Growth of Ammonium Bisulfate Clusters by Adsorption of Oxygenated Organic Molecules
Abstract
Quantum chemical calculations were employed to model the interactions of the [(NH4+)4(HSO4-)4] ammonium bisulfate cluster with one or more molecular products of monoterpene oxidation. A strong interaction was found between the bisulfate ion of the cluster and a carboxylic acid, aldehyde or ketone functionality of the organic molecule. Free energies of adsorption for carboxylic acids were in the -70 to -73 kJ/mol range, while those for aldehydes and ketones were in the -46 to -50 kJ/mol range. These values suggest that a small ambient ammonium bisulfate cluster, such as the [(NH4+)4(SO4-)4] cluster, is able to adsorb an oxygenated organic molecule. Although adsorption of the first molecule is highly favorable, adsorption of subsequent molecules is not, suggesting that sustained uptake of organic molecules does not occur, and thus is not a pathway for continuing growth of the cluster. This result is consistent with ambient measurements showing that particles below ~1 nm grow slowly, while those above 1 nm grow at an increasing rate presumably due to a lower surface energy barrier enabling the uptake of organic molecules. This work provides insight into the molecular level interactions which affect sustained cluster growth by uptake of organic molecules.
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of Delaware, Newark, DE (United States)
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Univ. of California, Davis, CA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1239790
- Report Number(s):
- BNL-111698-2015-JA
Journal ID: ISSN 1089-5639; R&D Project: 2016-BNL-EE630EECA-Budg; KP1701000
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012704; DE-AC02- 98CH10886
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, Molecules, Spectroscopy, Kinetics, Environment, and General Theory
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 119; Journal Issue: 45; Journal ID: ISSN 1089-5639
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 54 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Citation Formats
DePalma, Joseph W., Wang, Jian, Wexler, Anthony S., and Johnston, Murray V. Growth of Ammonium Bisulfate Clusters by Adsorption of Oxygenated Organic Molecules. United States: N. p., 2015.
Web. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.5b07744.
DePalma, Joseph W., Wang, Jian, Wexler, Anthony S., & Johnston, Murray V. Growth of Ammonium Bisulfate Clusters by Adsorption of Oxygenated Organic Molecules. United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.5b07744
DePalma, Joseph W., Wang, Jian, Wexler, Anthony S., and Johnston, Murray V. Wed .
"Growth of Ammonium Bisulfate Clusters by Adsorption of Oxygenated Organic Molecules". United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.5b07744. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1239790.
@article{osti_1239790,
title = {Growth of Ammonium Bisulfate Clusters by Adsorption of Oxygenated Organic Molecules},
author = {DePalma, Joseph W. and Wang, Jian and Wexler, Anthony S. and Johnston, Murray V.},
abstractNote = {Quantum chemical calculations were employed to model the interactions of the [(NH4+)4(HSO4-)4] ammonium bisulfate cluster with one or more molecular products of monoterpene oxidation. A strong interaction was found between the bisulfate ion of the cluster and a carboxylic acid, aldehyde or ketone functionality of the organic molecule. Free energies of adsorption for carboxylic acids were in the -70 to -73 kJ/mol range, while those for aldehydes and ketones were in the -46 to -50 kJ/mol range. These values suggest that a small ambient ammonium bisulfate cluster, such as the [(NH4+)4(SO4-)4] cluster, is able to adsorb an oxygenated organic molecule. Although adsorption of the first molecule is highly favorable, adsorption of subsequent molecules is not, suggesting that sustained uptake of organic molecules does not occur, and thus is not a pathway for continuing growth of the cluster. This result is consistent with ambient measurements showing that particles below ~1 nm grow slowly, while those above 1 nm grow at an increasing rate presumably due to a lower surface energy barrier enabling the uptake of organic molecules. This work provides insight into the molecular level interactions which affect sustained cluster growth by uptake of organic molecules.},
doi = {10.1021/acs.jpca.5b07744},
journal = {Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, Molecules, Spectroscopy, Kinetics, Environment, and General Theory},
number = 45,
volume = 119,
place = {United States},
year = {Wed Oct 21 00:00:00 EDT 2015},
month = {Wed Oct 21 00:00:00 EDT 2015}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
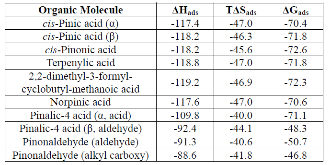 Table 1: Thermodynamic potentials (in kJ/mol) for adsorption of various α-pinene oxidation products to the [(NH4+)4(HSO4-)4] cluster. Values are computed for the gas phase standard state of 1 atmosphere and 298 K.
Table 1: Thermodynamic potentials (in kJ/mol) for adsorption of various α-pinene oxidation products to the [(NH4+)4(HSO4-)4] cluster. Values are computed for the gas phase standard state of 1 atmosphere and 298 K.
Works referenced in this record:
Formation and growth rates of ultrafine atmospheric particles: a review of observations
journal, March 2004
- Kulmala, M.; Vehkamäki, H.; Petäjä, T.
- Journal of Aerosol Science, Vol. 35, Issue 2
On the formation and growth of atmospheric nanoparticles
journal, November 2008
- Kulmala, Markku; Kerminen, Veli-Matti
- Atmospheric Research, Vol. 90, Issue 2-4
Getting to the Critical Nucleus of Aerosol Formation
journal, June 2010
- Zhang, R.
- Science, Vol. 328, Issue 5984
Impact of nucleation on global CCN
journal, January 2009
- Merikanto, J.; Spracklen, D. V.; Mann, G. W.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 9, Issue 21
Determination of cloud condensation nuclei production from measured new particle formation events
journal, January 2009
- Kuang, C.; McMurry, P. H.; McCormick, A. V.
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 36, Issue 9
Dependence of nucleation rates on sulfuric acid vapor concentration in diverse atmospheric locations
journal, January 2008
- Kuang, C.; McMurry, P. H.; McCormick, A. V.
- Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 113, Issue D10
Role of sulphuric acid, ammonia and galactic cosmic rays in atmospheric aerosol nucleation
journal, August 2011
- Kirkby, Jasper; Curtius, Joachim; Almeida, João
- Nature, Vol. 476, Issue 7361
Molecular understanding of sulphuric acid–amine particle nucleation in the atmosphere
journal, October 2013
- Almeida, João; Schobesberger, Siegfried; Kürten, Andreas
- Nature, Vol. 502, Issue 7471
Molecular understanding of atmospheric particle formation from sulfuric acid and large oxidized organic molecules
journal, October 2013
- Schobesberger, S.; Junninen, H.; Bianchi, F.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 110, Issue 43
On the composition of ammonia–sulfuric-acid ion clusters during aerosol particle formation
journal, January 2015
- Schobesberger, S.; Franchin, A.; Bianchi, F.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 15, Issue 1
The Role of Sulfuric Acid in Atmospheric Nucleation
journal, March 2010
- Sipila, M.; Berndt, T.; Petaja, T.
- Science, Vol. 327, Issue 5970
Ternary homogeneous nucleation of H 2 SO 4 , NH 3 , and H 2 O under conditions relevant to the lower troposphere
journal, January 2011
- Benson, D. R.; Yu, J. H.; Markovich, A.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 11, Issue 10
Composition and temporal behavior of ambient ions in the boreal forest
journal, January 2010
- Ehn, M.; Junninen, H.; Petäjä, T.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 10, Issue 17
Negative atmospheric ions and their potential role in ion-induced nucleation
journal, January 2006
- Eisele, F. L.; Lovejoy, E. R.; Kosciuch, E.
- Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 111, Issue D4
Multiphase chemistry of atmospheric amines
journal, January 2013
- Qiu, Chong; Zhang, Renyi
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Vol. 15, Issue 16
Simplified mechanism for new particle formation from methanesulfonic acid, amines, and water via experiments and ab initio calculations
journal, October 2012
- Dawson, M. L.; Varner, M. E.; Perraud, V.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 109, Issue 46
Atmospheric amines – Part I. A review
journal, January 2011
- Ge, Xinlei; Wexler, Anthony S.; Clegg, Simon L.
- Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 45, Issue 3
Heterogeneous Reactions of Alkylamines with Ammonium Sulfate and Ammonium Bisulfate
journal, June 2011
- Qiu, Chong; Wang, Lin; Lal, Vinita
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 45, Issue 11
The effect of trimethylamine on atmospheric nucleation involving H 2 SO 4
journal, January 2011
- Erupe, M. E.; Viggiano, A. A.; Lee, S. -H.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 11, Issue 10
Chemical composition of atmospheric nanoparticles formed from nucleation in Tecamac, Mexico: Evidence for an important role for organic species in nanoparticle growth
journal, January 2008
- Smith, J. N.; Dunn, M. J.; VanReken, T. M.
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 35, Issue 4
Atmospheric nanoparticles formed from heterogeneous reactions of organics
journal, February 2010
- Wang, Lin; Khalizov, Alexei F.; Zheng, Jun
- Nature Geoscience, Vol. 3, Issue 4
Direct Observations of Atmospheric Aerosol Nucleation
journal, February 2013
- Kulmala, M.; Kontkanen, J.; Junninen, H.
- Science, Vol. 339, Issue 6122
Size and time-resolved growth rate measurements of 1 to 5 nm freshly formed atmospheric nuclei
journal, January 2012
- Kuang, C.; Chen, M.; Zhao, J.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 12, Issue 7
Activation Barriers in the Growth of Molecular Clusters Derived from Sulfuric Acid and Ammonia
journal, November 2014
- DePalma, Joseph W.; Bzdek, Bryan R.; Ridge, Douglas P.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 118, Issue 49
Formation and Growth of Molecular Clusters Containing Sulfuric Acid, Water, Ammonia, and Dimethylamine
journal, July 2014
- DePalma, Joseph W.; Doren, Douglas J.; Johnston, Murray V.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 118, Issue 29
Structure and Energetics of Nanometer Size Clusters of Sulfuric Acid with Ammonia and Dimethylamine
journal, January 2012
- DePalma, Joseph W.; Bzdek, Bryan R.; Doren, Douglas J.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 116, Issue 3
Bond Energies and Structures of Ammonia–Sulfuric Acid Positive Cluster Ions
journal, December 2011
- Froyd, Karl D.; Lovejoy, Edward R.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 116, Issue 24
IMS–MS and IMS–IMS Investigation of the Structure and Stability of Dimethylamine-Sulfuric Acid Nanoclusters
journal, February 2015
- Ouyang, Hui; He, Siqin; Larriba-Andaluz, Carlos
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 119, Issue 10
A large source of low-volatility secondary organic aerosol
journal, February 2014
- Ehn, Mikael; Thornton, Joel A.; Kleist, Einhard
- Nature, Vol. 506, Issue 7489
Chemistry of secondary organic aerosol: Formation and evolution of low-volatility organics in the atmosphere
journal, May 2008
- Kroll, Jesse H.; Seinfeld, John H.
- Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 42, Issue 16
Measuring and simulating particulate organics in the atmosphere: problems and prospects
journal, January 2000
- Turpin, Barbara J.; Saxena, Pradeep; Andrews, Elisabeth
- Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 34, Issue 18
Ozonolysis of α -pinene at atmospherically relevant concentrations: Temperature dependence of aerosol mass fractions (yields)
journal, January 2007
- Pathak, Ravi K.; Stanier, Charles O.; Donahue, Neil M.
- Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 112, Issue D3
Equilibration time scales of organic aerosol inside thermodenuders: Evaporation kinetics versus thermodynamics
journal, February 2010
- Riipinen, Ilona; Pierce, Jeffrey R.; Donahue, Neil M.
- Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 44, Issue 5
Gas phase formation of extremely oxidized pinene reaction products in chamber and ambient air
journal, January 2012
- Ehn, M.; Kleist, E.; Junninen, H.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 12, Issue 11
Oligomers in the Early Stage of Biogenic Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation and Growth
journal, September 2007
- Heaton, Katherine J.; Dreyfus, Matthew A.; Wang, Shenyi
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 41, Issue 17
Composition Domains in Monoterpene Secondary Organic Aerosol
journal, September 2009
- Heaton, Katherine J.; Sleighter, Rachel L.; Hatcher, Patrick G.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 43, Issue 20
Oligomer Formation Pathways in Secondary Organic Aerosol from MS and MS/MS Measurements with High Mass Accuracy and Resolving Power
journal, April 2012
- Hall, Wiley A.; Johnston, Murray V.
- Journal of The American Society for Mass Spectrometry, Vol. 23, Issue 6
Oligomer Content of α-Pinene Secondary Organic Aerosol
journal, January 2011
- Hall, Wiley A.; Johnston, Murray V.
- Aerosol Science and Technology, Vol. 45, Issue 1
Thermodynamics of oligomer formation: implications for secondary organic aerosol formation and reactivity
journal, January 2013
- DePalma, Joseph W.; Horan, Andrew J.; Hall IV, Wiley A.
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Vol. 15, Issue 18
The contribution of organics to atmospheric nanoparticle growth
journal, June 2012
- Riipinen, Ilona; Yli-Juuti, Taina; Pierce, Jeffrey R.
- Nature Geoscience, Vol. 5, Issue 7
An absorption model of the gas/aerosol partitioning involved in the formation of secondary organic aerosol
journal, January 1994
- Pankow, James F.
- Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 28, Issue 2
Formation of nanoparticles of blue haze enhanced by anthropogenic pollution
journal, October 2009
- Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Khalizov, A. F.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 106, Issue 42
Atmospheric New Particle Formation Enhanced by Organic Acids
journal, June 2004
- Zhang, R.
- Science, Vol. 304, Issue 5676
Nucleation and Growth of Nanoparticles in the Atmosphere
journal, November 2011
- Zhang, Renyi; Khalizov, Alexei; Wang, Lin
- Chemical Reviews, Vol. 112, Issue 3
Energetics of Atmospherically Implicated Clusters Made of Sulfuric Acid, Ammonia, and Dimethyl Amine
journal, April 2013
- Leverentz, Hannah R.; Siepmann, J. Ilja; Truhlar, Donald G.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 117, Issue 18
Atmospheric Cluster Dynamics Code: a flexible method for solution of the birth-death equations
journal, January 2012
- McGrath, M. J.; Olenius, T.; Ortega, I. K.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 12, Issue 5
From quantum chemical formation free energies to evaporation rates
journal, January 2012
- Ortega, I. K.; Kupiainen, O.; Kurtén, T.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 12, Issue 1
Large ternary hydrogen-bonded pre-nucleation clusters in the Earth’s atmosphere
journal, December 2011
- Herb, Jason; Nadykto, Alexey B.; Yu, Fangqun
- Chemical Physics Letters, Vol. 518
Amines in the Earth’s Atmosphere: A Density Functional Theory Study of the Thermochemistry of Pre-Nucleation Clusters
journal, February 2011
- Nadykto, Alexey; Yu, Fangqun; Jakovleva, Marina
- Entropy, Vol. 13, Issue 2
A Comment on Nadytko et al., “Amines in the Earth’s Atmosphere: A Density Functional Theory Study of the Thermochemistry of Pre-Nucleation Clusters”. Entropy 2011, 13, 554–569
journal, April 2011
- Kurtén, Theo
- Entropy, Vol. 13, Issue 4
Ab Initio and Density Functional Theory Reinvestigation of Gas-Phase Sulfuric Acid Monohydrate and Ammonium Hydrogen Sulfate
journal, June 2006
- Kurtén, Theo; Sundberg, Markku R.; Vehkamäki, Hanna
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 110, Issue 22
Large Hydrogen-Bonded Pre-nucleation (HSO 4 – )(H 2 SO 4 ) m (H 2 O) k and (HSO 4 – )(NH 3 )(H 2 SO 4 ) m (H 2 O) k Clusters in the Earth’s Atmosphere
journal, December 2012
- Herb, Jason; Xu, Yisheng; Yu, Fangqun
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 117, Issue 1
Computational Study of the Reaction between Biogenic Stabilized Criegee Intermediates and Sulfuric Acid
journal, May 2007
- Kurtén, Theo; Bonn, Boris; Vehkamäki, Hanna
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 111, Issue 17
Strong hydrogen bonding between atmospheric nucleation precursors and common organics
journal, February 2007
- Nadykto, Alexey B.; Yu, Fangqun
- Chemical Physics Letters, Vol. 435, Issue 1-3
Theoretical investigation of reactions between ammonia and precursors from the ozonolysis of ethene
journal, July 2009
- Jørgensen, Solvejg; Gross, Allan
- Chemical Physics, Vol. 362, Issue 1-2
Theoretical Investigation of Interaction of Dicarboxylic Acids with Common Aerosol Nucleation Precursors
journal, May 2012
- Xu, Wen; Zhang, Renyi
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 116, Issue 18
A theoretical study of hydrated molecular clusters of amines and dicarboxylic acids
journal, August 2013
- Xu, Wen; Zhang, Renyi
- The Journal of Chemical Physics, Vol. 139, Issue 6
Hydrogen-Bonding Interaction in Molecular Complexes and Clusters of Aerosol Nucleation Precursors
journal, January 2009
- Zhao, Jun; Khalizov, Alexei; Zhang, Renyi
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 113, Issue 4
Formation and properties of hydrogen-bonded complexes of common organic oxalic acid with atmospheric nucleation precursors
journal, July 2010
- Xu, Yisheng; Nadykto, Alexey B.; Yu, Fangqun
- Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM, Vol. 951, Issue 1-3
Negative Ion Photoelectron Spectroscopy Reveals Thermodynamic Advantage of Organic Acids in Facilitating Formation of Bisulfate Ion Clusters: Atmospheric Implications
journal, February 2013
- Hou, Gao-Lei; Lin, Wei; Deng, S. H. M.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, Vol. 4, Issue 5
Communication: Vibrational spectroscopy of atmospherically relevant acid cluster anions: Bisulfate versus nitrate core structures
journal, June 2012
- Yacovitch, Tara I.; Heine, Nadja; Brieger, Claudia
- The Journal of Chemical Physics, Vol. 136, Issue 24
Vibrational Spectra and Fragmentation Pathways of Size-Selected, D 2 -Tagged Ammonium/Methylammonium Bisulfate Clusters
journal, August 2013
- Johnson, Christopher J.; Johnson, Mark A.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 117, Issue 50
Adsorption of organic molecules may explain growth of newly nucleated clusters and new particle formation: ADSORPTION ENHANCES PARTICLE GROWTH
journal, June 2013
- Wang, Jian; Wexler, Anthony S.
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 40, Issue 11
Structures, Hydration, and Electrical Mobilities of Bisulfate Ion–Sulfuric Acid–Ammonia/Dimethylamine Clusters: A Computational Study
journal, September 2015
- Tsona, Narcisse T.; Henschel, Henning; Bork, Nicolai
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 119, Issue 37
Hydration of Atmospherically Relevant Molecular Clusters: Computational Chemistry and Classical Thermodynamics
journal, March 2014
- Henschel, Henning; Navarro, Juan C. Acosta; Yli-Juuti, Taina
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, Vol. 118, Issue 14
Development and use of quantum mechanical molecular models. 76. AM1: a new general purpose quantum mechanical molecular model
journal, June 1985
- Dewar, Michael J. S.; Zoebisch, Eve G.; Healy, Eamonn F.
- Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 107, Issue 13
Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation
journal, September 1992
- Perdew, John P.; Chevary, J. A.; Vosko, S. H.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 46, Issue 11
Generalized gradient approximation for the exchange-correlation hole of a many-electron system
journal, December 1996
- Perdew, John P.; Burke, Kieron; Wang, Yue
- Physical Review B, Vol. 54, Issue 23
The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors
journal, October 1970
- Boys, S.F.; Bernardi, F.
- Molecular Physics, Vol. 19, Issue 4, p. 553-566
Enhancement in the production of nucleating clusters due to dimethylamine and large uncertainties in the thermochemistry of amine-enhanced nucleation
journal, August 2014
- Nadykto, Alexey B.; Herb, Jason; Yu, Fangqun
- Chemical Physics Letters, Vol. 609
Comment on ‘Enhancement in the production of nucleating clusters due to dimethylamine and large uncertainties in the thermochemistry of amine-enhanced nucleation’ by Nadykto et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 609 (2014) 42–49
journal, March 2015
- Kupiainen-Määttä, Oona; Henschel, Henning; Kurtén, Theo
- Chemical Physics Letters, Vol. 624
Reply to the ‘Comment on “Enhancement in the production of nucleating clusters due to dimethylamine and large uncertainties in the thermochemistry of amine-enhanced nucleation”’ by Kupiainen-Maatta et al.
journal, March 2015
- Nadykto, Alexey B.; Herb, Jason; Yu, Fangqun
- Chemical Physics Letters, Vol. 624
Vibrational dynamics of carboxylic acid dimers in gas and dilute solution
journal, January 2007
- Shipman, Steven T.; Douglass, Pamela C.; Yoo, Hyun S.
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Vol. 9, Issue 32
Infrared spectroscopy of acetic acid and formic acid aerosols: pure and compound acid/ice particles
journal, January 2007
- Gadermann, Moritz; Vollmar, Daniel; Signorell, Ruth
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Vol. 9, Issue 32
Diurnal variation in the concentration of α- and β-pinene in the landes forest (France)
journal, January 1987
- Riba, M. L.; Tathy, J. P.; Tsiropoulos, N.
- Atmospheric Environment (1967), Vol. 21, Issue 1
Characterizations of cis-pinonic acid and n-fatty acids on fine aerosols in the Lower Fraser Valley during Pacific 2001 Air Quality Study
journal, November 2004
- Cheng, Yu; Li, Shao-Meng; Leithead, Amy
- Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 38, Issue 34
Formation and occurrence of dimer esters of pinene oxidation products in atmospheric aerosols
journal, January 2013
- Kristensen, K.; Enggrob, K. L.; King, S. M.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 13, Issue 7
Works referencing / citing this record:
Impact of temperature dependence on the possible contribution of organics to new particle formation in the atmosphere
journal, January 2017
- Yu, Fangqun; Luo, Gan; Nadykto, Alexey B.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 17, Issue 8
Phosphoric acid – a potentially elusive participant in atmospheric new particle formation
journal, December 2016
- Elm, Jonas; Myllys, Nanna; Kurtén, Theo
- Molecular Physics, Vol. 115, Issue 17-18
Phosphoric acid – a potentially elusive participant in atmospheric new particle formation
text, January 2016
- Elm, Jonas; Myllys, Nanna; Kurtén, Theo
- Taylor & Francis
Phosphoric acid – a potentially elusive participant in atmospheric new particle formation
text, January 2016
- Elm, Jonas; Myllys, Nanna; Kurtén, Theo
- Taylor & Francis
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal