Extended magnetic exchange interactions in the high-temperature ferromagnet MnBi
Abstract
Here, the high-temperature ferromagnet MnBi continues to receive attention as a candidate to replace rare-earth-containing permanent magnets in applications above room temperature. This is due to a high Curie temperature, large magnetic moments, and a coercivity that increases with temperature. The synthesis of MnBi also allows for crystals that are free of interstitial Mn, enabling more direct access to the key interactions underlying the physical properties of binary Mn-based ferromagnets. In this work, we use inelastic neutron scattering to measure the spin waves of MnBi in order to characterize the magnetic exchange at low temperature. Consistent with the spin reorientation that occurs below 140~K, we do not observe a spin gap in this system above our experimental resolution. A Heisenberg model was fit to the spin wave data in order to characterize the long-range nature of the exchange. It was found that interactions up to sixth nearest neighbor are required to fully parameterize the spin waves. Surprisingly, the nearest-neighbor term is antiferromagnetic, and the realization of a ferromagnetic ground state relies on the more numerous ferromagnetic terms beyond nearest neighbor, suggesting that the ferromagnetic ground state arises as a consequence of the long-ranged interactions in the system.
- Authors:
-
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States); Univ. of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN (United States)
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1252153
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1252115
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Applied Physics Letters
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 108; Journal Issue: 19; Journal ID: ISSN 0003-6951
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 75 CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS, SUPERCONDUCTIVITY AND SUPERFLUIDITY; 71 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM MECHANICS, GENERAL PHYSICS; ferromagnetic materials; spin waves; antiferromagnetism; curie point; exchange interactions
Citation Formats
Christianson, Andrew D., Hahn, Steven E., Fishman, Randy Scott, Parker, David S., McGuire, Michael A., Sales, Brian C., Lumsden, Mark D., Williams, T. J., and Taylor, A. E. Extended magnetic exchange interactions in the high-temperature ferromagnet MnBi. United States: N. p., 2016.
Web. doi:10.1063/1.4948933.
Christianson, Andrew D., Hahn, Steven E., Fishman, Randy Scott, Parker, David S., McGuire, Michael A., Sales, Brian C., Lumsden, Mark D., Williams, T. J., & Taylor, A. E. Extended magnetic exchange interactions in the high-temperature ferromagnet MnBi. United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4948933
Christianson, Andrew D., Hahn, Steven E., Fishman, Randy Scott, Parker, David S., McGuire, Michael A., Sales, Brian C., Lumsden, Mark D., Williams, T. J., and Taylor, A. E. Mon .
"Extended magnetic exchange interactions in the high-temperature ferromagnet MnBi". United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4948933. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1252153.
@article{osti_1252153,
title = {Extended magnetic exchange interactions in the high-temperature ferromagnet MnBi},
author = {Christianson, Andrew D. and Hahn, Steven E. and Fishman, Randy Scott and Parker, David S. and McGuire, Michael A. and Sales, Brian C. and Lumsden, Mark D. and Williams, T. J. and Taylor, A. E.},
abstractNote = {Here, the high-temperature ferromagnet MnBi continues to receive attention as a candidate to replace rare-earth-containing permanent magnets in applications above room temperature. This is due to a high Curie temperature, large magnetic moments, and a coercivity that increases with temperature. The synthesis of MnBi also allows for crystals that are free of interstitial Mn, enabling more direct access to the key interactions underlying the physical properties of binary Mn-based ferromagnets. In this work, we use inelastic neutron scattering to measure the spin waves of MnBi in order to characterize the magnetic exchange at low temperature. Consistent with the spin reorientation that occurs below 140~K, we do not observe a spin gap in this system above our experimental resolution. A Heisenberg model was fit to the spin wave data in order to characterize the long-range nature of the exchange. It was found that interactions up to sixth nearest neighbor are required to fully parameterize the spin waves. Surprisingly, the nearest-neighbor term is antiferromagnetic, and the realization of a ferromagnetic ground state relies on the more numerous ferromagnetic terms beyond nearest neighbor, suggesting that the ferromagnetic ground state arises as a consequence of the long-ranged interactions in the system.},
doi = {10.1063/1.4948933},
journal = {Applied Physics Letters},
number = 19,
volume = 108,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon May 09 00:00:00 EDT 2016},
month = {Mon May 09 00:00:00 EDT 2016}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
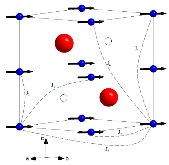 FIG. 1.: (Color online) The crystal structure of MnBi. The Mn atoms (small, blue) occupy the 2a position, while the Bi atoms (large, red) occupy the 2c position. The other half of the interstitial positions (Wyckoff symbol 2d), shown as open circles, can be occupied by Mn impurities. Charac- terizationmore »
FIG. 1.: (Color online) The crystal structure of MnBi. The Mn atoms (small, blue) occupy the 2a position, while the Bi atoms (large, red) occupy the 2c position. The other half of the interstitial positions (Wyckoff symbol 2d), shown as open circles, can be occupied by Mn impurities. Charac- terizationmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Microstructure, crystallization, and magnetization behaviors in composites aligned by applied magnetic field
journal, December 2005
- Liu, Yongsheng; Zhang, Jincang; Cao, Shixun
- Physical Review B, Vol. 72, Issue 21
Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple
journal, October 1996
- Perdew, John P.; Burke, Kieron; Ernzerhof, Matthias
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 77, Issue 18, p. 3865-3868
Advances in nanostructured permanent magnets research
journal, December 2012
- Poudyal, Narayan; Ping Liu, J.
- Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Vol. 46, Issue 4
A New Permanent Magnet from Powdered Manganese Bismuthide
journal, January 1953
- Adams, Edmond
- Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol. 25, Issue 1
Control of Precipitating Phase Alignment and Crystal Orientation by Imposition of a High Magnetic Field
journal, January 1998
- Morikawa, Hiroshi; Sassa, Kensuke; Asai, Shigeo
- Materials Transactions, JIM, Vol. 39, Issue 8
Magnetic properties of MnBi prepared by rapid solidification
journal, December 1992
- Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Altounian, Z.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 46, Issue 22
Magneto-optical and structural properties of nanocrystalline MnBi-based films
journal, November 1995
- Sellmyer, D. J.; Kirby, R. D.; Chen, J.
- Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, Vol. 56, Issue 11
Contribution to the equilibrium phase diagram of the Mn–Bi system near MnBi
journal, May 1974
- Chen, Tu
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 45, Issue 5
Influence of interstitial Mn on magnetism in the room-temperature ferromagnet
journal, June 2015
- Taylor, A. E.; Berlijn, T.; Hahn, S. E.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 91, Issue 22
Inelastic-neutron-scattering studies of spin-wave excitations in the pnictides MnSb and CrSb
journal, November 1996
- Radhakrishna, P.; Cable, J. W.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 54, Issue 17
Distances magnétiques efficaces dans les métaux, alliages et combinaisons ferromagnétiques et antiferromagnétiques du groupe du fer
journal, January 1952
- Forrer, Robert
- Annales de Physique, Vol. 12, Issue 7
Magnetic Writing on Thin Films of MnBi
journal, October 1957
- Williams, H. J.; Sherwood, R. C.; Foster, F. G.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 28, Issue 10
Structure and magnetic properties of the MnBi low temperature phase
journal, January 2002
- Yang, J. B.; Yelon, W. B.; James, W. J.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 91, Issue 10
Effect of composition and heat treatment on MnBi magnetic materials
journal, October 2014
- Cui, Jun; Choi, Jung-Pyung; Polikarpov, Evgueni
- Acta Materialia, Vol. 79
Design and operation of the wide angular-range chopper spectrometer ARCS at the Spallation Neutron Source
journal, January 2012
- Abernathy, D. L.; Stone, M. B.; Loguillo, M. J.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 83, Issue 1
The phase transformation and physical properties of the MnBi and Mn<inf>1.08</inf>Bi compounds
journal, September 1974
- Tu Chen, ; Stutius, W.
- IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, Vol. 10, Issue 3
Magnetic Properties of MnBi in High Magnetic Fields and High Temperature [一次相転移物質 MnBi の高温・強磁場磁気特性]
journal, January 2007
- Onogi, Tetsuya; Koyama, Keiichi; Watanabe, Kazuo
- Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals, Vol. 71, Issue 6
Magnetic anisotropic effects and electronic correlations in MnBi ferromagnet
journal, August 2014
- Antropov, V. P.; Antonov, V. N.; Bekenov, L. V.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 90, Issue 5
Magnetic Phase Transition of MnP Under Magnetic Field
journal, September 1980
- Obara, Hisashi; Endoh, Yasuo; Ishikawa, Yoshikazu
- Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol. 49, Issue 3
On the Magnetic Properties of the Compound Mn 2 As
journal, October 1960
- Yuzuri, Motoyoshi; Yamada, Motohiko
- Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol. 15, Issue 10
Anisotropic nanocrystalline MnBi with high coercivity at high temperature
journal, August 2011
- Yang, J. B.; Yang, Y. B.; Chen, X. G.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 99, Issue 8
Structural, Magnetic and Magneto-Optic Properties of Ferromagnetic MnCo x Sb [0≤ x ≤0.25]
journal, June 1992
- Elankumaran, K.; Markandeyulu, G.; V. S. Rama Rao, K.
- Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol. 61, Issue 6
Effects of Pressure on the Magnetic Properties of MnAs
journal, January 1969
- Menyuk, N.; Kafalas, J. A.; Dwight, K.
- Physical Review, Vol. 177, Issue 2
Neutron Diffraction Study of the Structures and Magnetic Properties of Manganese Bismuthide
journal, November 1956
- Roberts, B. W.
- Physical Review, Vol. 104, Issue 3
Coordination and chemical effects on the structural, electronic, and magnetic properties in Mn pnictides
journal, August 2001
- Continenza, A.; Picozzi, S.; Geng, W. T.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 64, Issue 8
Über Manganbronze und über die Synthese magnetisierbarer Legierungen aus unmagnetischen Metallen
journal, February 1904
- Heusler, Fr.
- Zeitschrift für Angewandte Chemie, Vol. 17, Issue 9
Symmetry-lowering lattice distortion at the spin reorientation in MnBi single crystals
journal, November 2014
- McGuire, Michael A.; Cao, Huibo; Chakoumakos, Bryan C.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 90, Issue 17
Pressure-Induced Colossal Magnetocaloric Effect in MnAs
journal, November 2004
- Gama, Sergio; Coelho, Adelino A.; de Campos, Ariana
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 93, Issue 23
Evidence of a critical Mn-Mn distance for the onset of ferromagnetism in NiAs type compounds
journal, April 1984
- Seshu Bai, V.; Rajasekharan, T.
- Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 42, Issue 2
Propriétés ferromagnétiques des alliages manganèse-antimoine et manganèse-arsenic
journal, January 1949
- Guillaud, Charles
- Annales de Physique, Vol. 12, Issue 4
Works referencing / citing this record:
Study of the Magnetic Properties of the Compound Mn Bi Using the Monte Carlo Simulations
journal, January 2020
- Aouini, S.; Sahdane, T.; Mhirech, A.
- Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, Vol. 33, Issue 6
Discovery of ferromagnetism with large magnetic anisotropy in ZrMnP and HfMnP
journal, August 2016
- Lamichhane, Tej N.; Taufour, Valentin; Masters, Morgan W.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 109, Issue 9
Giant magnetostriction effect near onset of spin reorientation in MnBi
journal, May 2018
- Choi, Y.; Ryan, P. J.; McGuire, M. A.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 112, Issue 19
Extended exchange interactions stabilize long-period magnetic structures in Cr 1∕3 NbS 2
journal, July 2018
- Aczel, A. A.; DeBeer-Schmitt, L. M.; Williams, T. J.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 113, Issue 3
Bootstrapping the long-range Ising model in three dimensions
journal, January 2019
- Behan, Connor
- Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, Vol. 52, Issue 7
Monte Carlo analysis for finite-temperature magnetism of permanent magnet
journal, November 2016
- Toga, Yuta; Matsumoto, Munehisa; Miyashita, Seiji
- Physical Review B, Vol. 94, Issue 17
Discovery of ferromagnetism with large magnetic anisotropy in ZrMnP and HfMnP
text, January 2016
- Lamichhane, Tej N.; Taufour, Valentin; Masters, Morgan W.
- arXiv
Flux growth in a horizontal configuration: an analogue to vapor transport growth
text, January 2017
- Yan, J. -Q.; Sales, B. C.; Susner, M. A.
- arXiv
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal