptake of Hg from Hg-cysteine (Hg(CYS)2) and Hg-glutathione (Hg(GSH)2) complexes occurred at the same rate as that of inorganic complexes of Hg(II) into Escherichia coli strains with and without intact Mer transport systems. However, higher rates of Hg uptake were observed in the strain with a functioning Mer transport system. These results demonstrate that thiol-bound Hg is bioavailable to E. coli and that this bioavailability is higher in Hg-resistant bacteria with a complete Mer system than in non-resistant strains. No difference in the uptake rate of Hg from Hg(GSH)2 was observed in E. coli strains with or without functioning glutathione transport systems. There was also no difference in uptake rates between a wildtype Bacillus subtilis strain with a functioning cystine/cysteine transport system, and a mutant strain where this transport system had been knocked out. These results cast doubt on the viability of the hypothesis that the entire Hg-thiol complex is taken up into the cell by a thiol transporter. It is more likely that the Hg in the Hg-thiol complex is transferred to a transport protein on the cell membrane and is subsequently internalized.},
doi = {10.1371/journal.pone.0138333},
journal = {PLoS ONE},
number = 9,
volume = 10,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue Sep 15 00:00:00 EDT 2015},
month = {Tue Sep 15 00:00:00 EDT 2015}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
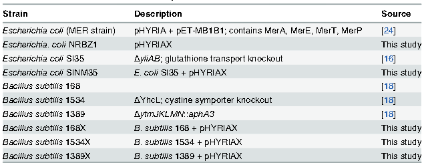 Table 1.: A list of strains used in this study.
Table 1.: A list of strains used in this study.
Works referenced in this record:
Versatile biosensor vectors for detection and quantification of mercury
journal, December 2000
- Hansen, Lars Hestbjerg; Sørensen, Søren Johannes
- FEMS Microbiology Letters, Vol. 193, Issue 1
Titration of sulphides and thiols in natural waters
journal, January 1986
- Dyrssen, David; Wedborg, Margareta
- Analytica Chimica Acta, Vol. 180
Mercury Reduction and Oxidation by Reduced Natural Organic Matter in Anoxic Environments
journal, November 2011
- Zheng, Wang; Liang, Liyuan; Gu, Baohua
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 46, Issue 1
The role of cysteine residues in the transport of mercuric ions by the Tn501 MerT and MerP mercury-resistance proteins
journal, July 1995
- Morby, Andrew P.; Hobman, Jon L.; Brown, Nigel L.
- Molecular Microbiology, Vol. 17, Issue 1
Aspects of Bioavailability of Mercury for Methylation in Pure Cultures of Desulfobulbus propionicus (1pr3)
journal, January 2001
- Benoit, J. M.; Gilmour, C. C.; Mason, R. P.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 67, Issue 1
Potential for Mercury Reduction by Microbes in the High Arctic
journal, February 2007
- Poulain, A. J.; Ni Chadhain, S. M.; Ariya, P. A.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 73, Issue 7
Construction of two lux-tagged Hg2+-specific biosensors and their luminescence performance
journal, April 2008
- Fu, Ya-Juan; Chen, Wen-Li; Huang, Qiao-Yun
- Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 79, Issue 3
The yliA, -B, -C, and -D Genes of Escherichia coli K-12 Encode a Novel Glutathione Importer with an ATP-Binding Cassette
journal, August 2005
- Suzuki, H.; Koyanagi, T.; Izuka, S.
- Journal of Bacteriology, Vol. 187, Issue 17
Simple and simultaneous determination of glutathione, thioacetamide and refractory organic matter in natural waters by DP-CSV
journal, October 2013
- Pernet-Coudrier, Benoît; Waeles, Matthieu; Filella, Montserrat
- Science of The Total Environment, Vol. 463-464
Bioluminescence Biosensor for the Detection of Organomercury Contamination
journal, July 2003
- Endo, G.; Yamagata, T.; Narita, M.
- Acta Biotechnologica, Vol. 23, Issue 23
Three Different Systems Participate in L-Cystine Uptake in Bacillus subtilis
journal, July 2004
- Burguiere, P.; Auger, S.; Hullo, M. -F.
- Journal of Bacteriology, Vol. 186, Issue 15
Dissolved Organic Carbon Thresholds Affect Mercury Bioaccumulation in Arctic Lakes
journal, February 2014
- French, Todd D.; Houben, Adam J.; Desforges, Jean-Pierre W.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 48, Issue 6
Mercury reduction and complexation by natural organic matter in anoxic environments
journal, January 2011
- Gu, B.; Bian, Y.; Miller, C. L.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 108, Issue 4
Organomercurials removal by heterogeneous merB genes harboring bacterial strains
journal, July 2010
- Chien, Mei-Fang; Narita, Masaru; Lin, Kuo-Hsing
- Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, Vol. 110, Issue 1
Adaptation of chemosynthetic microorganisms to elevated mercury concentrations in deep-sea hydrothermal vents
journal, January 2009
- Crepo-Medina, Melitza; Chatziefthimiou, Aspassia D.; Bloom, Nicolas S.
- Limnology and Oceanography, Vol. 54, Issue 1
Evidence for facilitated uptake of Hg(II) by Vibrio anguillarum and Escherichia coli under anaerobic and aerobic conditions
journal, July 2002
- Golding, George R.; Kelly, Carol A.; Sparling, Richard
- Limnology and Oceanography, Vol. 47, Issue 4
Role of MerT and MerP from Pseudomonas K-62 Plasmid pMR26 in the Transport of Phenylmercury.
journal, January 2000
- Kiyono, Masako; Uno, Yoshio; Omura, Tomoko
- Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, Vol. 23, Issue 3
Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems
journal, June 2003
- Barkay, Tamar; Miller, Susan M.; Summers, Anne O.
- FEMS Microbiology Reviews, Vol. 27, Issue 2-3
Factors influencing the oxidation, reduction, methylation and demethylation of mercury species in coastal waters
journal, December 2007
- Whalin, Lindsay; Kim, Eun-Hee; Mason, Robert
- Marine Chemistry, Vol. 107, Issue 3
Thiols in Coastal Waters of the Western North Sea and English Channel
journal, May 2001
- Al-Farawati, Radwan; van den Berg, Constant M. G.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 35, Issue 10
Roles of the Tn21 merT, merP, and merC gene products in mercury resistance and mercury binding.
journal, October 1992
- Hamlett, N. V.; Landale, E. C.; Davis, B. H.
- Journal of Bacteriology, Vol. 174, Issue 20
Oxidation of Dissolved Elemental Mercury by Thiol Compounds under Anoxic Conditions
journal, November 2013
- Zheng, Wang; Lin, Hui; Mann, Benjamin F.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 47, Issue 22
Changes in the non-protein thiol pool and production of dissolved gaseous mercury in the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii under mercury exposure
journal, December 2009
- Morelli, Elisabetta; Ferrara, Romano; Bellini, Barbara
- Science of The Total Environment, Vol. 408, Issue 2
Inorganic and Organic Sulfur Cycling in Salt-Marsh Pore Waters
journal, May 1986
- Luther, G. W.; Church, T. M.; Scudlark, J. R.
- Science, Vol. 232, Issue 4751
Stimulation of elemental mercury oxidation by SH compounds
journal, March 1995
- Yamamoto, M.; Hou, H.; Nakamura, K.
- Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, Vol. 54, Issue 3
Effects of dissolved organic carbon and salinity on bioavailability of mercury.
journal, January 1997
- Barkay, T.; Gillman, M.; Turner, R. R.
- Applied and environmental microbiology, Vol. 63, Issue 11
Cell-density-dependent sensitivity of a mer-lux bioassay.
journal, January 1997
- Rasmussen, L. D.; Turner, R. R.; Barkay, T.
- Applied and environmental microbiology, Vol. 63, Issue 8
Hypersensitivity to Hg2+ and hyperbinding activity associated with cloned fragments of the mercurial resistance operon of plasmid NR1.
journal, January 1979
- Nakahara, H.; Silver, S.; Miki, T.
- Journal of Bacteriology, Vol. 140, Issue 1
Bacterial Oxidation of Mercury Metal Vapor, Hg(0)
journal, April 1998
- Smith, Tracy; Pitts, Keith; McGarvey, Jeffery A.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 64, Issue 4
Data from: The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria
dataset, September 2015
- Ndu, Udonna; Barkay, Tamar; Mason, Robert P.
- Dryad Digital Repository-Supplementary information for journal article at DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138333, 2 XLSX files
Potential for Mercury Reduction by Microbes in the High Arctic
journal, June 2007
- Poulain, Alexandre J.; Ni Chadhain, Sinéad M.; Ariya, Parisa A.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 73, Issue 11
Data from: The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria
dataset, September 2015
- Ndu, Udonna; Barkay, Tamar; Mason, Robert P.
- Dryad Digital Repository-Supplementary information for journal article at DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138333, 2 XLSX files
Construction of two lux-tagged Hg2+-specific biosensors and their luminescence performance
journal, April 2008
- Fu, Ya-Juan; Chen, Wen-Li; Huang, Qiao-Yun
- Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 79, Issue 3
Titration of sulphides and thiols in natural waters
journal, January 1986
- Dyrssen, David; Wedborg, Margareta
- Analytica Chimica Acta, Vol. 180
Organomercurials removal by heterogeneous merB genes harboring bacterial strains
journal, July 2010
- Chien, Mei-Fang; Narita, Masaru; Lin, Kuo-Hsing
- Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, Vol. 110, Issue 1
Changes in the non-protein thiol pool and production of dissolved gaseous mercury in the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii under mercury exposure
journal, December 2009
- Morelli, Elisabetta; Ferrara, Romano; Bellini, Barbara
- Science of The Total Environment, Vol. 408, Issue 2
A GFP-based bacterial biosensor with chromosomally integrated sensing cassette for quantitative detection of Hg(II) in environment
journal, May 2012
- Priyadarshi, Himanshu; Alam, Absar; Gireesh-Babu, P.
- Journal of Environmental Sciences, Vol. 24, Issue 5
Thiols in Coastal Waters of the Western North Sea and English Channel
journal, May 2001
- Al-Farawati, Radwan; van den Berg, Constant M. G.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 35, Issue 10
Mercury Reduction and Oxidation by Reduced Natural Organic Matter in Anoxic Environments
journal, November 2011
- Zheng, Wang; Liang, Liyuan; Gu, Baohua
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 46, Issue 1
Oxidation of Dissolved Elemental Mercury by Thiol Compounds under Anoxic Conditions
journal, November 2013
- Zheng, Wang; Lin, Hui; Mann, Benjamin F.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 47, Issue 22
Dissolved Organic Carbon Thresholds Affect Mercury Bioaccumulation in Arctic Lakes
journal, February 2014
- French, Todd D.; Houben, Adam J.; Desforges, Jean-Pierre W.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 48, Issue 6
Mercury reduction and complexation by natural organic matter in anoxic environments
journal, January 2011
- Gu, B.; Bian, Y.; Miller, C. L.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 108, Issue 4
The role of cysteine residues in the transport of mercuric ions by the Tn501 MerT and MerP mercury-resistance proteins
journal, July 1995
- Morby, Andrew P.; Hobman, Jon L.; Brown, Nigel L.
- Molecular Microbiology, Vol. 17, Issue 1
Versatile biosensor vectors for detection and quantification of mercury
journal, December 2000
- Hansen, Lars Hestbjerg; Sørensen, Søren Johannes
- FEMS Microbiology Letters, Vol. 193, Issue 1
Inorganic and Organic Sulfur Cycling in Salt-Marsh Pore Waters
journal, May 1986
- Luther, G. W.; Church, T. M.; Scudlark, J. R.
- Science, Vol. 232, Issue 4751
Effect of Inorganic and Organic Ligands on the Bioavailability of Methylmercury as Determined by Using a mer-lux Bioreporter
journal, August 2012
- Ndu, Udonna; Mason, Robert P.; Zhang, Huan
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 78, Issue 20
Bioluminescent sensors for detection of bioavailable Hg(II) in the environment.
journal, January 1993
- Selifonova, O.; Burlage, R.; Barkay, T.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 59, Issue 9
Role of MerT and MerP from Pseudomonas K-62 Plasmid pMR26 in the Transport of Phenylmercury.
journal, January 2000
- Kiyono, Masako; Uno, Yoshio; Omura, Tomoko
- Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, Vol. 23, Issue 3
Works referencing / citing this record:
Mercury chloride toxicity in human erythrocytes: enhanced generation of ROS and RNS, hemoglobin oxidation, impaired antioxidant power, and inhibition of plasma membrane redox system
journal, January 2019
- Ahmad, Shahbaz; Mahmood, Riaz
- Environmental Science and Pollution Research, Vol. 26, Issue 6
A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use
journal, January 2018
- Obrist, Daniel; Kirk, Jane L.; Zhang, Lei
- Ambio, Vol. 47, Issue 2
The role of cysteine and sulfide in the interplay between microbial Hg( ii ) uptake and sulfur metabolism
journal, January 2019
- Thomas, Sara A.; Catty, Patrice; Hazemann, Jean-Louis
- Metallomics, Vol. 11, Issue 7
Data from: The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria
dataset, September 2015
- Ndu, Udonna; Barkay, Tamar; Mason, Robert P.
- Dryad Digital Repository-Supplementary information for journal article at DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138333, 2 XLSX files
A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use
text, January 2018
- Daniel, Obrist,; L., Kirk, Jane; Lei, Zhang,
- Springer
Data from: The use of a mercury biosensor to evaluate the bioavailability of mercury-thiol complexes and mechanisms of mercury uptake in bacteria
dataset, September 2015
- Ndu, Udonna; Barkay, Tamar; Mason, Robert P.
- Dryad Digital Repository-Supplementary information for journal article at DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138333, 2 XLSX files
A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use
journal, January 2018
- Obrist, Daniel; Kirk, Jane L.; Zhang, Lei
- Ambio, Vol. 47, Issue 2
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal